机器学习笔记(二十二):TensorFlow实战十四(图像风格迁移)
1 - 引言
相信大家都使用过一种滤镜,可以把一张照片转换成不同风格的照片,如下图所示:

那么我们就来利用TensorFlow来实现以下这个算法,这个算法出自Gatys的A Neural Algorithm of Artistic Style论文,十分有趣,让我们来详细的介绍一下这个算法吧
2 - 利用VGG提取特征
总得来说,就是利用一个训练好的卷积神经网络 VGG-19,这个网络在ImageNet 上已经训练过了。
给定一张风格图像 和一张普通图像 ,风格图像经过VGG-19 的时候在每个卷积层会得到很多 feature maps, 这些feature maps 组成一个集合 ,同样的,普通图像 通过 VGG-19 的时候也会得到很多 feature maps,这些feature maps 组成一个集合 ,然后生成一张随机噪声图像 , 随机噪声图像 通过VGG-19 的时候也会生成很多feature maps,这些 feature maps 构成集合 和 分别对应集合 和 , 最终的优化函数是希望调整 让 随机噪声图像 最后看起来既保持普通图像 的内容, 又有一定的风格图像 的风格。
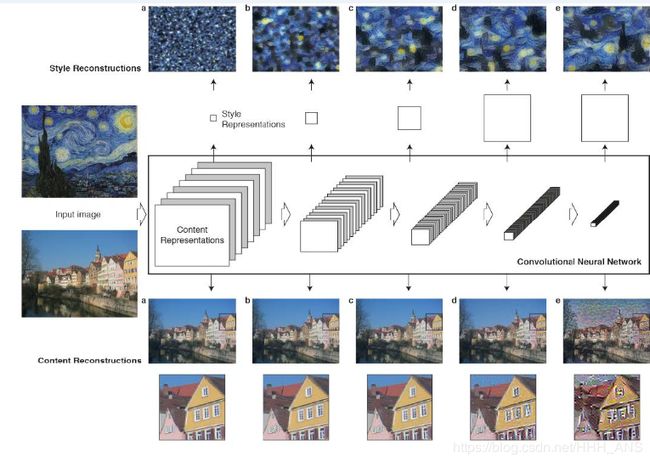
3 - 神经风格转换
总得来说,就是利用一个训练好的卷积神经网络 VGG-19,这个网络在ImageNet 上已经训练过了。
给定一张风格图像 和一张普通图像 ,风格图像经过VGG-19 的时候在每个卷积层会得到很多 feature maps, 这些feature maps 组成一个集合 ,同样的,普通图像 通过 VGG-19 的时候也会得到很多 feature maps,这些feature maps 组成一个集合 ,然后生成一张随机噪声图像 , 随机噪声图像 通过VGG-19 的时候也会生成很多feature maps,这些 feature maps 构成集合 和 分别对应集合 和 , 最终的优化函数是希望调整 让 随机噪声图像 最后看起来既保持普通图像 的内容, 又有一定的风格图像 的风格。
所以我们先要构建这些损失函数:
- 构建内容损失函数 j c o n t e n t ( C , G ) j_{content}(C,G) jcontent(C,G)
- 构建风格损失函数 J s t y l e ( S , G ) J_{style}(S,G) Jstyle(S,G)
- 把它们放在一起构造总代价函数 J ( G ) = α J c o n t e n t ( C , G ) + β J s t y l e ( S , G ) J(G)=\alpha J_{content}(C,G)+\beta J_{style}(S,G) J(G)=αJcontent(C,G)+βJstyle(S,G)
3.1 - 计算内容损失
根据内容损失函数
J c o n t e n t ( C , G ) = 1 4 ∗ n h ∗ n w ∗ n c ∑ 所 有 条 目 ( a ( C ) − a ( G ) ) 2 J_{content}(C,G)=\frac{1}{4*n_h*n_w*n_c}\sum_{所有条目}(a^{(C)}-a^{(G)})^2 Jcontent(C,G)=4∗nh∗nw∗nc1所有条目∑(a(C)−a(G))2
3.2 - 计算风格损失
根据风格损失函数
J s t y l e ( S , G ) = 1 4 ∗ n c 2 ∗ ( n h ∗ n w ) 2 ∑ i = 1 n c ∑ j = 1 n c ( G i j ( S ) − G i j ( G ) ) 2 J_{style}(S,G)=\frac{1}{4*n_c^2*(n_h*n_w)^2}\sum_{i=1}^{n_c}\sum_{j=1}^{n_c}(G_{ij}^(S)-G_{ij}^(G))^2 Jstyle(S,G)=4∗nc2∗(nh∗nw)21i=1∑ncj=1∑nc(Gij(S)−Gij(G))2
3.3 - 总体成本优化公式
最后我们要创建一个最小化风格的内容成本函数
J ( G ) = α J c o n t e n t ( C , G ) + β J s t y l e ( S , G ) J(G)= \alpha J_{content}(C,G)+\beta J_{style}(S,G) J(G)=αJcontent(C,G)+βJstyle(S,G)
4 - 使用TensorFlow实现算法
代码运行前先确保下载好了VGG-19模型
import os
import sys
import numpy as np
import scipy.io
import scipy.misc
import tensorflow as tf
# Output folder for the images.
OUTPUT_DIR = 'output/'
# Style image to use.
STYLE_IMAGE = '/images/ocean.jpg'
# Content image to use.
CONTENT_IMAGE = '/images/Taipei101.jpg'
# Image dimensions constants.
IMAGE_WIDTH = 800
IMAGE_HEIGHT = 600
COLOR_CHANNELS = 3
###############################################################################
# Algorithm constants
###############################################################################
# 设置随机噪声图像与内容图像的比率
NOISE_RATIO = 0.6
# 设置迭代次数
ITERATIONS = 1000
# 设置内容图像与风格图像的权重
alpha = 1
beta = 500
# 加载VGG-19 MODEL及设定均值
VGG_Model = 'Downloads/imagenet-vgg-verydeep-19.mat'
MEAN_VALUES = np.array([123.68, 116.779, 103.939]).reshape((1, 1, 1, 3))
# 设置需要用到的卷积层
CONTENT_LAYERS = [('conv4_2', 1.)]
STYLE_LAYERS = [('conv1_1', 0.2), ('conv2_1', 0.2), ('conv3_1', 0.2), ('conv4_1', 0.2), ('conv5_1', 0.2)]
# 生成随机噪声图,与content图以一定比率融合
def generate_noise_image(content_image, noise_ratio = NOISE_RATIO):
"""
Returns a noise image intermixed with the content image at a certain ratio.
"""
noise_image = np.random.uniform(
-20, 20,
(1, IMAGE_HEIGHT, IMAGE_WIDTH, COLOR_CHANNELS)).astype('float32')
# White noise image from the content representation. Take a weighted average
# of the values
img = noise_image * noise_ratio + content_image * (1 - noise_ratio)
return img
def load_image(path):
image = scipy.misc.imread(path)
# Resize the image for convnet input, there is no change but just
# add an extra dimension.
image = np.reshape(image, ((1,) + image.shape))
# Input to the VGG net expects the mean to be subtracted.
image = image - MEAN_VALUES
return image
def save_image(path, image):
# Output should add back the mean.
image = image + MEAN_VALUES
# Get rid of the first useless dimension, what remains is the image.
image = image[0]
image = np.clip(image, 0, 255).astype('uint8')
scipy.misc.imsave(path, image)
def build_net(ntype, nin, nwb=None):
if ntype == 'conv':
return tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.conv2d(nin, nwb[0], strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME') + nwb[1])
elif ntype == 'pool':
return tf.nn.avg_pool(nin, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],
strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
def get_weight_bias(vgg_layers, i):
weights = vgg_layers[i][0][0][2][0][0]
weights = tf.constant(weights)
bias = vgg_layers[i][0][0][2][0][1]
bias = tf.constant(np.reshape(bias, (bias.size)))
return weights, bias
def build_vgg19(path):
net = {}
vgg_rawnet = scipy.io.loadmat(path)
vgg_layers = vgg_rawnet['layers'][0]
net['input'] = tf.Variable(np.zeros((1, IMAGE_HEIGHT, IMAGE_WIDTH, 3)).astype('float32'))
net['conv1_1'] = build_net('conv', net['input'], get_weight_bias(vgg_layers, 0))
net['conv1_2'] = build_net('conv', net['conv1_1'], get_weight_bias(vgg_layers, 2))
net['pool1'] = build_net('pool', net['conv1_2'])
net['conv2_1'] = build_net('conv', net['pool1'], get_weight_bias(vgg_layers, 5))
net['conv2_2'] = build_net('conv', net['conv2_1'], get_weight_bias(vgg_layers, 7))
net['pool2'] = build_net('pool', net['conv2_2'])
net['conv3_1'] = build_net('conv', net['pool2'], get_weight_bias(vgg_layers, 10))
net['conv3_2'] = build_net('conv', net['conv3_1'], get_weight_bias(vgg_layers, 12))
net['conv3_3'] = build_net('conv', net['conv3_2'], get_weight_bias(vgg_layers, 14))
net['conv3_4'] = build_net('conv', net['conv3_3'], get_weight_bias(vgg_layers, 16))
net['pool3'] = build_net('pool', net['conv3_4'])
net['conv4_1'] = build_net('conv', net['pool3'], get_weight_bias(vgg_layers, 19))
net['conv4_2'] = build_net('conv', net['conv4_1'], get_weight_bias(vgg_layers, 21))
net['conv4_3'] = build_net('conv', net['conv4_2'], get_weight_bias(vgg_layers, 23))
net['conv4_4'] = build_net('conv', net['conv4_3'], get_weight_bias(vgg_layers, 25))
net['pool4'] = build_net('pool', net['conv4_4'])
net['conv5_1'] = build_net('conv', net['pool4'], get_weight_bias(vgg_layers, 28))
net['conv5_2'] = build_net('conv', net['conv5_1'], get_weight_bias(vgg_layers, 30))
net['conv5_3'] = build_net('conv', net['conv5_2'], get_weight_bias(vgg_layers, 32))
net['conv5_4'] = build_net('conv', net['conv5_3'], get_weight_bias(vgg_layers, 34))
net['pool5'] = build_net('pool', net['conv5_4'])
return net
def content_layer_loss(p, x):
M = p.shape[1] * p.shape[2]
N = p.shape[3]
loss = (1. / (2 * N * M)) * tf.reduce_sum(tf.pow((x - p), 2))
return loss
def content_loss_func(sess, net):
layers = CONTENT_LAYERS
total_content_loss = 0.0
for layer_name, weight in layers:
p = sess.run(net[layer_name])
x = net[layer_name]
total_content_loss += content_layer_loss(p, x)*weight
total_content_loss /= float(len(layers))
return total_content_loss
def gram_matrix(x, area, depth):
x1 = tf.reshape(x, (area, depth))
g = tf.matmul(tf.transpose(x1), x1)
return g
def style_layer_loss(a, x):
M = a.shape[1] * a.shape[2]
N = a.shape[3]
A = gram_matrix(a, M, N)
G = gram_matrix(x, M, N)
loss = (1. / (4 * N ** 2 * M ** 2)) * tf.reduce_sum(tf.pow((G - A), 2))
return loss
def style_loss_func(sess, net):
layers = STYLE_LAYERS
total_style_loss = 0.0
for layer_name, weight in layers:
a = sess.run(net[layer_name])
x = net[layer_name]
total_style_loss += style_layer_loss(a, x) * weight
total_style_loss /= float(len(layers))
return total_style_loss
def main():
net = build_vgg19(VGG_Model)
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(tf.initialize_all_variables())
content_img = load_image(CONTENT_IMAGE)
style_img = load_image(STYLE_IMAGE)
sess.run([net['input'].assign(content_img)])
cost_content = content_loss_func(sess, net)
sess.run([net['input'].assign(style_img)])
cost_style = style_loss_func(sess, net)
total_loss = alpha * cost_content + beta * cost_style
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(2.0)
init_img = generate_noise_image(content_img)
train_op = optimizer.minimize(total_loss)
sess.run(tf.initialize_all_variables())
sess.run(net['input'].assign(init_img))
for it in range(ITERATIONS):
sess.run(train_op)
if it % 100 == 0:
# Print every 100 iteration.
mixed_image = sess.run(net['input'])
print('Iteration %d' % (it))
print('sum : ', sess.run(tf.reduce_sum(mixed_image)))
print('cost: ', sess.run(total_loss))
if not os.path.exists(OUTPUT_DIR):
os.mkdir(OUTPUT_DIR)
filename = 'output/%d.png' % (it)
save_image(filename, mixed_image)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
5 - 实验结果
那么我们利用图像风格迁移融合的效果是什么呢?
是不是很酷呢?你们也可以换成其他图片来试一试效果。

