【数据科学系列】基于Python的Web应用框架Dash-交互式可视化
基于Python的Web应用框架Dash-交互式可视化
该dash_core_components库包含一个名为的组件Graph。
Graph使用开源plotly.js JavaScript图形库呈现交互式数据可视化 。Plotly.js支持超过35种图表类型,并在矢量质量SVG和高性能WebGL中呈现图表。
dash_core_components.Graph组件的figure参数与Plotly的开放源码Python图形库plotly.py的figure参数是一致的。查看plotly.py文档和图库 以了解更多信息。
Dash组件由一组属性以声明方式来描述。所有这些属性都可以通过回调函数进行更新,但只有这些属性的子集才会通过用户交互进行更新,例如,
当用户单击dcc.Dropdown组件中的选项并且该组件的 value属性发生更改时。
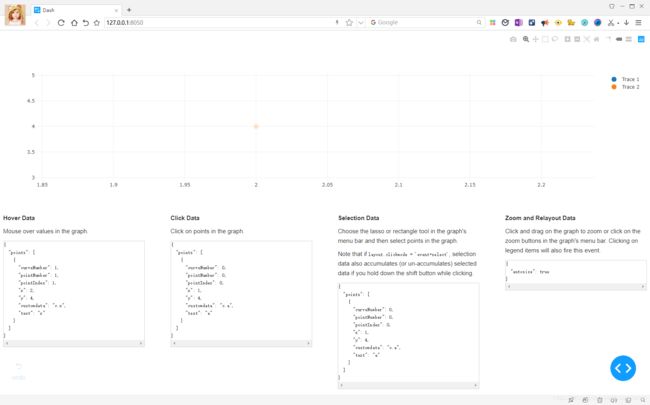
该dcc.Graph部件有四个属性,可以通过用户交互改变:hoverData,clickData,selectedData, relayoutData。将鼠标悬停,单击或者选择图形中的点区域时,这些属性会更新。
在屏幕上打印属性
import json
from textwrap import dedent as d
import dash
import dash_core_components as dcc
import dash_html_components as html
from dash.dependencies import Input, Output
external_stylesheets = ['https://codepen.io/chriddyp/pen/bWLwgP.css']
app = dash.Dash(__name__, external_stylesheets=external_stylesheets)
styles = {
'pre': {
'border': 'thin lightgrey solid',
'overflowX': 'scroll'
}
}
app.layout = html.Div([
dcc.Graph(
id='basic-interactions',
figure={
'data': [
{
'x': [1, 2, 3, 4],
'y': [4, 1, 3, 5],
'text': ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'],
'customdata': ['c.a', 'c.b', 'c.c', 'c.d'],
'name': 'Trace 1',
'mode': 'markers',
'marker': {'size': 12}
},
{
'x': [1, 2, 3, 4],
'y': [9, 4, 1, 4],
'text': ['w', 'x', 'y', 'z'],
'customdata': ['c.w', 'c.x', 'c.y', 'c.z'],
'name': 'Trace 2',
'mode': 'markers',
'marker': {'size': 12}
}
],
'layout': {
'clickmode': 'event+select'
}
}
),
html.Div(className='row', children=[
html.Div([
dcc.Markdown(d("""
**Hover Data**
Mouse over values in the graph.
""")),
html.Pre(id='hover-data', style=styles['pre'])
], className='three columns'),
html.Div([
dcc.Markdown(d("""
**Click Data**
Click on points in the graph.
""")),
html.Pre(id='click-data', style=styles['pre']),
], className='three columns'),
html.Div([
dcc.Markdown(d("""
**Selection Data**
Choose the lasso or rectangle tool in the graph's menu
bar and then select points in the graph.
Note that if `layout.clickmode = 'event+select'`, selection data also
accumulates (or un-accumulates) selected data if you hold down the shift
button while clicking.
""")),
html.Pre(id='selected-data', style=styles['pre']),
], className='three columns'),
html.Div([
dcc.Markdown(d("""
**Zoom and Relayout Data**
Click and drag on the graph to zoom or click on the zoom
buttons in the graph's menu bar.
Clicking on legend items will also fire
this event.
""")),
html.Pre(id='relayout-data', style=styles['pre']),
], className='three columns')
])
])
@app.callback(
Output('hover-data', 'children'),
[Input('basic-interactions', 'hoverData')])
def display_hover_data(hoverData):
return json.dumps(hoverData, indent=2)
@app.callback(
Output('click-data', 'children'),
[Input('basic-interactions', 'clickData')])
def display_click_data(clickData):
return json.dumps(clickData, indent=2)
@app.callback(
Output('selected-data', 'children'),
[Input('basic-interactions', 'selectedData')])
def display_selected_data(selectedData):
return json.dumps(selectedData, indent=2)
@app.callback(
Output('relayout-data', 'children'),
[Input('basic-interactions', 'relayoutData')])
def display_selected_data(relayoutData):
return json.dumps(relayoutData, indent=2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run_server(debug=True)
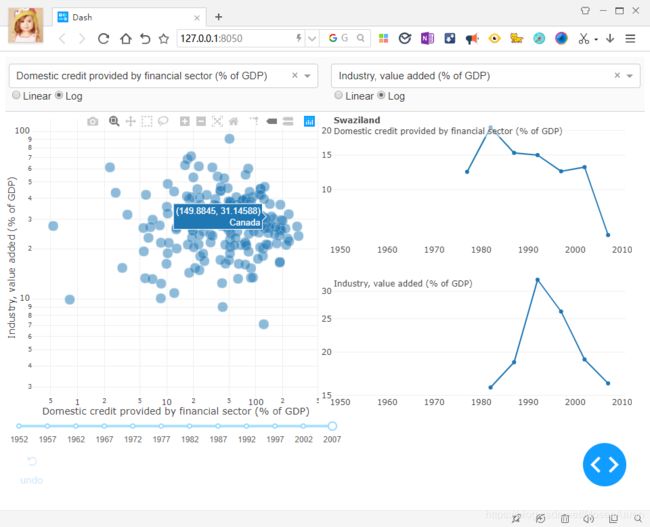
在悬停时更新图表
当用户将鼠标悬停在散点图中的点上时,让用户通过更新时间序列来更新世界指标示例。
import dash
import dash_core_components as dcc
import dash_html_components as html
import pandas as pd
import plotly.graph_objs as go
external_stylesheets = ['https://codepen.io/chriddyp/pen/bWLwgP.css']
app = dash.Dash(__name__, external_stylesheets=external_stylesheets)
df = pd.read_csv(
'https://gist.githubusercontent.com/chriddyp/'
'cb5392c35661370d95f300086accea51/raw/'
'8e0768211f6b747c0db42a9ce9a0937dafcbd8b2/'
'indicators.csv')
available_indicators = df['Indicator Name'].unique()
app.layout = html.Div([
html.Div([
html.Div([
dcc.Dropdown(
id='crossfilter-xaxis-column',
options=[{'label': i, 'value': i} for i in available_indicators],
value='Fertility rate, total (births per woman)'
),
dcc.RadioItems(
id='crossfilter-xaxis-type',
options=[{'label': i, 'value': i} for i in ['Linear', 'Log']],
value='Linear',
labelStyle={'display': 'inline-block'}
)
],
style={'width': '49%', 'display': 'inline-block'}),
html.Div([
dcc.Dropdown(
id='crossfilter-yaxis-column',
options=[{'label': i, 'value': i} for i in available_indicators],
value='Life expectancy at birth, total (years)'
),
dcc.RadioItems(
id='crossfilter-yaxis-type',
options=[{'label': i, 'value': i} for i in ['Linear', 'Log']],
value='Linear',
labelStyle={'display': 'inline-block'}
)
], style={'width': '49%', 'float': 'right', 'display': 'inline-block'})
], style={
'borderBottom': 'thin lightgrey solid',
'backgroundColor': 'rgb(250, 250, 250)',
'padding': '10px 5px'
}),
html.Div([
dcc.Graph(
id='crossfilter-indicator-scatter',
hoverData={'points': [{'customdata': 'Japan'}]}
)
], style={'width': '49%', 'display': 'inline-block', 'padding': '0 20'}),
html.Div([
dcc.Graph(id='x-time-series'),
dcc.Graph(id='y-time-series'),
], style={'display': 'inline-block', 'width': '49%'}),
html.Div(dcc.Slider(
id='crossfilter-year--slider',
min=df['Year'].min(),
max=df['Year'].max(),
value=df['Year'].max(),
marks={str(year): str(year) for year in df['Year'].unique()}
), style={'width': '49%', 'padding': '0px 20px 20px 20px'})
])
@app.callback(
dash.dependencies.Output('crossfilter-indicator-scatter', 'figure'),
[dash.dependencies.Input('crossfilter-xaxis-column', 'value'),
dash.dependencies.Input('crossfilter-yaxis-column', 'value'),
dash.dependencies.Input('crossfilter-xaxis-type', 'value'),
dash.dependencies.Input('crossfilter-yaxis-type', 'value'),
dash.dependencies.Input('crossfilter-year--slider', 'value')])
def update_graph(xaxis_column_name, yaxis_column_name,
xaxis_type, yaxis_type,
year_value):
dff = df[df['Year'] == year_value]
return {
'data': [go.Scatter(
x=dff[dff['Indicator Name'] == xaxis_column_name]['Value'],
y=dff[dff['Indicator Name'] == yaxis_column_name]['Value'],
text=dff[dff['Indicator Name'] == yaxis_column_name]['Country Name'],
customdata=dff[dff['Indicator Name'] == yaxis_column_name]['Country Name'],
mode='markers',
marker={
'size': 15,
'opacity': 0.5,
'line': {'width': 0.5, 'color': 'white'}
}
)],
'layout': go.Layout(
xaxis={
'title': xaxis_column_name,
'type': 'linear' if xaxis_type == 'Linear' else 'log'
},
yaxis={
'title': yaxis_column_name,
'type': 'linear' if yaxis_type == 'Linear' else 'log'
},
margin={'l': 40, 'b': 30, 't': 10, 'r': 0},
height=450,
hovermode='closest'
)
}
def create_time_series(dff, axis_type, title):
return {
'data': [go.Scatter(
x=dff['Year'],
y=dff['Value'],
mode='lines+markers'
)],
'layout': {
'height': 225,
'margin': {'l': 20, 'b': 30, 'r': 10, 't': 10},
'annotations': [{
'x': 0, 'y': 0.85, 'xanchor': 'left', 'yanchor': 'bottom',
'xref': 'paper', 'yref': 'paper', 'showarrow': False,
'align': 'left', 'bgcolor': 'rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.5)',
'text': title
}],
'yaxis': {'type': 'linear' if axis_type == 'Linear' else 'log'},
'xaxis': {'showgrid': False}
}
}
@app.callback(
dash.dependencies.Output('x-time-series', 'figure'),
[dash.dependencies.Input('crossfilter-indicator-scatter', 'hoverData'),
dash.dependencies.Input('crossfilter-xaxis-column', 'value'),
dash.dependencies.Input('crossfilter-xaxis-type', 'value')])
def update_y_timeseries(hoverData, xaxis_column_name, axis_type):
country_name = hoverData['points'][0]['customdata']
dff = df[df['Country Name'] == country_name]
dff = dff[dff['Indicator Name'] == xaxis_column_name]
title = '{}
{}'.format(country_name, xaxis_column_name)
return create_time_series(dff, axis_type, title)
@app.callback(
dash.dependencies.Output('y-time-series', 'figure'),
[dash.dependencies.Input('crossfilter-indicator-scatter', 'hoverData'),
dash.dependencies.Input('crossfilter-yaxis-column', 'value'),
dash.dependencies.Input('crossfilter-yaxis-type', 'value')])
def update_x_timeseries(hoverData, yaxis_column_name, axis_type):
dff = df[df['Country Name'] == hoverData['points'][0]['customdata']]
dff = dff[dff['Indicator Name'] == yaxis_column_name]
return create_time_series(dff, axis_type, yaxis_column_name)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run_server(debug=True)
通用交叉过滤方法
每个散点图的选择都会过滤基础数据集。
import dash
import dash_core_components as dcc
import dash_html_components as html
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from dash.dependencies import Input, Output
external_stylesheets = ['https://codepen.io/chriddyp/pen/bWLwgP.css']
app = dash.Dash(__name__, external_stylesheets=external_stylesheets)
np.random.seed(0)
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Column {}'.format(i): np.random.rand(30) + i*10
for i in range(6)})
app.layout = html.Div([
html.Div(
dcc.Graph(
id='g1',
config={'displayModeBar': False}
), className='four columns'
),
html.Div(
dcc.Graph(
id='g2',
config={'displayModeBar': False}
), className='four columns'),
html.Div(
dcc.Graph(
id='g3',
config={'displayModeBar': False}
), className='four columns')
], className='row')
def highlight(x, y):
def callback(*selectedDatas):
selectedpoints = df.index
for i, selected_data in enumerate(selectedDatas):
if selected_data is not None:
selected_index = [
p['customdata'] for p in selected_data['points']
]
if len(selected_index) > 0:
selectedpoints = np.intersect1d(
selectedpoints, selected_index)
# set which points are selected with the `selectedpoints` property
# and style those points with the `selected` and `unselected`
# attribute. see
# https://medium.com/@plotlygraphs/notes-from-the-latest-plotly-js-release-b035a5b43e21
# for an explanation
figure = {
'data': [
{
'x': df[x],
'y': df[y],
'text': df.index,
'textposition': 'top',
'selectedpoints': selectedpoints,
'customdata': df.index,
'type': 'scatter',
'mode': 'markers+text',
'marker': {
'color': 'rgba(0, 116, 217, 0.7)',
'size': 12,
'line': {
'color': 'rgb(0, 116, 217)',
'width': 0.5
}
},
'textfont': {
'color': 'rgba(30, 30, 30, 1)'
},
'unselected': {
'marker': {
'opacity': 0.3,
},
'textfont': {
# make text transparent when not selected
'color': 'rgba(0, 0, 0, 0)'
}
}
},
],
'layout': {
'clickmode': 'event+select',
'margin': {'l': 15, 'r': 0, 'b': 15, 't': 5},
'dragmode': 'select',
'hovermode': 'closest',
'showlegend': False
}
}
# Display a rectangle to highlight the previously selected region
shape = {
'type': 'rect',
'line': {
'width': 1,
'dash': 'dot',
'color': 'darkgrey'
}
}
if selectedDatas[0] and selectedDatas[0]['range']:
figure['layout']['shapes'] = [dict({
'x0': selectedDatas[0]['range']['x'][0],
'x1': selectedDatas[0]['range']['x'][1],
'y0': selectedDatas[0]['range']['y'][0],
'y1': selectedDatas[0]['range']['y'][1]
}, **shape)]
else:
figure['layout']['shapes'] = [dict({
'type': 'rect',
'x0': np.min(df[x]),
'x1': np.max(df[x]),
'y0': np.min(df[y]),
'y1': np.max(df[y])
}, **shape)]
return figure
return callback
# app.callback is a decorator which means that it takes a function
# as its argument.
# highlight is a function "generator": it's a function that returns function
app.callback(
Output('g1', 'figure'),
[Input('g1', 'selectedData'),
Input('g2', 'selectedData'),
Input('g3', 'selectedData')]
)(highlight('Column 0', 'Column 1'))
app.callback(
Output('g2', 'figure'),
[Input('g2', 'selectedData'),
Input('g1', 'selectedData'),
Input('g3', 'selectedData')]
)(highlight('Column 2', 'Column 3'))
app.callback(
Output('g3', 'figure'),
[Input('g3', 'selectedData'),
Input('g1', 'selectedData'),
Input('g2', 'selectedData')]
)(highlight('Column 4', 'Column 5'))
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run_server(debug=True)
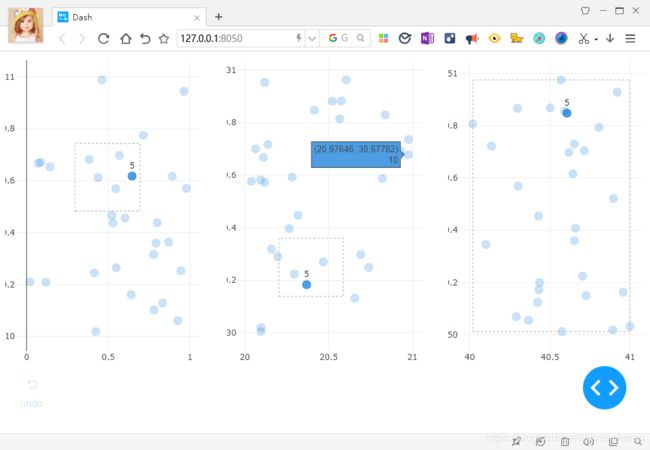
尝试在任何图中单击并拖动以过滤不同的区域。在每个选择中,将使用每个绘图的最新选定区域触发三个图形回调。基于所选择的点过滤pandas数据帧,并重新绘制图形,突出显示所选择的点,并将所选区域绘制为虚线矩形。
另外,如果您发现自己过滤并可视化高维数据集,则应考虑检出 并行坐标 图表类型。
目前的局限
目前图形交互存在一些局限。
- 目前无法自定义悬停交互或选择框的样式。
更多资料,请访问:https://community.plot.ly/c/dash?_ga=2.67963033.940349663.1557058115-366694202.1557058115