0.what is Netty?
简单来说,Netty是异步的,事务驱动的,高性能的NIO框架
Netty官网
其中有详细的netty介绍,刚开始学习,有什么不对,欢迎指出。
1.Netty中几个比较重要的概念
1.0 Handler
Handler其实就是事件的处理器,Netty通过Channel读入请求内容后会分配给Handler进行事件处理,Handler能够处理的事件包括:数据接收,异常处理,数据转换,编码解码等问题,其中包含两个非常重要的接口ChannelInboundHandler,ChannelOutboundHandler,前者负责处理客户端发送到服务端的请求,后者反之。关于Handler执行顺序的一些介绍可以看一看这篇文章: handler的执行顺序
在这个地方有一个值得注意的点,无论是InboundHandler还是OutboundHandler都不适合用于做耗时操作,官方要求耗时操作应当使用单独的EventExcutorGroup+专门的Handler来进行操作
static final EventExecutorGroup group = new DefaultEventExecutorGroup(16);
...
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast("decoder", new MyProtocolDecoder()); pipeline.addLast("encoder", new MyProtocolEncoder());
// Tell the pipeline to run MyBusinessLogicHandler's event handler methods
// in a different thread than an I/O thread so that the I/O thread is not blocked by
// a time-consuming task.
// If your business logic is fully asynchronous or finished very quickly, you don't
// need to specify a group.
pipeline.addLast(group, "handler", new MyBusinessLogicHandler());
1.1 Channel
这里的Channel的概念和NIO中Channel的概念是一样的,相当于一个Socket连接
1.2 Bootstrap
Bootstrap其实就是Netty服务的启动器,服务端使用的是ServerBootstrap,客户端使用的是Bootstrap,我们可以通过配置Bootstrap来配置Netty使用哪种的Channel,Group,Handler和Encoder,Decoder……
1.3 LoopGroup
一个LoopGroup可以包含多个EventLoop,我目前的理解是将其理解为一个线程池,其中的EventLoop为其中的线程
1.4 ChannelFuture
这点在官方的Guide中也有提到,在Netty中,所有的处理都是异步的,因此需要一个Future对象,可以注册监听在异步线程处理完以后进行一些处理
2.HelloWorld
2.0 Server端代码
public class Server{
public void start(int port) throws InterruptedException {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventExecutorGroup bussinessGroup = new DefaultEventExecutorGroup(16);
try {
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
//使用哪一种Channel
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
//添加http请求所需要的编码器与解码器
ch.pipeline().addLast(new HttpResponseEncoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new HttpRequestDecoder());
//ch.pipeline().addLast(new ServerOutboundHandler()); //如果存在OutboundHandler则必须在最后一个inbound前面
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ServerHandler());
//耗时操作使用的group和专门的handler
ch.pipeline().addLast(bussinessGroup, "handler", new BusinessHandler());
}
})
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);
ChannelFuture f = b.bind(port);
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Server server = new Server();
server.start(8090);
}
}
2.1 ServerHandler
public class ServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
private HttpRequest request;
private HttpContent content;
private FullHttpResponse response;
private StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
if (msg instanceof HttpRequest) {
request = (HttpRequest) msg;
System.out.println(request.uri());
System.out.println("request received success");
sb.append("request received success \n");
}
if (msg instanceof HttpContent) {
content = (HttpContent) msg;
ByteBuf buf = content.content();
String result = buf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8);
System.out.println(result);
buf.release();
System.out.println("content received success");
sb.append("content received success");
response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.OK, Unpooled.wrappedBuffer(sb.toString().getBytes()));
ctx.writeAndFlush(response);
}
}
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.close();
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
HttpResponse response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.BAD_GATEWAY);
ctx.writeAndFlush(response);
ctx.close();
}
}
3. 请求服务器
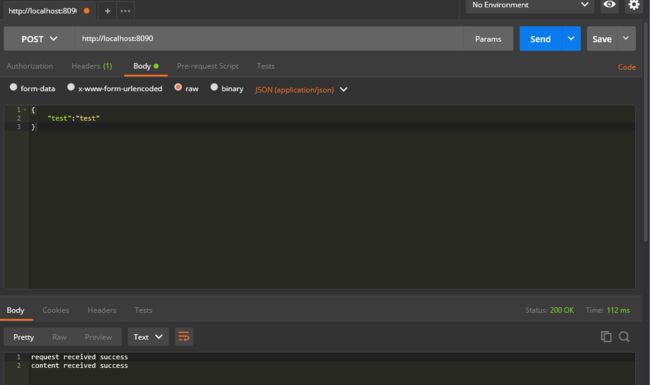
3.0 使用postman来请求服务器
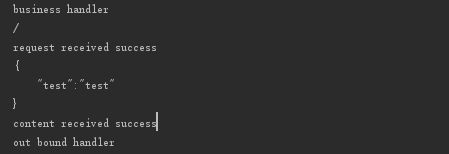
我使用post方式随意发送了任意内容到服务器,能够得到返回内容,并且idea控制台输出如下,表明可以获得postman发送的数据
3.1 使用NettyClient访问Netty服务器
3.1.0 Client
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
b.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new HttpClientCodec());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ClientHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture f = b.connect("127.0.0.1", 8090).sync();
Channel ch = f.channel();
FullHttpRequest request = new DefaultFullHttpRequest(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpMethod.POST, "http://127.0.0.1:8090", Unpooled.wrappedBuffer("{ \"test\" : \"test\" }".getBytes())); //发送请求道服务端
request.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_TYPE, HttpHeaderValues.APPLICATION_JSON);
request.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_LENGTH, 1024); //必须设置Content length否则服务端收不到content
System.out.println(request.content().toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
ch.writeAndFlush(request);
//wait until server to close the connection
ch.closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
3.1.1 ClientHandler
public class ClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
HttpContent content;
HttpResponse response;
if (msg instanceof HttpResponse) {
response = (HttpResponse) msg;
System.out.println(response.status().toString());
}
if (msg instanceof HttpContent) {
content = (HttpContent) msg;
ByteBuf buf = content.content();
String responseContent = buf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8);
System.out.println(responseContent);
buf.release();
}
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
以上代码也能获得和postman访问相同的效果
4.其中思考的问题
- Q:耗时的业务逻辑操作应该放在哪里
A:使用EventExcutorGroup和单独的Handler来实现业务逻辑代码(在上面的代码中有提到) - Q :如何将InboundMessageHandler读到的msg传到其他Handler
A:使用ctx.pipeline().channel().attr()可以设置属性来在Handler传递属性值