使用tensorflow实现gan简单小demo
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
tf.set_random_seed(1)
np.random.seed(1)
BATCH_SIZE = 64
LR_G = 0.0001
LR_D = 0.0001
N_IDEAS = 5
ART_COMPONENTS = 15
PAINT_POINTS = np.vstack([np.linspace(-1,1,ART_COMPONENTS)for _ in range(BATCH_SIZE)]) #shape = (64,15)
print(PAINT_POINTS)
plt.plot(PAINT_POINTS[0],2*np.power(PAINT_POINTS[0],2)+1,c = '#74BCFF',lw = 3,label='upper bound')
plt.plot(PAINT_POINTS[0],1*np.power(PAINT_POINTS[0],2)+0,c = '#FF9359',lw = 3,label='lower bound')
plt.legend(loc = 'upper right')
plt.show()
def artist_works(): #即真实的数据
a = np.random.uniform(1,2,size=BATCH_SIZE)[:,np.newaxis] #shape = (64,1)
paintings = a*np.power(PAINT_POINTS,2)+(a-1) #shape = (64,15)
return paintings
with tf.variable_scope('Generator'): #使用生成器伪造假的数据
G_in = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,N_IDEAS]) #shape = (64,5)
G_l1 = tf.layers.dense(G_in,128,tf.nn.relu)
G_out = tf.layers.dense(G_l1,ART_COMPONENTS)
with tf.variable_scope('Discriminator'):
real_art = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,ART_COMPONENTS],name='real_in') #使用鉴别器来鉴别真实数据
D_l0 = tf.layers.dense(real_art,128,tf.nn.relu,name='1') #并将它判别为1
prob_artist0 = tf.layers.dense(D_l0,1,tf.nn.sigmoid,name='out')
#fake art
D_l1 = tf.layers.dense(G_out,128,tf.nn.relu,name='1',reuse=True) #使用费鉴别器来判别伪造数据
prob_artist1 = tf.layers.dense(D_l1,1,tf.nn.sigmoid,name='out',reuse=True) #并将其判别为0
D_loss = -tf.reduce_mean(tf.log(prob_artist0)+tf.log(1-prob_artist1)) #定义误差函数
G_loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.log(1-prob_artist1))
train_D = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(LR_D).minimize( #定义优化函数
D_loss,var_list=tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES,scope='Discriminator'))
train_G = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(LR_G).minimize(
G_loss,var_list=tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES,scope='Generator'))
sess= tf.Session() #初始化流图
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
plt.ion()
for step in range(5000):
artist_paintings = artist_works()
G_ideas = np.random.randn(BATCH_SIZE,N_IDEAS)
G_paintings,pa0,D1 = sess.run([G_out,prob_artist0,D_loss,train_D,train_G],
{G_in:G_ideas,real_art:artist_paintings})[:3]
if step%50==0: #可视化
plt.cla()
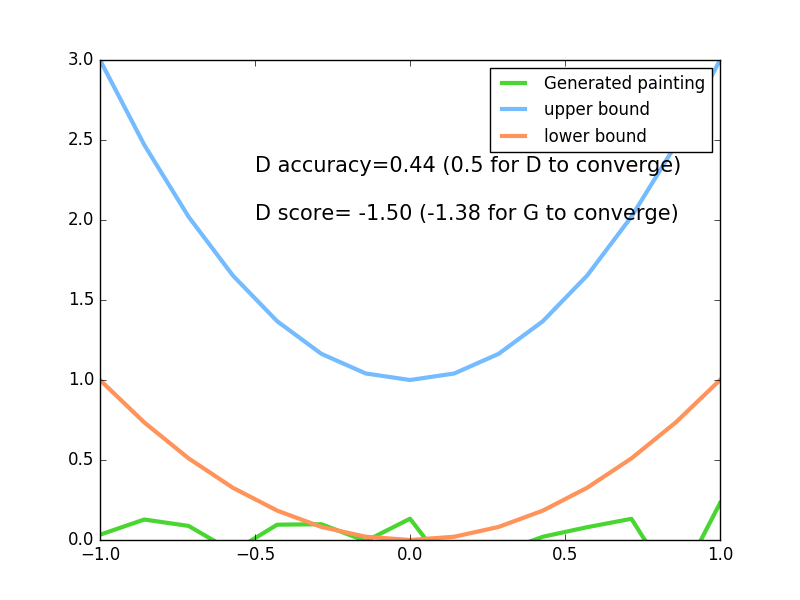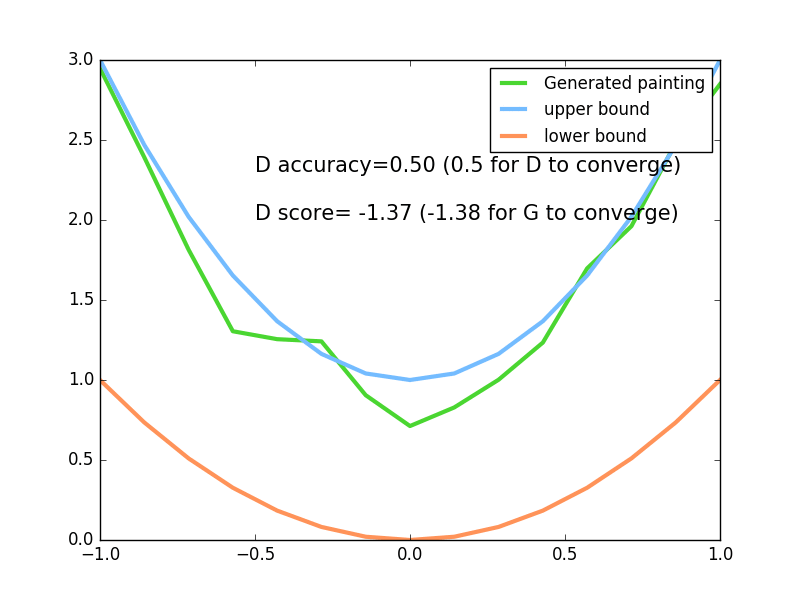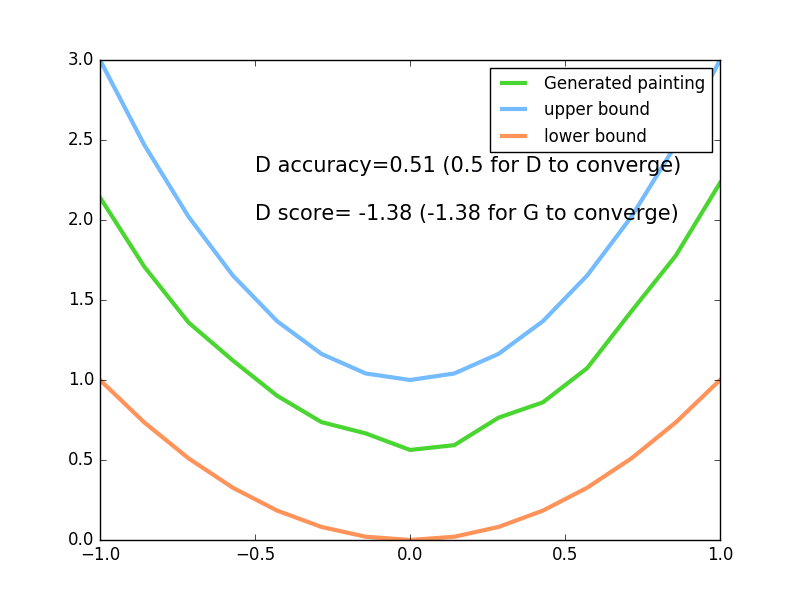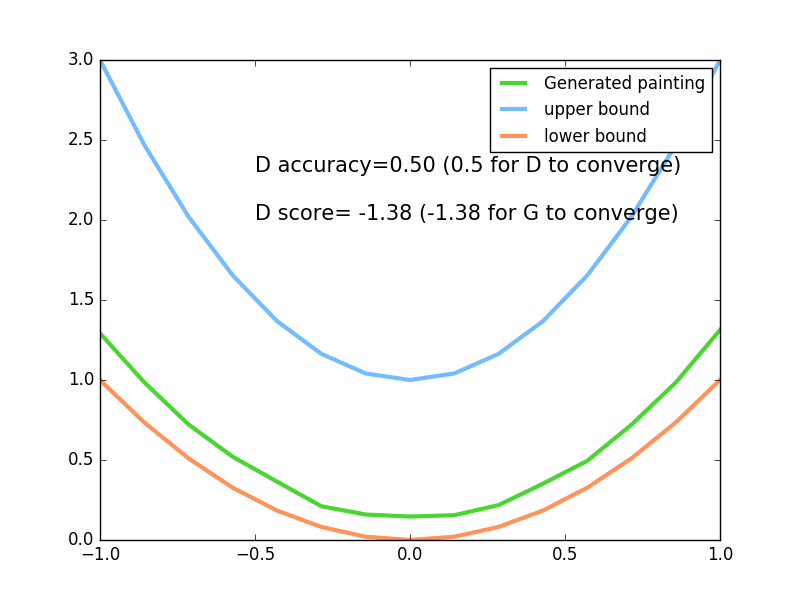
plt.plot(PAINT_POINTS[0],G_paintings[0],c='#4AD631',lw=3,label='Generated painting')
plt.plot(PAINT_POINTS[0],2*np.power(PAINT_POINTS[0],2)+1,c='#74BCFF',lw=3,label='upper bound')
plt.plot(PAINT_POINTS[0],1*np.power(PAINT_POINTS[0],2)+0,c='#FF9359',lw=3,label='lower bound')
plt.text(-.5,2.3,'D accuracy=%.2f (0.5 for D to converge)'%pa0.mean(),fontdict={'size':15})
plt.text(-.5,2,'D score=%.2f (-1.38 for G to converge)'%-D1,fontdict={'size':15})
plt.ylim((0,3));plt.legend(loc='upper right',fontsize=12);plt.draw();plt.pause(0.01)
plt.ioff()
plt.show()
本程序使用生成对抗网络(GAN)来实现一个小Demo:
目的 :使用生成器拟合形如:a*X2+(a-1)
对于a 我们使用np.random.uniform函数随机生成(1-2之间)
为了直观的看到生成器生成的数据,我们设置了上下两个边界。
最终实验效果:
注释:此文为莫凡Python学习笔记 莫凡tensorflow