Tensorflow学习——6 LeNet-5的研究
LeNet-5的学习
- 1、LeNet-5的成就
- 2、LeNet-5的优点
- 3、LeNet-5的网络图
- 4、LeNet-5的代码
1、LeNet-5的成就
LeNet-5是Yann LeCun在1998年设计的用于手写数字识别的卷积神经网络,当年美国大多数银行就是用它来识别支票上面的手写数字的,它是早期卷积神经网络中最有代表性的实验系统之一,LeNet-5在MNIST数据集上可以达到99.2%的准确率。
2、LeNet-5的优点
LeNet-5一共有七层
- 每一个卷积层包含三个部分:卷积操作、池化操作和非线性激活函数
- 使用卷积来提取空间特征
- 下采样层的平均池化层
- 层与层之间的稀疏连接减少计算复杂度
3、LeNet-5的网络图
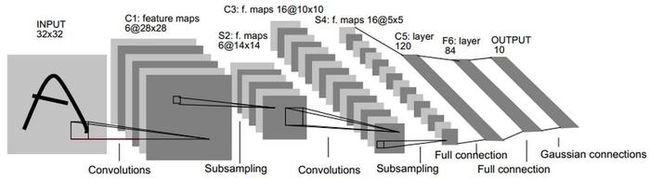
LeNet有七层,卷积–>池化–>卷积–>池化–>全连接–>全连接–>全连接
第一层,卷积层
输入是原始的图像像素,LeNet-5接受的输入是32×32×1的,第一个卷积层的过滤器大小是5×5,深度为6,不使用全0补充,步长为1。
所以这一层的输出为(32-5+1=28)【注out_length = (in_length-filter_length+1)/stride_length】,所以第一次的参数有5×5×1×6+6=158个,其中5×5是卷积核的length和width,1是输入层的通道数,第一个6是卷积核深度,第2个6是偏置项的参数。
连接数是122304个,因为下一层的节点是28×28×6=4704个节点,每一个节点和5×5个当前节点相连,所以本层有(5×5+1)×28×28×6=122304个连接。
第二层,池化层
输入的矩阵是28×28×6的矩阵,过滤器的大小是2×2,长和宽都是2,使用全0填充,所以输出矩阵是14×14×6
(input_width+2*pad-pool_size)/stride+1
(28+2×0-2)/2 + 1
第三层,卷积层
输入是14×14×6的矩阵节点,第二个卷积层的过滤器大小是5×5,深度为16,不使用全0补充,步长为1。
所以这一层的输出为10×10×16 (14-5+1=10)【注out_length = (in_length-filter_length+1)/stride_length】,所以第一次的参数有5×5×6×16+16=2416个,其中5×5是卷积核的length和width,6是输入层的通道数,第一个16是卷积核深度,第2个16是偏置项的参数。
连接数是41600个,因为下一层的节点是10×10×16个节点,每一个节点和5×5个当前节点相连,所以本层有(5×5+1)×10×10×16=41600个连接。
第四层,池化层
输入的矩阵是10×10×16的矩阵,过滤器的大小是2×2,长和宽都是2,使用全0填充,所以输出矩阵是5×5×16
第五层,全连接层
输入的矩阵是5×5×16的矩阵,输出的节点个数是120,所以参数为5×5×16×120+120=48120
第六层,全连接层
输入的节点是120个,输出是84个,参数120×84 +84 = 10164
第五层,全连接层
输入的节点是84个,输出是10个,参数84×10+10= 850
4、LeNet-5的代码
# _*_ encoding=utf8 _*_
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
import tensorflow as tf
import os
import numpy as np
# 配置神经网络的参数
INPUT_NODE = 784
OUTPUT_NODE = 10
IMAGE_SIZE = 28 #像素
NUM_CHANNELS = 1 #通道数
NUM_LABELS = 10
#第一层卷积层的深度大小
CONV1_DEEP = 32
CONV1_SIZE = 5
#第二层卷积层的深度大小
CONV2_DEEP = 64
CONV2_SIZE = 5
# 全连接层的节点个数
FC_SIZE = 512
# 定义神经网络的前向传播v
def inference(input_tensor,train,regularizer):
# 第一层,输入是28*28*1 input_tensor, 卷积核 5 *5 *1*6 最后两个是图像通道数和卷积核个数,
# strides 为1 用0补齐
# 输出是28*28*32
with tf.variable_scope("layer-conv1"):
conv1_weights = tf.get_variable("weight",[CONV1_SIZE,CONV1_SIZE,NUM_CHANNELS,CONV1_DEEP],
initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.1))
conv1_biases = tf.get_variable("biases",[CONV1_DEEP],initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.0))
#使用边长为5,深度32的过滤器,移动的步长为1,
conv1 = tf.nn.conv2d(input_tensor,conv1_weights,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding="SAME")
relu1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(conv1,conv1_biases))
# 第二层,池化层,最大池化,输入是28*28*32的矩阵,输入是14*14*32
with tf.name_scope('layer2-pool1'):
pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(
relu1,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding="SAME"
)
# 第三层,卷积层 输入14*14*32 输出是14*14*64
with tf.name_scope("layer-conv2"):
conv2_weights = tf.get_variable(
"weight",[CONV2_SIZE,CONV2_SIZE,CONV1_DEEP,CONV2_DEEP],initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.1)
)
conv2_biases = tf.get_variable("biased",[CONV2_DEEP],initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.0))
conv2 = tf.nn.conv2d(pool1,conv2_weights,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding="SAME")
relu2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(conv2,conv2_biases))
#第四层,池化层
# 输入是14*14*64 输出7*7*64
with tf.name_scope('layer-pool2'):
pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(
relu2,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding="SAME"
)
# 将池化层的输出转化为全连接层的数据格式,也是就是reshape一下,第四层输出是矩阵,第五层输入是一个向量,batch不变
pool_shape = pool2.get_shape().as_list()
# 将矩阵拉直成向量的长度,长度也就是矩阵长宽高的乘积,pool_shape[0]是一个batch中数据的个数
nodes = pool_shape[1]*pool_shape[2]*pool_shape[3]
# 通过tf.reshape将第四层的输出变成一个batch的向量
reshaped = tf.reshape(pool2,[pool_shape[0],nodes])
# 第五层,全连接层
# 拉直后向量的长度为3136,输出是512的向量,加入dropout,避免过拟合,这个一般只是在全连接层使用,
with tf.variable_scope("layer-fc1"):
fc1_weights = tf.get_variable(
"weight",[nodes,FC_SIZE],
initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.1)
)
if regularizer != None:
tf.add_to_collection("losses",regularizer(fc1_weights))
fc1_biases = tf.get_variable(
"biased",[FC_SIZE],initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.1)
)
fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(reshaped,fc1_weights) + fc1_biases)
if train:
fc1 = tf.nn.dropout(fc1,0.5)
#第六层,全连接层,输入512,输出10,通过softmax可以得到最后的分类
with tf.variable_scope("layer-fc2"):
fc2_weights = tf.get_variable(
"weight",[FC_SIZE,NUM_LABELS],
initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.1)
)
if regularizer != None:
tf.add_to_collection("losses",regularizer(fc2_weights))
fc2_biases = tf.get_variable(
"biases",[NUM_CHANNELS],
initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.1)
)
logit = tf.matmul(fc1,fc2_weights) + fc2_biases
return logit
BATCH_SIZE = 100
LEARNING_RATE_BASE = 0.01
LEARNING_RATE_DECAY = 0.99
REGULARIZATION_RATE = 0.0001
TRAINING_STEPS = 6000
MOVING_AVERAGE_DECAY = 0.99
# 训练模型的过程
def train(mnist):
# 定义输出为4维矩阵的placeholder
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [
BATCH_SIZE,
IMAGE_SIZE,
IMAGE_SIZE,
NUM_CHANNELS],
name='x-input')
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, OUTPUT_NODE], name='y-input')
regularizer = tf.contrib.layers.l2_regularizer(REGULARIZATION_RATE)
y = inference(x, False, regularizer)
global_step = tf.Variable(0, trainable=False)
# 定义损失函数、学习率、滑动平均操作以及训练过程。
variable_averages = tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage(MOVING_AVERAGE_DECAY, global_step)
variables_averages_op = variable_averages.apply(tf.trainable_variables())
cross_entropy = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=y, labels=tf.argmax(y_, 1))
cross_entropy_mean = tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy)
loss = cross_entropy_mean + tf.add_n(tf.get_collection('losses'))
learning_rate = tf.train.exponential_decay(
LEARNING_RATE_BASE,
global_step,
mnist.train.num_examples / BATCH_SIZE, LEARNING_RATE_DECAY,
staircase=True)
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(loss, global_step=global_step)
with tf.control_dependencies([train_step, variables_averages_op]):
train_op = tf.no_op(name='train')
# 初始化TensorFlow持久化类。
saver = tf.train.Saver()
with tf.Session() as sess:
tf.global_variables_initializer().run()
for i in range(TRAINING_STEPS):
xs, ys = mnist.train.next_batch(BATCH_SIZE)
reshaped_xs = np.reshape(xs, (
BATCH_SIZE,
IMAGE_SIZE,
IMAGE_SIZE,
NUM_CHANNELS))
_, loss_value, step = sess.run([train_op, loss, global_step], feed_dict={x: reshaped_xs, y_: ys})
if i % 1000 == 0:
print("After %d training step(s), loss on training batch is %g." % (step, loss_value))
if __name__ == '__main__':
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("../bin/data", one_hot=True)
train(mnist)