Android——启动过程详解
Android从Kernel启动有4个步骤(以android4.2为例)
(1) init进程启动
(2) Native服务启动
(3) System Server,Android服务启动
(4) Home启动
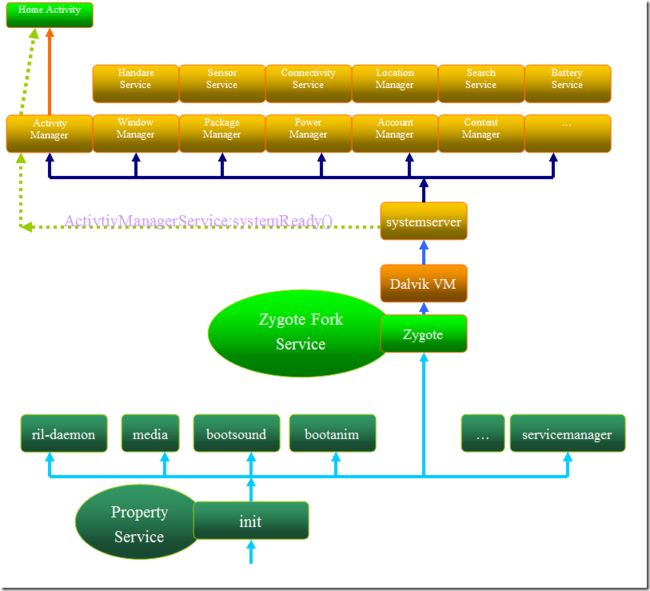
总体启动框架图如:
第一步:initial进程(system/core/init)
init进程,它是一个由内核启动的用户级进程。内核自行启动(已经被载入内存,开始运行,并已初始化所有的设备驱动程序和数据结构等)之后,就通过启动一个用户级程序init的方式,完成引导进程。init始终是第一个进程.
Init进程一起来就根据init.rc脚本文件建立了几个基本的服务:
- servicemanamger
- zygote
最后Init并不退出,而是担当起property service的功能。
1.1进程启动
/system/core/Init中的init.c入口:
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
...
...
/* clear the umask */
umask(0);
/* Get the basic filesystem setup we need put
* together in the initramdisk on / and then we'll
* let the rc file figure out the rest.
*/
/*创建基本的文件系统*/
mkdir("/dev", 0755);
mkdir("/proc", 0755);
mkdir("/sys", 0755);
...
INFO("reading config file\n");
/*解析init.rc文件*/
init_parse_config_file("/init.rc");
...
/* execute all the boot actions to get us started */
/*触发需要执行的action*/
action_for_each_trigger("init", action_add_queue_tail);
...
for(;;)
{
int nr, i, timeout = -1;
/*执行当前action的一个command*/
execute_one_command();
...
/*loop 处理来自property, signal的event*/
for (i = 0; i < fd_count; i++)
{
if (ufds[i].revents == POLLIN)
{
if (ufds[i].fd == get_property_set_fd())
handle_property_set_fd();
else if (ufds[i].fd == get_keychord_fd())
handle_keychord();
else if (ufds[i].fd == get_signal_fd())
handle_signal();
}
}
}
}
Init.rc是Android自己规定的初始化脚本(Android Init Language, system/core/init/readme.txt)
该脚本包含四个类型的声明:
- Actions
- Commands
- Services
- Options.
1.2 解析init.rc中的service
system/core/init/下的init_parser.c中的 init_parse_config_file("/init.rc")——> parse_config(fn, data)——>parse_new_section(&state, kw, nargs, args)——>parse_service(state, nargs, args)——> list_add_tail(&service_list, &svc->slist);
添加service到service_list
init_parser.c解析:
static list_declare(service_list);
static list_declare(action_list);
static list_declare(action_queue);1.3 启动native service
execute_one_command():从action_queue链表上移除头结点(action)
class_start default对应的入口函数,主要用于启动native service
system/core/init/ builtins.c中的:
int do_class_start(int nargs, char **args)
{
/* Starting a class does not start services
* which are explicitly disabled. They must
* be started individually.
*/
service_for_each_class(args[1], service_start_if_not_disabled);
return 0;
}init_parser.c中的 service_for_each_class(...):遍历service_list链表上的所有结点
static void service_start_if_not_disabled(struct service *svc)
{
if (!(svc->flags & SVC_DISABLED)) {
service_start(svc, NULL);
}
}如果不是disabled就启动service。
init.c中的service_start(...)调用fork()创建进程,调用execve(...)调用执行新的service。
system/core/init/property_service.c中的handle_property_set_fd处理系统属性服务请求,如:service, wlan和dhcp.
property_service服务可以参考Android——SystemProperties的应用
system/core/init/keycords.c中的handle_keychord处理注册在service structure上的keychord,通常是启动service.
system/core/init/signal_handler.c中的handle_signal处理SIGCHLD signal(僵尸进程).
第二步 Zygote
Servicemanager和zygote进程就奠定了Android的基础。Zygote这个进程起来才会建立起真正的Android运行空间,初始化建立的Service都是Navtive service.在.rc脚本文件中zygote的描述:
service zygote /system/bin/app_process -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server
所以Zygote从frameworks/base/cmds/app_main.cpp的main(…)开始。
其中:
AppRuntime runtime;初始化运行时间.
if (zygote) {
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit",
startSystemServer ? "start-system-server" : "");
}runtime调用start方法,但是AppRuntime没有此方法,而在其父类AndroidRuntime
class AppRuntime : public AndroidRuntime所以调用AndroidRuntime的start方法:
void AndroidRuntime::start(const char* className, const char* options)
{
ALOGD("\n>>>>>> AndroidRuntime START %s <<<<<<\n",
className != NULL ? className : "(unknown)");
blockSigpipe();
...
/* start the virtual machine */
JNIEnv* env;
if (startVm(&mJavaVM, &env) != 0) {
return;
}
onVmCreated(env);
/*
* Register android functions.
*/
if (startReg(env) < 0) {
ALOGE("Unable to register all android natives\n");
return;
}
...
env->CallStaticVoidMethod(startClass, startMeth, strArray);
...
}调用startVM(...)新建VM:
int AndroidRuntime::startVm(JavaVM** pJavaVM, JNIEnv** pEnv)
{
int result = -1;
JavaVMInitArgs initArgs;
...
/*
* Initialize the VM.
*
* The JavaVM* is essentially per-process, and the JNIEnv* is per-thread.
* If this call succeeds, the VM is ready, and we can start issuing
* JNI calls.
*/
if (JNI_CreateJavaVM(pJavaVM, pEnv, &initArgs) < 0) {
ALOGE("JNI_CreateJavaVM failed\n");
goto bail;
}
...
}其中调用到的是JNI_CreateJavaVM(...)创建VM.
onVmCreated(env)为空函数,没用!
startReg()函数用于注册JNI接口:
/*
* Register android native functions with the VM.
*/
/*static*/ int AndroidRuntime::startReg(JNIEnv* env)
{
/*
* This hook causes all future threads created in this process to be
* attached to the JavaVM. (This needs to go away in favor of JNI
* Attach calls.)
*/
androidSetCreateThreadFunc((android_create_thread_fn) javaCreateThreadEtc);
ALOGV("--- registering native functions ---\n");
/*
* Every "register" function calls one or more things that return
* a local reference (e.g. FindClass). Because we haven't really
* started the VM yet, they're all getting stored in the base frame
* and never released. Use Push/Pop to manage the storage.
*/
env->PushLocalFrame(200);
if (register_jni_procs(gRegJNI, NELEM(gRegJNI), env) < 0) {
env->PopLocalFrame(NULL);
return -1;
}
env->PopLocalFrame(NULL);
//createJavaThread("fubar", quickTest, (void*) "hello");
return 0;/fameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java
}
env->CallStaticVoidMethod(startClass, startMeth, strArray)调用/fameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java中的main(...)函数.
public static void main(String argv[]) {
try {
// Start profiling the zygote initialization.
SamplingProfilerIntegration.start();
registerZygoteSocket();
...
preload();
...
if (argv[1].equals("start-system-server")) {
startSystemServer();
} else if (!argv[1].equals("")) {
throw new RuntimeException(argv[0] + USAGE_STRING);
}
...
}registerZygoteSocket();//来注册Socket的Listen端口,用来接受请求
/**
* Registers a server socket for zygote command connections
*
* @throws RuntimeException when open fails
*/
private static void registerZygoteSocket() {
if (sServerSocket == null) {
int fileDesc;
try {
String env = System.getenv(ANDROID_SOCKET_ENV);
fileDesc = Integer.parseInt(env);
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
ANDROID_SOCKET_ENV + " unset or invalid", ex);
}
try {
sServerSocket = new LocalServerSocket(
createFileDescriptor(fileDesc));
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Error binding to local socket '" + fileDesc + "'", ex);
}
}
}preload() 主要进行预加载类和资源,以加快启动速度。preload的class列表保存在/frameworks/base/preloaded-classes文件中 。
static void preload() {
preloadClasses();
preloadResources();
}startSystemServer() ,fork进程:
int pid;
try {
parsedArgs = new ZygoteConnection.Arguments(args);
ZygoteConnection.applyDebuggerSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
ZygoteConnection.applyInvokeWithSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
/* Request to fork the system server process */
pid = Zygote.forkSystemServer(
parsedArgs.uid, parsedArgs.gid,
parsedArgs.gids,
parsedArgs.debugFlags,
null,
parsedArgs.permittedCapabilities,
parsedArgs.effectiveCapabilities);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}经过这几个步骤,Zygote就建立好了,利用Socket通讯,接收ActivityManangerService的请求
第三步 System Server
Zygote上fork的systemserver进程入口在/frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java的main(...)。Android的所有服务循环框架都是建立SystemServer上。在SystemServer.java中看不到循环结构。
public static void main(String[] args) {
...
...
System.loadLibrary("android_servers");
init1(args);
}加载一个叫android_servers的本地库,他提供本 地方法的接口(源程序在framework/base/services/jni/目录中)。然后调用本地方法设置服务。具体执行设置的代码在 frameworks/base/cmds/system_server/library/system_init.cpp中。
Init1()是在Native空间实现的(com_andoird_server_SystemServer.cpp)
JNI如下:
static JNINativeMethod gMethods[] = {
/* name, signature, funcPtr */
{ "init1", "([Ljava/lang/String;)V", (void*) android_server_SystemServer_init1 },
};static void android_server_SystemServer_init1(JNIEnv* env, jobject clazz)
{
system_init();
}system_init.cpp中的system_init()实现如下:
extern "C" status_t system_init()
{
...
property_get("system_init.startsurfaceflinger", propBuf, "1");
if (strcmp(propBuf, "1") == 0) {
// Start the SurfaceFlinger
SurfaceFlinger::instantiate();
}
property_get("system_init.startsensorservice", propBuf, "1");
if (strcmp(propBuf, "1") == 0) {
// Start the sensor service
SensorService::instantiate();
}
...
ALOGI("System server: starting Android services.\n");
JNIEnv* env = runtime->getJNIEnv();
if (env == NULL) {
return UNKNOWN_ERROR;
}
jclass clazz = env->FindClass("com/android/server/SystemServer");
if (clazz == NULL) {
return UNKNOWN_ERROR;
}
jmethodID methodId = env->GetStaticMethodID(clazz, "init2", "()V");
if (methodId == NULL) {
return UNKNOWN_ERROR;
}
env->CallStaticVoidMethod(clazz, methodId);
ALOGI("System server: entering thread pool.\n");
ProcessState::self()->startThreadPool();
IPCThreadState::self()->joinThreadPool();
ALOGI("System server: exiting thread pool.\n");
return NO_ERROR;
}可以看到等初始化传感器,视频,音频等服务后通过env->CallStaticVoidMethod(clazz, methodId)回调到了SystemServer的init2().
SystemServer.java有这么一段话:
/**
* This method is called from Zygote to initialize the system. This will cause the native
* services (SurfaceFlinger, AudioFlinger, etc..) to be started. After that it will call back
* up into init2() to start the Android services.
*/
native public static void init1(String[] args);system_init()开启了线程池,join_threadpool() 将当前线程挂起,等待binder的请求,启动了循环状态。
SystemServer.java中init2()建立了Android中主要的系统服务(WindowManagerServer(Wms)、ActivityManagerSystemService(AmS)、PackageManagerServer(PmS)......).
public static final void init2() {
Slog.i(TAG, "Entered the Android system server!");
Thread thr = new ServerThread();
thr.setName("android.server.ServerThread");
thr.start();
}
class ServerThread extends Thread {
private static final String TAG = "SystemServer";
private static final String ENCRYPTING_STATE = "trigger_restart_min_framework";
private static final String ENCRYPTED_STATE = "1";
ContentResolver mContentResolver;
...
Slog.i(TAG, "Entropy Mixer");
ServiceManager.addService("entropy", new EntropyMixer());
Slog.i(TAG, "Power Manager");
power = new PowerManagerService();
ServiceManager.addService(Context.POWER_SERVICE, power);
Slog.i(TAG, "Activity Manager");
context = ActivityManagerService.main(factoryTest);
...
// We now tell the activity manager it is okay to run third party
// code. It will call back into us once it has gotten to the state
// where third party code can really run (but before it has actually
// started launching the initial applications), for us to complete our
// initialization.
ActivityManagerService.self().systemReady(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
Slog.i(TAG, "Making services ready");
if (!headless) startSystemUi(contextF);
try {
if (mountServiceF != null) mountServiceF.systemReady();
} catch (Throwable e) {
reportWtf("making Mount Service ready", e);
}
...
}执行完systemReady()后,会相继启动相关联服务的systemReady()函数,完成整体初始化。
第三步 Home启动
上面的ServerThread调用到ActivityManagerService的systemReady()然后回调到/frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerServcie.java的systemReady(...).
public final class ActivityManagerService extends ActivityManagerNative
implements Watchdog.Monitor, BatteryStatsImpl.BatteryCallback {
......
public void systemReady(final Runnable goingCallback) {
......
synchronized (this) {
......
mMainStack.resumeTopActivityLocked(null);
}
}
......
}调用/frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityStack.java中:
final boolean resumeTopActivityLocked(ActivityRecord prev, Bundle options) {
// Find the first activity that is not finishing.
ActivityRecord next = topRunningActivityLocked(null);
...
if (next == null) {
Log.d(TAG,"jscese start Launcher");
// There are no more activities! Let's just start up the
// Launcher...
if (mMainStack) {
ActivityOptions.abort(options);
return mService.startHomeActivityLocked(mCurrentUser);
}
}
...
}next为当前系统Activity堆栈最顶端的Activity,如果没有,next == null那么就启动home!
回调到ActivityManagerServcie.java的:
boolean startHomeActivityLocked(int userId) {
...
Intent intent = new Intent(
mTopAction,
mTopData != null ? Uri.parse(mTopData) : null);
intent.setComponent(mTopComponent);
if (mFactoryTest != SystemServer.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL) {
intent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_HOME);
}
ActivityInfo aInfo =
resolveActivityInfo(intent, STOCK_PM_FLAGS, userId);
if (aInfo != null) {
intent.setComponent(new ComponentName(
aInfo.applicationInfo.packageName, aInfo.name));
Log.d(TAG,"jscese first packageName== "+aInfo.applicationInfo.packageName);
// Don't do this if the home app is currently being
// instrumented.
aInfo = new ActivityInfo(aInfo);
aInfo.applicationInfo = getAppInfoForUser(aInfo.applicationInfo, userId);
ProcessRecord app = getProcessRecordLocked(aInfo.processName,
aInfo.applicationInfo.uid);
if (app == null || app.instrumentationClass == null) {
intent.setFlags(intent.getFlags() | Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
mMainStack.startActivityLocked(null, intent, null, aInfo,
null, null, 0, 0, 0, 0, null, false, null);
}
}
return true;
}首先创建一个CATEGORY_HOME类型的Intent,然后通过Intent.resolveActivityInfo函数向PackageManagerService查询Category类型为HOME的Activity!
launcher的AndroidManifest.xml文件中可见:
...跑到ActivityStack.java的:
final int startActivityLocked(IApplicationThread caller,
Intent intent, String resolvedType,
Uri[] grantedUriPermissions,
int grantedMode, ActivityInfo aInfo, IBinder resultTo,
......
ActivityRecord r = new ActivityRecord(mService, this, callerApp, callingUid,
intent, resolvedType, aInfo, mService.mConfiguration,
resultRecord, resultWho, requestCode, componentSpecified);
......
err = startActivityUncheckedLocked(r, sourceRecord, startFlags, true, options);
...
}往后走就是启动一个activity的流程了,最终启动的是launcher的onCreate方法!
至此启动完成!
此博文图片模型来自http://blog.csdn.net/maxleng/article/details/5508372
撰写不易,转载请注明出处http://blog.csdn.net/jscese/article/details/17115395