解密 RubyEncoder
0x00 前言
RubyEncoder 是一款对 Ruby 代码进行混淆加密的软件,因为最近我要破解某个使用 RubyEncoder 加密的 Ruby 程序, 所以工作就转移到如何解密 RubyEncoder 加密的程序。
0x01 信息收集
要想了解 RubyEncoder,那肯定是要去官网下载一份试用版,但是无论你怎么填写试用资料:
我隐约记得 Hacking Team RCS 也用了 RubyEncoder,所以比较幸运的, 我从 Hacking Team 邮件 中找到了一个可以登陆账号密码:
Username: [email protected]
Password: Oyf4GSy0
下载到了 RubyEncoder-2.3,并偷偷的使用 Hacking Team 一个 License Key 成功激活了 RubyEncoder
先简单试用一下 RubyEncoder
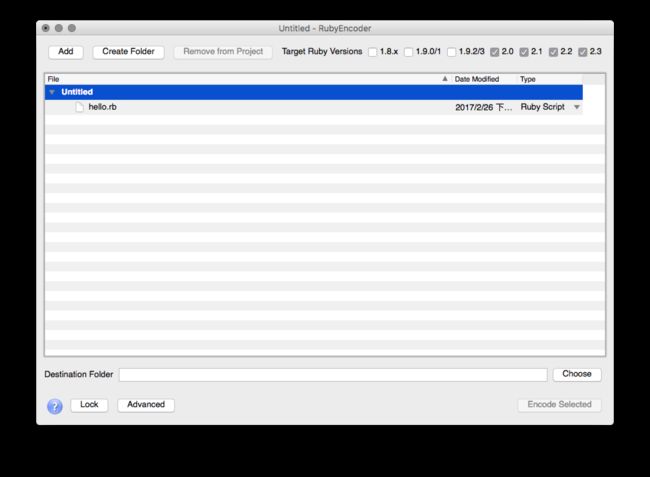
上图是 RubyEncoder 对某个项目加密的主界面,在这个界面中可以看到,我们可以选择支持的 Ruby 版本。 由于因为可以选多个版本号以及 1.8.x 也在支持的版本内,所以可以判定加密后的文件不会是 iseq 或者修改后的 iseq。
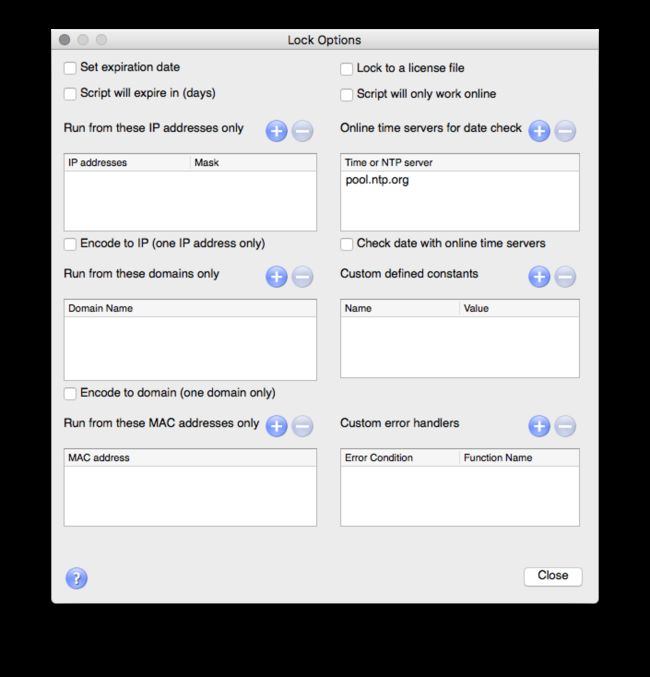
图是 RubyEncoder 支持的加密选项,可以进行 IP、Domain、MAC、联网、时间、License 限制。其中除了 License 文件之外,其他都是纸老虎, 如果 License 文件没有参与对文件的加密,那 License 限制也是纸老虎。不过根据官方文档描述
The algorithm uses an idea of two keys. The first key (Project Id) is stored in the encrypted area of the protected script and is used to decrypt an external license file. The second key (Project Key) is stored in the license file and it is used to decrypt the bytecode from the protected script.
所以如果没有 License 文件是很难将程序跑起来的,不过这篇文章的目的不是怎么样解除这些限制,而是如何解密 RubyEncoder 加密后的 Ruby 代码。
我们再来看一下 RubyEncoder 的目录结构:
.
├── Loaders
│ ├── Linux
│ │ ├── loader.rb
│ │ ├── my.so
│ │ ├── rgloader.linux.so
│ │ ├── rgloader.linux.x86_64.so
│ │ ├── rgloader19.linux.so
│ │ ├── rgloader19.linux.x86_64.so
│ │ ├── rgloader192.linux.so
│ │ ├── rgloader192.linux.x86_64.so
│ │ ├── rgloader193.linux.so
│ │ ├── rgloader193.linux.x86_64.so
│ │ ├── rgloader20.linux.so
│ │ ├── rgloader20.linux.x86_64.so
│ │ ├── rgloader21.linux.so
│ │ ├── rgloader21.linux.x86_64.so
│ │ ├── rgloader22.linux.so
│ │ ├── rgloader22.linux.x86_64.so
│ │ ├── rgloader23.linux.so
│ │ └── rgloader23.linux.x86_64.so
│ ├── Mac\ OS\ X // 省略 ..
│ ├── MinGW // 省略 ...
│ └── Windows // 省略 ...
├── RubyEncoder
├── license.txt
├── licgen
├── rgencoder
├── rginfo
├── rubyencoder18.bundle
├── rubyencoder19.bundle
├── rubyencoder192.bundle
├── rubyencoder20.bundle
├── rubyencoder21.bundle
├── rubyencoder22.bundle
├── rubyencoder23.bundle
└── update
简单看了一下 rubyencoder*.bundle 文件,应该是直接把整个 Ruby 给打包进来了,应该是加密的过程中需要 Ruby 的一些功能, 不过我并不是特别关注加密过程,所以直接看 Loaders 目录下的文件,这个目录下包含了所支持的平台下、Ruby 版本的解密 so 文件。
当然除了需要下载 RubyEncoder 程序,还需要找一找有没有前辈已经搞定这个程序的, google 一番之后找到 I found way to protect Source Code! 这个帖子。
这个帖子的思路是:
- 将 ruby_exec 修改成 ruby_exic 以便获得 AST
- 使用修改后的 ParseTree 将 Ruby 内部的 AST 转成 sexp
- 使用 ruby2ruby 将 sexp 转成 Ruby 代码
不过这个帖子当时使用的是 Ruby 1.8.7,也就是当时 Ruby 还是构建完 AST 之后就直接执行,1.9.x 后的 Ruby 需要编译成 iseq。 另外由于 Ruby 1.8 和 Ruby 2.x 有很大的不同,上面的 ParseTree 在 Ruby 使用 iseq 之后就再也不能使用了。 所以上面的方法在 Ruby 2.x 中行不通了。
0x02 简单逆向
我们使用 RubyEncoder 对以下代码进行加密
puts "Hello World!"
得到下面加密后的代码
# RubyEncoder v2.3.0
if not self.respond_to?(:RGLoader_load,:include_private) then _d = _d0 = File.expand_path(File.dirname(__FILE__)); while 1 do _f = _d + '/rgloader/loader.rb'; break if File.exist?(_f); _d1 = File.dirname(_d); if _d1 == _d then raise "Ruby script '"+__FILE__+"' is protected by RubyEncoder and requires a RubyEncoder loader to be installed. Please visit the http://www.rubyencoder.com/loaders/ RubyEncoder web site to download the required loader and unpack it into '"+_d0+"/rgloader/' directory in order to run this protected file."; exit; else _d = _d1; end; end; require _f; end; RGLoader_load('AAIAAAAEgAAAAIAAAAAA/0R/d65ujW/5OhgbeUf0jhTRfPXr0uXNuC7gK8ycmR473fPEIlsgFP1/KF+CYBVbQy4xoLUhBFtBlYwH2aDOtcTasNDJPMDtoEgRuRdFRDgJoX1oKhrm0ZKm9OdIM6MbXRc/fh4n984TVew76DqbxQTplVhMxzOCp/mKgLU+shxBFAAAAGAAAAA7Nu8kj4NtO8BQECP2bW1TonmX+NADX/HETWg1j5fvbB8gptZ38XCzJxOccT2CTUsTT8GFq67RttUD7IR/xN2FBCWKMZ1BlGYVlhSmSUc6hS5RfglTuyvdVdjnsgcnkTAVAAAAYAAAAIrxSQfPHlMc89mPBUXSQ6vxmM9yoDu7Rf+O87mTUW4L0VuAWkIhvFUBxXRVm6Q7kkWHg7D7cdIwwA62+ewy91l56aMIQujAKZrVn4T1zreKf1QdGvK+QGY4rIpGEmTBhBYAAABoAAAADdYzBFrSrrZ4o9uzaoq+Yxjk44lzEa+/oxXM7fmbm8gJ1W3MlUZyPqIjW01KUb6nZjWIAz629+KP5nL/GMP0BClkOjpXQ9b95R/qvlDzuP7UZHPeqaIJq2yMN7Mh9WROfAhLlhmK86AXAAAAcAAAAGgSDy/YvPJQsKnC+JvR+ITlVdWPGodUNT10I0CPLu9d81hMtEL9hU4t9yVfBcS2BWDqBg3ahhUTvqNYxwvX8NCHmZU4LQmdd3dJneWJzGy6VbAQeVDNeaJl8/SPdRn1VXaspqWGYFn1cXqp7rhHLUcAAAAA');
可以看到最关键的函数就是 RGLoader_load,所以直接将 rgloader22.linux.x86_64.so 丢进 IDA,找到 RGLoader_load 的实现:
int __cdecl rgloader_load(int a1, _DWORD *a2, int a3, int a4) {
// 省略 ...
v126 = v124;
v127 = _decode_node(v124);
mstream_close(v126);
ruby_xfree(v23);
if ( !v127 || decoder_error )
goto LABEL_243;
v128 = *(_DWORD *)(rb_thread_current() + 16);
v210 = *(_DWORD *)(v128 + 60);
if ( a1 == rgloader_module )
*(_DWORD *)(v128 + 60) = *(_DWORD *)(*(_DWORD *)(v128 + 24) + 56);
else
*(_DWORD *)(v128 + 60) = *(_DWORD *)(*(_DWORD *)(v128 + 24) + 16);
v129 = (char *)rg_current_realfilepath();
v130 = rb_sourcefile();
v131 = rb_str_new_cstr(v130);
v132 = rb_str_new_static("", 9);
v133 = rb_iseq_new(v127, v132, v131, v129, 0, 0);
result = rb_iseq_eval(v133);
*(_DWORD *)(v128 + 60) = v210;
return result;
}
嗯,事实上,RubyEncoder 就算是到了 2.3 版本,还是和上面那个帖子所说的一样:
It turns out, that RubyEncoder uses following scheme: modified Ruby-1.8.7 interpreter, that stores encoded AST nodes along with encoding/restriction options, while rgloader simply decodes it back to AST and executes.
只不过这里多了一步 v133 = rb_iseq_new(v127, v132, v131, v129, 0, 0); 将 AST 编译成 iseq。
我们可以通过 hook rb_iseq_new 拿到 AST,hook rb_iseq_eval 拿到 iseq。
下面我们修改 Ruby 代码将 AST 以及 iseq dump 出来。
- one byte hack
cp rgloader22.linux.x86_64.so bak.so
sed 's/rb_iseq_eval/rb_iseq_evax/g' rgloader22.linux.x86_64.so > tmp.so
sed 's/rb_iseq_new/rb_iseq_nex/g' tmp.so > rgloader22.linux.x86_64.so
-
在 iseq.c 中实现 rb_iseq_nex
VALUE rb_iseq_nex(NODE *node, VALUE name, VALUE path, VALUE absolute_path, VALUE parent, enum iseq_type type) { rb_io_write(rb_stdout, rb_parser_dump_tree(node, 0)); printf("\n\n"); return rb_iseq_new(node, name, path, absolute_path, parent, type); } -
实现 vm.c 中实现 rb_iseq_evax
VALUE
rb_iseq_evax(VALUE iseqval)
{
rb_io_write(rb_stdout, rb_iseq_disasm(iseqval));
return 0;
}
结果:
###########################################################
## Do NOT use this node dump for any purpose other than ##
## debug and research. Compatibility is not guaranteed. ##
###########################################################
# @ NODE_SCOPE (line: 1)
# +- nd_tbl: (empty)
# +- nd_args:
# | (null node)
# +- nd_body:
# @ NODE_FCALL (line: 1)
# +- nd_mid: :puts
# +- nd_args:
# @ NODE_ARRAY (line: 1)
# +- nd_alen: 1
# +- nd_head:
# | @ NODE_STR (line: 1)
# | +- nd_lit: "Hello World!"
# +- nd_next:
# (null node)
== disasm: @./ruby-2.2.6/hello.rb>
0000 trace 1 ( 1)
0002 putself
0003 putstring "Hello World!"
0005 opt_send_without_block
0007 leave
上面就是 dump 出来的 AST 和 iseq,不过这些离我们的最终目标还有一点点距离。
0x03 生成代码
由于之前的 parsetree 已经不能再使用了,google了一番之后,也没有找到现成的, 之前的打算是写一个类似 Python 的 uncompyle 之类的东西, 解析 iseq 结构、构建 AST、生成代码, 不过后面发现自己实在没那么多时间,于是就偷懒直接从 Ruby 的 AST 直接生成代码。
对照着 Ruby 的 node.c、parse.y、compile.c 就可以写出
node2ruby.c
试试看这个代码反编译的效果,测试文件 http.rb

感觉效果还是差强人意,代码算是可以能看的,但是想要执行起来还要继续对代码进行修改(因为node2ruby.c 还有挺多地方没考虑到的)
总的来说,Ruby 写的代码还是比较友好的,像我这样的新手都能很快上手,嗯,除了有些小错误外,顺手给 Ruby 提交了两 PR:
- node.c: fix NODE_OP_ASGN1 operator
- node.c: fix nd_ainfo->kw_rest_arg
0x04 总结
写 node2ruby.c 的时候就觉得如果不是特别熟悉 Ruby 的话,有些比较奇怪的语句还是想不到的。
对了,还记得我们上面所说的,如果没有 License 文件,就很难将程序跑起来么? 嗯,我要解密的 Ruby 代码就是必须要 License 文件的,而且我还没有 License。