【转载】目标检测之二(传统算法和深度学习的源码学习)
【转载】目标检测之二(传统算法和深度学习的源码学习)
本系列写一写关于目标检测的东西,包括传统算法和深度学习的方法都会涉及到,注重实验而不着重理论,理论相关的看论文去哈,主要依赖opencv。
本文主要内容:简单分析下yolo9000的原理,然后使用opencv的dnn模块进行目标检测.
接着上一篇提到的车辆检测(http://blog.csdn.net/baolinq/article/details/78579317),使用了Haar+Adaboost算法进行车辆检测,对于简单场景的检测效果还不错,但是对于稍微复杂点的场景或者由于光照等原因的影响,检测效果不尽人意,但是我们看到深度学习的检测方法,比如YOLO的检测效果仍然很好。
YOLO9000秉承着“奥运理念”, Better, Faster, Stronger,翻译出来的意思就是检测精度更高,检测速度更快,性能更强(更鲁棒),主要原理和YOLO v1一样,YOLO9000增加了更多的深度学习的训练tricks和借鉴了其他算法的优点,
上图是YOLOv1论文(https://arxiv.org/abs/1506.02640)里面的截图,我们简单看一下它的原理:
(1) 给个一个输入图像,首先将图像划分成7 * 7的网格。
(2) 对于每个网格,每个网格预测2个boudingbox(每个box包含5个预测量)以及20个类别概率,总共输出7×7×(2*5+20)=1470个tensor
(3) 根据上一步可以预测出7 * 7 * 2 = 98个目标窗口,然后根据阈值去除可能性比较低的目标窗口,再由NMS去除冗余窗口即可。
YOLOv1使用了end-to-end的回归方法,没有regionproposal步骤,直接回归便完成了位置和类别的判定。种种原因使得YOLOv1在目标定位上不那么精准,直接导致YOLO的检测精度并不是很高。
YOLO9000用了这么多tricks,每一种提高一点点,组合起来就很强大了
YOLO9000略有不同,YOLOv2最后输出的是S * S * (B * (5 + C))维,它直接使用每个boxes进行预测,而yolov1不是这样的,它是每个cell只负责一个object。其中参数S,B,C的取值也不同:
S=13,YOLOv2对输入图像(416*416,yolov1是448*448)进行了卷积和池化等,最终输出的特征图尺寸是13 * 13。
B=5,这是由Dimension Clusters得到的。Fast-RCNN中使用3种scales和3中aspectratios(1:1,1:2,2:1)在每个位置产生了9个anchor boxes。作者认为这种手动选取的anchor不够好,虽然网络最终可以学出来,但如果我们可以给出更好的anchor,那么网络肯定更加容易训练而且效果更好。作者使用kmeans算法进行训练,使用基于IOU的度量方式d(box,centroid)=1−IOU(box,centroid)代替一般场景下的欧氏距离。作者的实验表明这种做法比手动选取的效果更好
C=20,表示object的种类,如果是用voc数据集的话,C=20。如果是coco数据集,C=80。
详细的原理自己去网上搜一下有一大堆,不过还是建议看下原文(https://arxiv.org/abs/1612.08242),项目主页(https://pjreddie.com/darknet/yolo/)上面有关于YOLO的详细介绍以及很多训练好的model可以使用以及yolo的源代码,作者可以说是非常良心了,点个赞。
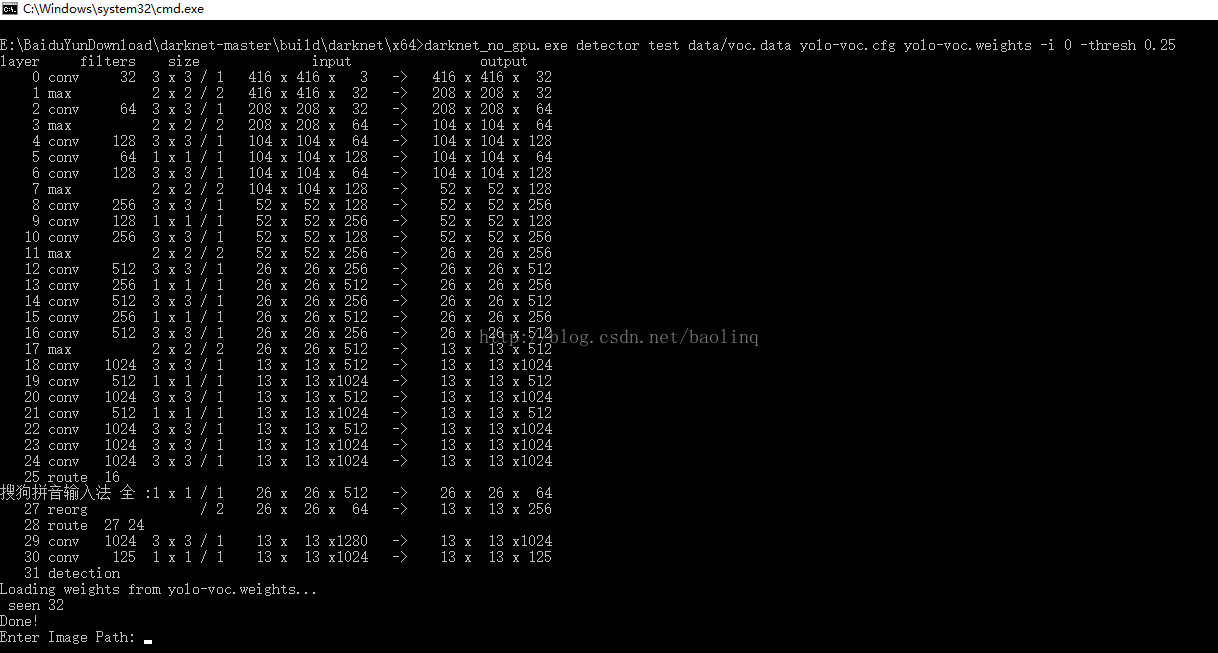
直接先去github上面下载YOLO的源代码(https://github.com/pjreddie/darknet),代码写的非常nice,使用darknet网络结构,几乎不用环境就可以独立运行的,当然如果你要显示窗口的话,最好还是要有一个opencv,他也会自动把运行结果保存到当前目录,不过看起来不方便。根据自己的环境编译一下,使用命令行cmd窗口就可以运行了。输入图片路径即可进行检测。
运行截图:
电脑显卡很渣,暂时使用的是no gpu版本的。
运行结果:
按任意键关闭窗口,即可继续输入图片路径继续进行目标检测
这样测试很不方便,每次只能测试一张图像,我想测试序列图像或者测试视频该怎么办呢?有两种方法,一种修改源代码,改写输入文件的类型;第二种更简单使用opencv的dnn模块(Depth neural network)。详情见opencv官方文档https://docs.opencv.org/master/d6/d0f/group__dnn.html
我以第二种方法为例,我使用的是opencv3.3。Dnn模块是opencv新推出的用于深度学习的一个模块,目前支持Caffe、TensorFlow、Torch、PyTorch、darknet等深度学习框架。我觉得这个功能真的很赞,以后训练好的模型,移植就非常方便了,用来做一些日常测试也是很不错的。
dnn::Net net=readNetFromDarknet()就可以从参数中读取darknet网络参数以及训练好的模型权重。
先把输入图像归一化一下,然后输入图像到网络中,再进行前向传播,就OK了,是不是非常的easy啊。剩下的只是怎么显示和保存数据的问题了,处理结果已经保存到detectionMat里面去了。
-
//! [
Prepare
blob]
-
Mat inputBlob = blobFromImage(resized,
1 /
255.F); //Convert Mat to batch of images
-
//! [
Prepare
blob]
-
//! [
Set
input
blob]
-
net.setInput(inputBlob,
"data"); //
set the network
input
-
//! [
Set
input
blob]
-
-
//! [Make forward pass]
-
cv::Mat detectionMat = net.forward(
"detection_out"); //compute output
-
//! [Make forward pass]
Talk is cheap,show me thecode。给出测试源码,其实也就是稍微改了一下opencv的samples。
-
#include
-
#include
-
#include
-
#include
-
#include
-
using namespace cv;
-
using namespace cv::dnn;
-
-
#include
-
#include
-
#include
-
#include
-
using namespace std;
-
-
const size_t network_width =
416;
-
const size_t network_height =
416;
-
-
const
char* about =
"This sample uses You only look once (YOLO)-Detector "
-
"(https://arxiv.org/abs/1612.08242)"
-
"to detect objects on image\n";
// TODO: link
-
-
const
char* params
-
=
"{ help | false | print usage }"
-
"{ cfg | yolo-voc.cfg | model configuration }"
//写入训练好的网络参数文件cfg格式
-
"{ model | yolo-voc.weights | model weights }"
//写入训练好的模型的权重文件
-
"{ image | | image for detection }"
//测试的图片名,我没有使用
-
"{ min_confidence | 0.24 | min confidence }";
//信心度阈值,低于该阈值的不输出,判断为没有检测到
-
-
vector
color = { Scalar(
0,
205,
150),Scalar(
255,
0,
0),Scalar(
0,
0,
255),Scalar(
200,
150,
0) };
-
int main(
int argc,
char** argv)
-
{
-
cv::CommandLineParser parser(argc, argv, params);
//读入params参数文件
-
-
if (parser.get<
bool>(
"help"))
-
{
-
std::cout << about << std::endl;
-
parser.printMessage();
-
return
0;
-
}
-
-
//String modelConfiguration = "yolo.cfg"; // parser.get
("cfg");
-
//String modelBinary = "yolo.weights"; //parser.get
("model");
-
String modelConfiguration = parser.get
(
"cfg");
-
String modelBinary =parser.get
(
"model");
-
-
//! [Initialize network]
-
dnn::Net net = readNetFromDarknet(modelConfiguration, modelBinary);
//读取网络模型和参数,初始化
-
//! [Initialize network]
-
-
if (net.empty())
-
{
-
cerr <<
"Can't load network by using the following files: " << endl;
-
cerr <<
"cfg-file: " << modelConfiguration << endl;
-
cerr <<
"weights-file: " << modelBinary << endl;
-
cerr <<
"Models can be downloaded here:" << endl;
-
cerr <<
"https://pjreddie.com/darknet/yolo/" << endl;
-
exit(
-1);
-
}
-
-
// String imgpath =parser.get
("image")
-
//cv::Mat frame = cv::imread(imgpath);
-
-
// 检测目标种类的名称在voc.txt,读入保存到tag_names向量中
-
vector
tag_names;
-
ifstream fin;
-
fin.open(
"voc.txt");
-
string buf;
-
while(fin && getline(fin, buf)) {
-
tag_names.push_back(buf);
-
}
-
fin.close();
-
-
//打开默认摄像头,用于检测摄像头的图像
-
//VideoCapture cap(0);
-
//if (!cap.isOpened())
-
// return -1;
-
-
//图片的存放地址(相对路径),在当前目录的test_image文件夹里面
-
String imgpath =
"test_image/";
-
vector
imgvec;
-
cv::glob(imgpath, imgvec);
//保存文件名到imgvec向量中,便于批量处理
-
Mat frame;
-
bool stop =
false;
-
//while(!stop){
-
-
int64 start = getTickCount();
//计算运行时间
-
for (
int imgnum =
0; (imgnum < imgvec.size())&&(!stop); ++imgnum) {
-
-
//if (!cap.read(frame))
-
// break;
-
frame = imread(imgvec[imgnum]);
-
//imshow("原图",frame);
-
//waitKey(5);
-
//! [Resizing without keeping aspect ratio]
-
cv::Mat resized;
-
cv::resize(frame, resized, cv::Size(network_width, network_height));
-
//! [Resizing without keeping aspect ratio]
-
-
//! [Prepare blob]
-
Mat inputBlob = blobFromImage(resized,
1 /
255.F);
//Convert Mat to batch of images
-
//! [Prepare blob]
-
-
//! [Set input blob]输入归一化的图像
-
net.setInput(inputBlob,
"data");
//set the network input
-
//! [Set input blob]
-
-
//! [Make forward pass]前向传播进行计算
-
cv::Mat detectionMat = net.forward(
"detection_out");
//compute output
-
//! [Make forward pass]
-
-
-
float confidenceThreshold = parser.get<
float>(
"min_confidence");
-
for (
int i =
0; i < detectionMat.rows; i++)
-
{
-
const
int probability_index =
5;
//前5个参数为每一个bounding box包含5个值:x,y,w,h和confidence(置信度),置信值代表box包含一个目标的置信度
-
const
int probability_size = detectionMat.cols - probability_index;
//后20个为voc数据集中有20个类别,每个类的概率
-
float *prob_array_ptr = &detectionMat.at<
float>(i, probability_index);
-
-
size_t objectClass = std::max_element(prob_array_ptr, prob_array_ptr + probability_size) - prob_array_ptr;
//选择一个概率最大的作为检测结果
-
float confidence = detectionMat.at<
float>(i, (
int)objectClass + probability_index);
-
-
if (confidence > confidenceThreshold)
//大于信心度阈值才输出
-
{
-
float x = detectionMat.at<
float>(i,
0);
//检测的矩形框的计算,本来是中心点和长宽,这都是被归一化后的
-
float y = detectionMat.at<
float>(i,
1);
-
float width = detectionMat.at<
float>(i,
2);
-
float height = detectionMat.at<
float>(i,
3);
-
float xLeftBottom = (x - width /
2) * frame.cols;
//得到图像上的矩形框的左上角和右下角坐标,要反归一化
-
float yLeftBottom = (y - height /
2) * frame.rows;
-
float xRightTop = (x + width /
2) * frame.cols;
-
float yRightTop = (y + height /
2) * frame.rows;
-
-
//std::cout << "Class: " << tag_names[objectClass] << std::endl;
-
//std::cout << "Confidence: " << confidence << std::endl;
-
-
//std::cout << " " << xLeftBottom
-
// << " " << yLeftBottom
-
// << " " << xRightTop
-
// << " " << yRightTop << std::endl;
-
stringstream ss;
-
ss << confidence;
-
string str_text = tag_names[objectClass] +
": "+ss.str();
//输出类别和信心度
-
-
Rect object((
int)xLeftBottom, (
int)yLeftBottom,
-
(
int)(xRightTop - xLeftBottom),
-
(
int)(yRightTop - yLeftBottom));
-
-
rectangle(frame, object, color[objectClass %
4],
2);
//显示矩形框,我给了一个颜色数组,避免都是一个色的不好看
-
int baseline =
0;
-
Size labelSize = getTextSize(str_text, FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
0.5,
1, &baseline);
//设置字体
-
//int x = xLeftBottom - labelSize.width >= 0 ? xLeftBottom - labelSize.width : xLeftBottom + labelSize.width;
-
int rect_y = yLeftBottom - labelSize.height >=
0 ? yLeftBottom - labelSize.height : yLeftBottom ;
//避免在边界时,显示的内容看不到
-
-
rectangle(frame, Rect(Point(xLeftBottom, rect_y),Size(labelSize.width,labelSize.height+baseline)), Scalar(
0,
255,
0),CV_FILLED);
-
//输出显示内容
-
cv::putText(frame, str_text, Point(xLeftBottom, rect_y+labelSize.height), FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
0.5, color[objectClass%
4]);
-
-
}
-
}
-
//cout << "用时: "<<1.0*(getTickCount() - start) / getTickFrequency() << endl;
-
imshow(
"detections", frame);
//显示图像
-
//waitKey();
-
if (waitKey(
5) ==
'q')
-
stop =
true;
-
}
-
//cout << "用时: " << 1.0*(getTickCount() - start) / getTickFrequency() << endl;//计算所有图片共运行的时间
-
return
0;
-
}
// main
代码上都有比较详细的注释,稍微看过论文或者看过其他人的写的论文笔记的,了解yolo的原理的都应该能看懂。我们简单分析一下网络的输出矩阵detectionMat,根据上面的分析。我们知道YOLO9000的输出是13*13*5*(5+20)维 的向量。
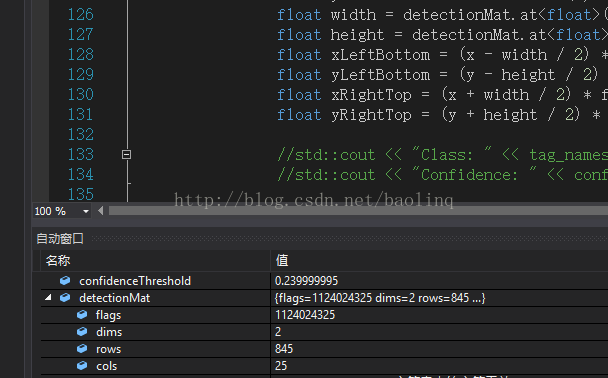
果然像我们分析的一样,调试时可以看到detectionMat是一个845*25维的矩阵,相当于一共845个boxes,每行表示一个boxes,每行有25列,分别表示矩形框的定位(4),该boxes的置信值(confidence score)。置信值代表box包含一个目标的置信度,以及20个类别的概率值。
知道了网络输出矩阵的意义,我们只需要分别取出来即可,每次只取类别概率最大的那一类,作为预测结果,然后跟confidenceThreshold作比较,超过阈值才认为是正确的预测,否则认为没有预测到。
最后就是预测框的计算了,因为作者模仿了faster-rcnn的做法,使用偏移量表示位置,而不是直接预测,实验表明这样做更容易训练,且可以提高mAP。作者就没有采用预测直接的offset的方法,而使用了预测相对于grid cell的坐标位置的办法,作者又把ground truth限制在了0到1之间,利用logistic回归函数来进行这一限制。所以最后计算出来的坐标需要去归一化,乘以图像的宽或者高。
最后部分的显示,我就不多说了,自己看看opencv的函数就可以了。
搞定收工。写的有点啰嗦,本来想和第一篇写在一起,结果写了这么多,如果你看到了这里,我只能说给你真有耐心,给你点个赞。下篇见~~
参考文献
[1] Redmon J, Farhadi A. YOLO9000: Better, Faster, Stronger[J]. 2016.
[2]http://blog.csdn.net/jesse_mx/article/details/53925356