深入理解为什么AsyncTask只能被执行一次
看该篇文章前,我推荐了另外一篇博客,看完再来看该篇博客。
Android源码分析—带你认识不一样的AsyncTask
接下来,就来分析为什么AsyncTask只能被执行一次:
public final AsyncTask execute(Params... params) {
return executeOnExecutor(sDefaultExecutor, params);
} 我们都知道,当外界调用AsyncTask.execute的时候,他就会执行doInBackground中的代码。而该函数又调用了该函数
public final AsyncTask executeOnExecutor(Executor exec,Params... params) {
if (mStatus != Status.PENDING) {
switch (mStatus) {
case RUNNING:
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot execute task:"
+ " the task is already running.");
case FINISHED:
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot execute task:"
+ " the task has already been executed "
+ "(a task can be executed only once)");
}
}
mStatus = Status.RUNNING;
onPreExecute();
mWorker.mParams = params;
exec.execute(mFuture);
return this;
} 该函数中,首先对状态进行了判断,如果状态不是pending的话就会抛出异常,要么是正在执行,要么是已经被执行过的异常。
然后我将该段代码注释掉
// if (mStatus != Status.PENDING) {
// switch (mStatus) {
/ case RUNNING:
// throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot execute task:"
// + " the task is already running.");
// case FINISHED:
// throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot execute task:"
// + " the task has already been executed "
// + "(a task can be executed only once)");
// }
// }然后让该AsyncTask执行两遍(调用execute两次)。发现并没有报错,但是发现doInBackground中的代码并没有被执行两遍,而是执行了一遍(第一次调用Execute被执行,第二次没有执行)。
再回看该函数,里面执行doInBackground中最重要的代码就是
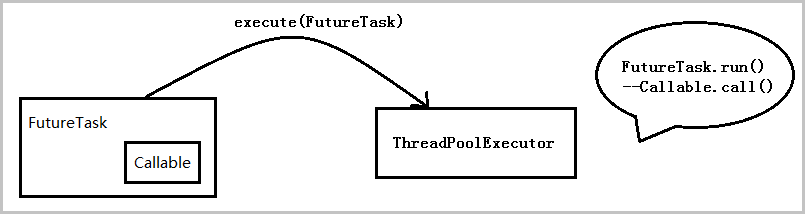
exec.execute(mFuture);Callable和Runnable是类似的,只是Runnable是调用run函数,Callable调用call函数,而且call函数会返回执行结果,FutureTask就是去获取执行结果的一个类。具体可以看这篇文章: Runnable、Callable、Executor、Future、FutureTask关系解读
FutureTask主要是在FutureTask的构造函数中传入callable。当通过ThreadPoolExecutor.execute(FutureTask)后,会调用FutureTask.run,在run中会调用Callable.call函数,执行完后会将callable清空,所以FutureTask只能被执行一次,第二次执行时会发现callable已经为空。看下代码
public void run() {
if (state != NEW ||
!UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, runnerOffset,
null, Thread.currentThread()))
return;
try {
Callable c = callable;
if (c != null && state == NEW) {
V result;
boolean ran;
try {
result = c.call();
ran = true;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
result = null;
ran = false;
setException(ex);
}
if (ran)
set(result);
}
} finally {
// runner must be non-null until state is settled to
// prevent concurrent calls to run()
runner = null;
// state must be re-read after nulling runner to prevent
// leaked interrupts
int s = state;
if (s >= INTERRUPTING)
handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s);
}
} 在set(Rsult)和setException(ex)中会调用finishCompletion()。
private void finishCompletion() {
// assert state > COMPLETING;
for (WaitNode q; (q = waiters) != null;) {
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset, q, null)) {
for (;;) {
Thread t = q.thread;
if (t != null) {
q.thread = null;
LockSupport.unpark(t);
}
WaitNode next = q.next;
if (next == null)
break;
q.next = null; // unlink to help gc
q = next;
}
break;
}
}
done();
callable = null; // to reduce footprint
}看到了吗,在最后一句会将callable置成null。讲了这么多最主要的就是FutureTask只能被执行一次。
而且在AsyckTask中FutureTask被声明称final的,即只能被初始化一次。后来我做了如下改变,将FutureTask和Callable去掉final,在execute函数中去初始化它,如下代码所示:
public final MyAsyncTask executeOnExecutor(Executor exec,
Params... params) {
// if (mStatus != Status.PENDING) {
// switch (mStatus) {
// case RUNNING:
// throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot execute task:"
// + " the task is already running.");
// case FINISHED:
// throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot execute task:"
// + " the task has already been executed "
// + "(a task can be executed only once)");
// }
// }
mStatus = Status.RUNNING;
onPreExecute();
mWorker = new WorkerRunnable() {
public Result call() throws Exception {
mTaskInvoked.set(true);
android.os.Process.setThreadPriority(android.os.Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND);
//noinspection unchecked
return postResult(doInBackground(mParams));
}
};
mFuture = new FutureTask(mWorker) {
@Override
protected void done() {
try {
postResultIfNotInvoked(get());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
android.util.Log.w(LOG_TAG, e);
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("An error occured while executing doInBackground()",
e.getCause());
} catch (CancellationException e) {
postResultIfNotInvoked(null);
}
}
};
mWorker.mParams = params;
exec.execute(mFuture);
return this;
} 现在无论外面调用execute多少次,都可以执行多遍了。