CA认证原理以及实现(上)
原理基础
数字证书为发布公钥提供了一种简便的途径,其数字证书则成为加密算法以及公钥的载体,依靠数字证书,我们可以构建一个简单的加密网络应用平台,数字证书就好比我们生活中的身份证,现实中,身份证由公安机关签发,而网络用户的身份凭证由数字证书颁发认证机构—CA签发,只有经过CA签发的证书在网络中才具备可认证性,CA并不是一个单纯的防御手段,它集合了多种密码学算法:
消息摘要算法:MD5、和SHA(对数字证书本省做摘要处理,用于验证数据完整性服务器)
对称加密算法:RC2、RC4、IDEA、DES、AES(对数据进行加密/解密操作,用于保证数据保密性服务)
非对称加密算法:RSA、DH(对数据进行加密/解密操作,用于保证数据保密性服务)
数字签名算法:RSA、DSA(对数据进行签名/验证操作,保证数据的完整性和抗否认性)。
证书的签发过程实际上是对申请数字证书的公钥做数字签名,证书的验证过程实际上是对数字证书的公钥做验证签名,其中还包含证书有效期验证,通过CA数字证书,我们对网络上传输的数据进行加密/解密和签名/验证操作,确保数据机密性、完整性、抗否认性、认证性,保证交易实体身份的真实性,保证网络安全性。
所有证书有多种文件编码格式,主要包括:
CER编码(规范编码格式):是数字证书的一种编码格式,它是BER(基本编码格式)的一个变种,比BER规定得更严格
DER(卓越编码格式):同样是BER的一个变种,与CER的不同在于,DER使用定长模式,而CER使用变长模式。
所有证书都符合公钥基础设施(PKI)制定的ITU-T X509国际标准,PKCS(公钥加密标准)由RSA实验室和其他安全系统开发商为促进公钥密码的发展而制定的一系列标准,比如:PKCS#7(密码消息语法标准----文件后缀名:.p7b、.p7c、.spc)、PKCS#10(证书请求语法标准----文件后缀名:.p10、.csr)、PKCS#12(个人信息交换语法标准----文件后缀名:.p12、.pfx)等
在获得数字证书后,可以将其保存在电脑中,也可以保存在USB Key等相应的设备中。
我们先来看一个简单的证书机构签发的流程:
这里的认证机构如何是证书申请者本身,将获得自签名证书。
当客户端获得服务器下发的数字证书后,即可使用数字证书进行加密交互:
数字证书的应用环境是在https安全协议中,使用流程远比上述加密交互流程复杂,但是相关操作封装在传输层,对于应用层透明,在https安全协议中使用非对称加密算法交换密钥,使用对称加密算法对数据进行加密/解密操作,提高加密/解密效率
要获得数字证书,我们需要使用数字证书管理工具:KeyTool和OpenSSL构建CSR(数字证书签发申请),交由CA机构签发,形成最终的数字证书,这里我们不对KeyTool做讲解(KeyTool不含有根证书,因此KeyTool没有办法作为CA),网上资料对keytool讲解的也挺多的,我们下面针对OpenSSL进行讲解。
在我们搭建OPEN SSL环境前,我们要知道HTTPS协议和SSL/TLS协议,简单的说,HTTPS就是HTTP+SSL(secure socket layer)/TLS(Transport Layer Security)协议,HTTPS协议为数字证书提供了最佳的应用环境,HTTPS协议一般在服务器中配置,如HTTP服务器APACHE、TOMCAT等。
SSL:位于TCP/IP中的网络传输层,作为网络通讯提供安全以及数据完整性的一种安全协议
TLS:作为SSL协议的继承者,成为下一代网络安全性和数据完整性安全协议
SSL共有3个版本:1.0、2.0、3.0,TLS也有1.0、2.0、3.0,通常我们说的SSL/TLS协议指的是SSL3.0/TLS1.0的网络传输层安全协议
SSL/TLS协议分为两层:
记录协议:建议在可靠的传输协议之上,为高层协议提供数据封装、压缩、加密等基本功能的支持
握手协议:建立在SSL记录协议之上,用于在实际的数据传输开始前,通讯双方进行身份认证、协商加密算法、交换加密密钥等
经过了SSL/TLS握手协议交互后,数据交互双方确定了本次会话使用的对称加密算法以及密钥,就可以开始进行加密数据交互了,以下是握手协议服务器端和客户端构建加密交互的相关流程图:
协商算法
1、 随机数为后续构建密钥准备
2、 其他信息包括服务器证书、甚至包含获取客户端证书的请求
验证算法
如果服务器端回复客户端时带有其他信息,则进入数字证书验证阶段
客户端验证服务器端证书: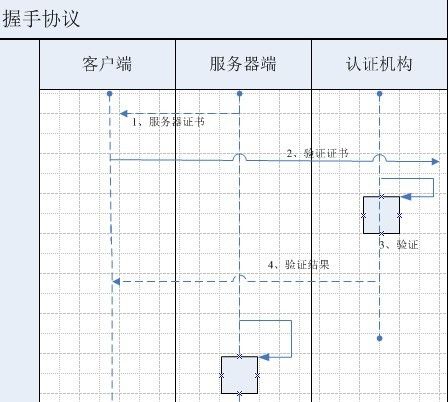
服务器端验证客户端证书:
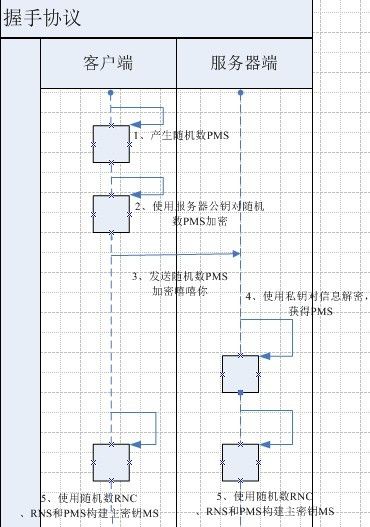
产生密钥
当服务器端和客户端经过上述流程后,就开始密钥构建交互了,服务器端和客户端最初需要主密钥为构建会话密钥做准备:
上述5、6不存在次序关系,因为是异步完成
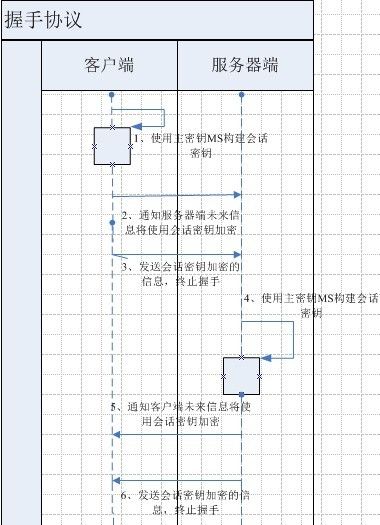
会话密钥
完成上述主密钥构建操作后,服务器端和客户端将建立会话密钥,完成握手协议:
加密交互
上述服务器端和客户端完成了握手协议以后就进入正式会话阶段,如果上述流程中有任何一端受到外界因素干扰发生异常,则重新进入协商算法阶段,下面流程表现进入会话阶段后,服务器端和客户端将使用会话密钥进行加密交互:
代码解释
在JAVA 6 以上版本中提供了完善的数字证书管理的实现,我们不需要关注相关具体算法,仅通过操作密钥库和数字证书就可以完成相应的加密/解密和签名/验证操作,密钥库管理私钥,数字证书管理公钥,私钥和密钥分属消息传递两方,进行加密消息的传递。
因此,我们可以将密钥库看做私钥相关操作的入口,数字证书则是公钥相关操作的入口:
- /****
- * 获得私钥,获得私钥后,通过RSA算方法实现进行"私钥加密,公钥解密"和"公钥加密,私钥解密"操作
- * @param keyStorePath 密钥库路径
- * @param alias 别名
- * @param password 密码
- * @return 私钥
- */
- private static PrivateKey getPrivateKeyByKeyStore(String keyStorePath,String alias,String password)throws Exception{
- //获得密钥库
- KeyStore ks = getKeyStore(keyStorePath,password);
- //获得私钥
- return (PrivateKey)ks.getKey(alias, password.toCharArray());
- }
- /****
- * 由Certificate获得公钥,获得公钥后,通过RSA算方法实现进行"私钥加密,公钥解密"和"公钥加密,私钥解密"操作
- * @param certificatePath 证书路径
- * @return 公钥
- */
- private static PublicKey getPublicKeyByCertificate(String certificatePath)throws Exception {
- //获得证书
- Certificate certificate = getCertificate(certificatePath);
- //获得公钥
- return certificate.getPublicKey();
- }
- /****
- * 加载数字证书,JAVA 6仅支持x.509的数字证书
- * @param certificatePath 证书路径
- * @return 证书
- * @throws Exception
- */
- private static Certificate getCertificate(String certificatePath) throws Exception{
- //实例化证书工厂
- CertificateFactory certificateFactory = CertificateFactory.getInstance("x.509");
- //取得证书文件流
- FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(certificatePath);
- //生成证书
- Certificate certificate = certificateFactory.generateCertificate(in);
- //关闭证书文件流
- in.close();
- return certificate;
- }
- /****
- * 获得Certificate
- * @param keyStorePath 密钥库路径
- * @param alias 别名
- * @param password 密码
- * @return 证书
- * @throws Exception
- */
- private static Certificate getCertificate(String keyStorePath,String alias,String password) throws Exception{
- //由密钥库获得数字证书构建数字签名对象
- //获得密钥库
- KeyStore ks = getKeyStore(keyStorePath,password);
- //获得证书
- return ks.getCertificate(alias);
- }
- /****
- * 加载密钥库,加载了以后,我们就能通过相应的方法获得私钥,也可以获得数字证书
- * @param keyStorePath 密钥库路径
- * @param password 密码
- * @return 密钥库
- * @throws Exception
- */
- private static KeyStore getKeyStore(String keyStorePath,String password) throws Exception{
- //实例化密钥库
- KeyStore ks = KeyStore.getInstance(KeyStore.getDefaultType());
- //获得密钥库文件流
- FileInputStream is = new FileInputStream(keyStorePath);
- //加载密钥库
- ks.load(is,password.toCharArray());
- //关闭密钥库文件流
- is.close();
- return ks;
- }
- /****
- * 私钥加密
- * @param data 待加密的数据
- * @param keyStorePath 密钥库路径
- * @param alias 别名
- * @param password 密码
- * @return 加密数据
- * @throws Exception
- */
- public static byte[] encryptByPriateKey(byte[] data,String keyStorePath,String alias,String password) throws Exception{
- //获得私钥
- PrivateKey privateKey = getPrivateKeyByKeyStore(keyStorePath,alias,password);
- //对数据加密
- Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(privateKey.getAlgorithm());
- return cipher.doFinal(data);
- }
- /****
- * 私钥解密
- * @param data 待解密数据
- * @param keyStorePath 密钥库路径
- * @param alias 别名
- * @param password 密码
- * @return 解密数据
- * @throws Exception
- */
- public static byte[] decryptByPrivateKey(byte[] data,String keyStorePath,String alias,String password) throws Exception{
- //取得私钥
- PrivateKey privateKey = getPrivateKeyByKeyStore(keyStorePath,alias,password);
- //对数据解密
- Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(privateKey.getAlgorithm());
- cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE,privateKey);
- return cipher.doFinal(data);
- }
- /****
- * 公钥加密
- * @param data 等待加密数据
- * @param certificatePath 证书路径
- * @return 加密数据
- * @throws Exception
- */
- public static byte[] encryptByPublicKey(byte[] data,String certificatePath) throws Exception{
- //取得公钥
- PublicKey publicKey = getPublicKeyByCertificate(certificatePath);
- //对数据加密
- Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(publicKey.getAlgorithm());
- cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE,publicKey);
- return cipher.doFinal(data);
- }
- /****
- * 公钥解密
- * @param data 等待解密的数据
- * @param certificatePath 证书路径
- * @return 解密数据
- * @throws Exception
- */
- public static byte[] decryptByPublicKey(byte[] data,String certificatePath)throws Exception{
- //取得公钥
- PublicKey publicKey = getPublicKeyByCertificate(certificatePath);
- //对数据解密
- Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(publicKey.getAlgorithm());
- cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, publicKey);
- return cipher.doFinal(data);
- }
- /****
- * @param sign 签名
- * @param keyStorePath 密钥库路径
- * @param alias 别名
- * @param password 密码
- * @return 签名
- * @throws Exception
- */
- public static byte[] sign(byte[] sign,String keyStorePath,String alias,String password)throws Exception{
- //获得证书
- X509Certificate x509Certificate = (X509Certificate) getCertificate(keyStorePath,alias,password);
- //构建签名,由证书指定签名算法
- Signature signature = Signature.getInstance(x509Certificate.getSigAlgName());
- //获取私钥
- PrivateKey privateKey = getPrivateKeyByKeyStore(keyStorePath,alias,password);
- //初始化签名,由私钥构建
- signature.initSign(privateKey);
- signature.update(sign);
- return signature.sign();
- }
- /****
- * 验证签名
- * @param data 数据
- * @param sign 签名
- * @param certificatePath 证书路径
- * @return 验证通过为真
- * @throws Exception
- */
- public static boolean verify(byte[] data,byte[] sign,String certificatePath) throws Exception{
- //获得证书
- X509Certificate x509Certificate = (X509Certificate)getCertificate(certificatePath);
- //由证书构建签名
- Signature signature = Signature.getInstance(x509Certificate.getSigAlgName());
- //由证书初始化签名,实际上是使用了证书中的公钥
- signature.initVerify(x509Certificate);
- signature.update(data);
- return signature.verify(sign);
- }
- //我们假定密钥库文件yale.keystore存储在D盘根目录,数字证书文件yale.cer也存储在D盘根目录
- /****
- * 公钥加密---私钥解密
- * @throws Exception
- */
- public static void test1() throws Exception{
- System.err.println("公钥加密---私钥解密");
- String inputStr = "数字证书";
- byte[] data = inputStr.getBytes();
- //公钥加密
- byte[] encrypt = CertificateCoder.encryptByPublicKey(data, certificatePath);
- //私钥解密
- byte[] decrypt = CertificateCoder.decryptByPrivateKey(encrypt, keyStorePath, alias, password);
- String outputStr = new String(decrypt);
- System.err.println("加密前:\n" + inputStr);
- System.err.println("解密后:\n" + outputStr);
- }
- /****
- * 私钥加密---公钥解密
- * @throws Exception
- */
- public static void test2()throws Exception{
- System.err.println("私钥加密---公钥解密");
- String inputStr = "数字签名";
- byte[] data = inputStr.getBytes();
- //私钥加密
- byte[] encodedData = CertificateCoder.encryptByPriateKey(data, keyStorePath, alias, password);
- //公钥加密
- byte[] decodeData = CertificateCoder.decryptByPublicKey(encodedData, certificatePath);
- String outputStr = new String (decodeData);
- System.err.println("加密前:\n" + inputStr);
- System.err.println("解密后:\n" + outputStr);
- }
- public static void testSign()throws Exception{
- String inputStr = "签名";
- byte[] data = inputStr.getBytes();
- System.err.println("私钥签名---公钥验证");
- //产生签名
- byte[] sign = CertificateCoder.sign(data, keyStorePath, alias, password);
- System.err.println("签名:\n" + Hex.encodeHexString(sign));
- //验证签名
- boolean status = CertificateCoder.verify(data, sign, certificatePath);
- System.err.println("状态:\n " + status);
- }