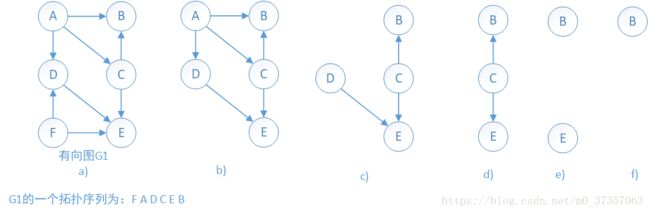
有向图_拓扑排序_AOE关键路径_判断图中是否存在环
目录
0.图——判环
0.1.1无向图判断是否存在环
0.1.2有向图判断是否存在环
0.2无向图判环
0.3有向图判环
1.有向图的拓扑排序
2.关键路径
2.1.邻接链表存储AOE网
2.1.1拓扑排序: bool TopologicalOrder():
2.1.2关键路径:bool CriticalPath()
求关键路径的完整代码与测试用例:
无向图、有向图判环的完整代码和测试用例
0.图——判环
0.1.1无向图判断是否存在环
0.1.1无向图,若深度优先遍历过程中遇到回边(即指向已访问过的顶点的边),则该无向图必定存在环路。
参考图的关节点与重连通分量,图的深度优先生成树。
定义visited[]数组为深度优先遍历时访问连通图的顶点v的序号。
如果某个顶点的visited值比其邻边的顶点的visited的值要大,说明,该顶点是后访问到了,存在一条回边连接到了其祖先节点!
因为对于任意一个顶点v而言,其孩子节点为在它之后才访问的节点,而其双亲结点和又回边连接的祖先结点是在它之前就访问过的结点!
0.1.2有向图判断是否存在环
0.2.1对于有向图,利用拓扑排序来判断是否存在环:
对于无环的有向图,对其进行拓扑排序可输出其所有顶点,而有环的图则不行!
0.2无向图判环
//用邻接表来存图
//先定义图的顶点数据结构,
typedef struct Node
{
int num;//顶点编号
char Alphabet;
//int visited;
}Node;
//无向图的邻接表表示,每个顶点对应一个列表
class UDGALGraph
{
private:
vector vecNodes;//图的结点地址向量,依次存每一个结点的地址
vector*> vexLists;//存储图中有向边的信息:每个顶点有一个邻接表,该邻接表上依次挂有其邻接顶点的地址
int vexNum, edgeNum;
vector visitedOrder;
public:
UDGALGraph()
{
CreateUDG();
}
~UDGALGraph()
{
DestroyDUG();
}
void CreateUDG();
void DestroyDUG();
void DFS(int v,int& count,bool& hasLoop);
//从图al的顶点v出发,递归地深度优先遍历图G
bool DFSTraverse();
bool hasLoop();
}; 无向图利用深度优先遍历来判断是否存在环:
void DFS(int v,int& count,bool& hasLoop)
{//从图al的顶点v出发,递归地深度优先遍历图G
visitedOrder[v] = count++;
cout << vecNodes[v]->Alphabet << " ";
for (int i = 0; i < (vexLists[v]->size()); i++)
{
int nodeNum = vexLists[v]->at(i)->num;
if (visitedOrder[nodeNum] == 0)
{
DFS(nodeNum, count, hasLoop);
}
else if (visitedOrder[nodeNum]>visitedOrder[v])
{
hasLoop = true;
}
}
}
bool DFSTraverse()
{
int count = 1;
bool hasLoop = false;
for (int i = 0; i < vexNum; i++)
{
if (visitedOrder[i] == 0)
{
DFS(i, count, hasLoop);
}
}
/*
algraph是在堆中分配的结点,每次范围后,其每一个结点的标志位都设置为1了,退出时,
下次再遍历前要清一下标志位。
*/
for (int i = 0; i < vexNum; i++)
{
visitedOrder[i] = 0;
}
return hasLoop;
}
bool hasLoop()
{//对于无向图来说,若深度优先遍历过程中遇到回边(即连接已经访问过的顶点的邻边),则说明该无向图存在环!
if (DFSTraverse())
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
0.3有向图判环
//有向图的邻接表表示,每个顶点对应一个邻接链表
class DGALGraph
{
private:
vector vecNodes;//图的结点地址向量,依次存每一个结点的地址
vector*> vexLists;//存储图中有向边的信息:每个顶点有一个邻接表,该邻接表上依次挂有其邻接顶点的地址
int vexNum, edgeNum;
vector InDegree;
vector visited;
deque topologicalSequence;//有向无环图的拓扑序列
public:
DGALGraph()
{
CreateUDG();
}
~DGALGraph()
{
DestroyDUG();
}
void CreateUDG();
void DestroyDUG();
bool topologicalSort();
bool hasLoop();
void printTopoSeq()
}; 有向图利用拓扑排序来判断是否存在环:
bool topologicalSort()
{
cout << "有向图的拓扑排序:" << endl;
stack inDegree0VexStack;
for (int i = 0; i < vexNum; i++)
{
if (InDegree[i] == 0)
{
inDegree0VexStack.push(i);
}
}
int count = 0;//对输出顶点计数
while (!inDegree0VexStack.empty())
{
int i = inDegree0VexStack.top();//输入i号顶点,并计数
inDegree0VexStack.pop();
//cout << vecNodes[i]->Alphabet << " ";
cout << i + 1 << " ";
++count;
for (int j = 0; j < vexLists[i]->size(); j++)
{//对i号顶点的每一个邻接顶点j的入度减1,即i->i的邻接顶点
int nodeNum = vexLists[i]->at(j)->num;
if ((--InDegree[nodeNum] == 0))
{//若入度减到了0,则入栈
inDegree0VexStack.push(nodeNum);
}
}
}
if (count < vexNum)
{//该有向图有环
return true;
}
else
{//该有向图无环,可将所有顶点按拓扑有序输出。
return false;
}
}
bool hasLoop()
{
if (topologicalSort())
{
cout << endl;
cout << "该有向图有环!" << endl;
return true;
}
else
{
cout << endl;
cout << "该有向图无环!" << endl;
return false;
}
}//topologicalSort
1.有向图的拓扑排序
2.关键路径
2.1.邻接链表存储AOE网
typedef struct ArcNode{
int v1; //弧尾
int v2;//弧头:该弧指向的顶点的位置
int weight; //数据域
}ArcNode;
typedef struct VNode{
int vexNo; //顶点编号
}VNode;
class AOEALGraph{
private://用邻接链表存储AOE网!
int vexNum, arcNum;
vector nodesPtrVector;
vector*> nodeArcPtrVector;//每个顶点的出弧指针向量
stack ReverseTopoOrder;//逆拓扑排序
vector InDegree;//各个顶点的入度
vector ve;//各个顶点的最早发生时间向量
vector vl;//各个顶点的最晚发生时间向量
vector CP;//关键路径!存弧,即活动
public:
AOEALGraph()
{
CreateAOE();
}
void CreateAOE();
bool TopologicalOrder();
bool CriticalPath()
}; 2.1.1拓扑排序: bool TopologicalOrder():
bool TopologicalOrder()
{
int count=0;
stack _0InDegreeStack;
for (int i = 0; i < vexNum; i++)
{
if (InDegree[i] == 0)
{
_0InDegreeStack.push(i);
}
}
while (!_0InDegreeStack.empty())
{
int j = _0InDegreeStack.top();
_0InDegreeStack.pop();
ReverseTopoOrder.push(j);//j号顶点入逆拓扑排序栈!
count++;
for (int i = 0; i < nodeArcPtrVector[j]->size(); i++)
{//遍历j号顶点的所有邻接点k
int k = nodeArcPtrVector[j]->at(i)->v2;
if (--InDegree[k] == 0)
{//对j号顶点的每一个邻接顶点的入度-1,若入度为0则入0入度栈
_0InDegreeStack.push(k);
}
if (ve[j] + nodeArcPtrVector[j]->at(i)->weight > ve[k])
{
ve[k] = ve[j] + nodeArcPtrVector[j]->at(i)->weight;
}
}
}
if (count < vexNum)
{
return false;
}
else
{
return true;
}
} 2.1.2关键路径:bool CriticalPath()
bool CriticalPath()
{
if (!TopologicalOrder())
{
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < vexNum; i++)
{//初始化各个顶点事件的最迟发生时间!
vl[i] = ve[vexNum - 1];
}
while (!ReverseTopoOrder.empty())//按拓扑逆序求各个顶点的vl值
{
int j = ReverseTopoOrder.top();
ReverseTopoOrder.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < nodeArcPtrVector[j]->size(); i++)
{
int k = nodeArcPtrVector[j]->at(i)->v2;
int dut = nodeArcPtrVector[j]->at(i)->weight;
if (vl[k] - dut < vl[j])
{
vl[j] = vl[k] - dut;
}
}//for
}
for (int j = 0; j < vexNum; j++)
{//求没一条弧的最早开始时间ee(i)和最晚开始时间el(i),若ee=el则为关键活动!将关键活动的这条弧的指针存入CP向量
for (int i = 0; i < nodeArcPtrVector[j]->size(); i++)
{
int k = nodeArcPtrVector[j]->at(i)->v2;
int dut = nodeArcPtrVector[j]->at(i)->weight;
int ee = ve[j];
int el = vl[k] - dut;
if (ee == el)
{
CP.push_back(nodeArcPtrVector[j]->at(i));
}
}
}
//输出关键活动弧
for (int i = 0; i < CP.size(); i++)
{
cout << CP[i]->v1 << "->" << CP[i]->v2 << ",weight=" << CP[i]->weight << endl;
}
return true;
}
求关键路径的完整代码与测试用例:
// CriticalPath2.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
typedef struct ArcNode{
int v1; //弧尾
int v2;//弧头:该弧指向的顶点的位置
int weight; //数据域
}ArcNode;
typedef struct VNode{
int vexNo; //顶点编号
}VNode;
class AOEALGraph{
private://用邻接链表存储AOE网!
int vexNum, arcNum;
vector nodesPtrVector;
vector*> nodeArcPtrVector;//每个顶点的出弧指针向量
stack ReverseTopoOrder;//逆拓扑排序
vector InDegree;//各个顶点的入度
vector ve;//各个顶点的最早发生时间向量
vector vl;//各个顶点的最晚发生时间向量
vector CP;//关键路径!存弧,即活动
public:
AOEALGraph()
{
CreateAOE();
}
void CreateAOE()
{
cin >> vexNum >> arcNum;
for (int i = 0; i < vexNum; i++)
{
VNode* vexNodePtr = new VNode;
vexNodePtr->vexNo = i;
nodesPtrVector.push_back(vexNodePtr);
vector* arcALPtr = new vector < ArcNode* > ;
nodeArcPtrVector.push_back(arcALPtr);
InDegree.push_back(0);
ve.push_back(0);
vl.push_back(0);
}
int v1, v2, weight;
int v1No, v2No;
for (int i = 0; i < arcNum; i++)
{
cin >> v1 >> v2 >> weight;
v1No = v1 - 1;
v2No = v2 - 1;
ArcNode* arcNodePtr = new ArcNode;
arcNodePtr->v1 = v1No;
arcNodePtr->v2 = v2No;
arcNodePtr->weight = weight;
nodeArcPtrVector[v1No]->push_back(arcNodePtr);
InDegree[v2No]++;//顶点V2的入度+1
}
}
bool TopologicalOrder()
{
int count=0;
stack _0InDegreeStack;
for (int i = 0; i < vexNum; i++)
{
if (InDegree[i] == 0)
{
_0InDegreeStack.push(i);
}
}
while (!_0InDegreeStack.empty())
{
int j = _0InDegreeStack.top();
_0InDegreeStack.pop();
ReverseTopoOrder.push(j);//j号顶点入逆拓扑排序栈!
count++;
for (int i = 0; i < nodeArcPtrVector[j]->size(); i++)
{//遍历j号顶点的所有邻接点k
int k = nodeArcPtrVector[j]->at(i)->v2;
if (--InDegree[k] == 0)
{//对j号顶点的每一个邻接顶点的入度-1,若入度为0则入0入度栈
_0InDegreeStack.push(k);
}
if (ve[j] + nodeArcPtrVector[j]->at(i)->weight > ve[k])
{
ve[k] = ve[j] + nodeArcPtrVector[j]->at(i)->weight;
}
}
}
if (count < vexNum)
{
return false;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
bool CriticalPath()
{
if (!TopologicalOrder())
{
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < vexNum; i++)
{//初始化各个顶点事件的最迟发生时间!
vl[i] = ve[vexNum - 1];
}
while (!ReverseTopoOrder.empty())//按拓扑逆序求各个顶点的vl值
{
int j = ReverseTopoOrder.top();
ReverseTopoOrder.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < nodeArcPtrVector[j]->size(); i++)
{
int k = nodeArcPtrVector[j]->at(i)->v2;
int dut = nodeArcPtrVector[j]->at(i)->weight;
if (vl[k] - dut < vl[j])
{
vl[j] = vl[k] - dut;
}
}//for
}
for (int j = 0; j < vexNum; j++)
{//求没一条弧的最早开始时间ee(i)和最晚开始时间el(i),若ee=el则为关键活动!将关键活动的这条弧的指针存入CP向量
for (int i = 0; i < nodeArcPtrVector[j]->size(); i++)
{
int k = nodeArcPtrVector[j]->at(i)->v2;
int dut = nodeArcPtrVector[j]->at(i)->weight;
int ee = ve[j];
int el = vl[k] - dut;
if (ee == el)
{
CP.push_back(nodeArcPtrVector[j]->at(i));
}
}
}
//输出关键活动弧
for (int i = 0; i < CP.size(); i++)
{
cout << CP[i]->v1 << "->" << CP[i]->v2 << ",weight=" << CP[i]->weight << endl;
}
return true;
}
};
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
AOEALGraph aoe;
aoe.CriticalPath();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
/*
9 11
1 2 6
1 3 4
1 4 5
2 5 1
3 5 1
4 6 2
5 7 9
5 8 7
6 8 4
7 9 2
8 9 4
0->1,weight=6
1->4,weight=1
4->6,weight=9
4->7,weight=7
6->8,weight=2
7->8,weight=4
请按任意键继续. . .
6 8
1 2 3
1 3 2
2 4 2
2 5 3
3 4 4
3 6 3
4 6 2
5 6 1
0->2,weight=2
2->3,weight=4
3->5,weight=2
请按任意键继续. . .
*/ 无向图、有向图判环的完整代码和测试用例
// TopoSort.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
//用邻接表来存图
//先定义图的顶点数据结构,
typedef struct Node
{
int num;//顶点编号
char Alphabet;
//int visited;
}Node;
//无向图的邻接表表示,每个顶点对应一个列表
class UDGALGraph
{
private:
vector vecNodes;//图的结点地址向量,依次存每一个结点的地址
vector*> vexLists;//存储图中有向边的信息:每个顶点有一个邻接表,该邻接表上依次挂有其邻接顶点的地址
int vexNum, edgeNum;
vector visitedOrder;
public:
UDGALGraph()
{
CreateUDG();
}
~UDGALGraph()
{
DestroyDUG();
}
void CreateUDG()
{
cout << "请输入无向图的顶点个数和边数目,然后依次输入各条边的两个顶点信息:" << endl;
cin >> vexNum >> edgeNum;
for (int i = 0; i < vexNum; i++)
{
Node* nodePtr = new Node;
nodePtr->num = i;
nodePtr->Alphabet = 'A' + i;
//nodePtr->visited = 0;
vecNodes.push_back(nodePtr);
vector* vexVecPtr = new vector < Node* >;
vexLists.push_back(vexVecPtr);
visitedOrder.push_back(0);
}
char VexAlphabet1, VexAlphabet2;
int vexNo1, vexNo2;
for (int i = 0; i < edgeNum; i++)
{
cin >> VexAlphabet1 >> VexAlphabet2;
vexNo1 = VexAlphabet1 - 'A';
vexNo2 = VexAlphabet2 - 'A';
//无向图,在邻接表中存双向边
vexLists[vexNo1]->push_back(vecNodes[vexNo2]);
vexLists[vexNo2]->push_back(vecNodes[vexNo1]);
}
}
void DestroyDUG()
{
for (int i = 0; i < vexNum; i++)
{
delete vecNodes[i];
vecNodes[i] = nullptr;
}
for (int i = 0; i < vexLists.size(); i++)
{
delete vexLists[i];
}
}
void DFS(int v,int& count,bool& hasLoop)
{//从图al的顶点v出发,递归地深度优先遍历图G
visitedOrder[v] = count++;
cout << vecNodes[v]->Alphabet << " ";
for (int i = 0; i < (vexLists[v]->size()); i++)
{
int nodeNum = vexLists[v]->at(i)->num;
if (visitedOrder[nodeNum] == 0)
{
DFS(nodeNum, count, hasLoop);
}
else if (visitedOrder[nodeNum]>visitedOrder[v])
{
hasLoop = true;
}
}
}
bool DFSTraverse()
{
int count = 1;
bool hasLoop = false;
for (int i = 0; i < vexNum; i++)
{
if (visitedOrder[i] == 0)
{
DFS(i, count, hasLoop);
}
}
/*
algraph是在堆中分配的结点,每次范围后,其每一个结点的标志位都设置为1了,退出时,
下次再遍历前要清一下标志位。
*/
for (int i = 0; i < vexNum; i++)
{
visitedOrder[i] = 0;
}
return hasLoop;
}
bool hasLoop()
{//对于无向图来说,若深度优先遍历过程中遇到回边(即连接已经访问过的顶点的邻边),则说明该无向图存在环!
if (DFSTraverse())
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
};
//有向图的邻接表表示,每个顶点对应一个邻接链表
class DGALGraph
{
private:
vector vecNodes;//图的结点地址向量,依次存每一个结点的地址
vector*> vexLists;//存储图中有向边的信息:每个顶点有一个邻接表,该邻接表上依次挂有其邻接顶点的地址
int vexNum, edgeNum;
vector InDegree;
vector visited;
deque topologicalSequence;//有向无环图的拓扑序列
public:
DGALGraph()
{
CreateUDG();
}
~DGALGraph()
{
DestroyDUG();
}
void CreateUDG()
{
cout << "请输入有向图的顶点个数和边数目,然后依次输入各条边的两个顶点信息:" << endl;
cin >> vexNum >> edgeNum;
for (int i = 0; i < vexNum; i++)
{
Node* nodePtr = new Node;
nodePtr->num = i;
nodePtr->Alphabet = 'A' + i;
//nodePtr->visited = 0;
vecNodes.push_back(nodePtr);
vector* vexVecPtr = new vector < Node* >;
vexLists.push_back(vexVecPtr);
visited.push_back(0);
InDegree.push_back(0);
}
char VexAlphabet1, VexAlphabet2;
int vexNo1, vexNo2;
for (int i = 0; i < edgeNum; i++)
{
cin >> VexAlphabet1 >> VexAlphabet2;
vexNo1 = VexAlphabet1 - 'A';
vexNo2 = VexAlphabet2 - 'A';
//有向图
vexLists[vexNo1]->push_back(vecNodes[vexNo2]);
InDegree[vexNo2]++;//
}
}
void DestroyDUG()
{
for (int i = 0; i < vexNum; i++)
{
delete vecNodes[i];
vecNodes[i] = nullptr;
}
for (int i = 0; i < vexLists.size(); i++)
{
delete vexLists[i];
}
}
bool topologicalSort()
{
cout << "有向图的拓扑排序:" << endl;
stack inDegree0VexStack;
for (int i = 0; i < vexNum; i++)
{
if (InDegree[i] == 0)
{
inDegree0VexStack.push(i);
}
}
int count = 0;//对输出顶点计数
while (!inDegree0VexStack.empty())
{
int i = inDegree0VexStack.top();//输入i号顶点,并计数
inDegree0VexStack.pop();
//cout << vecNodes[i]->Alphabet << " ";
cout << i + 1 << " ";
++count;
for (int j = 0; j < vexLists[i]->size(); j++)
{//对i号顶点的每一个邻接顶点j的入度减1,即i->i的邻接顶点
int nodeNum = vexLists[i]->at(j)->num;
if ((--InDegree[nodeNum] == 0))
{//若入度减到了0,则入栈
inDegree0VexStack.push(nodeNum);
}
}
}
if (count < vexNum)
{//该有向图有环
return true;
}
else
{//该有向图无环,可将所有顶点按拓扑有序输出。
return false;
}
}
bool hasLoop()
{
if (topologicalSort())
{
cout << endl;
cout << "该有向图有环!" << endl;
return true;
}
else
{
cout << endl;
cout << "该有向图无环!" << endl;
return false;
}
}//topologicalSort
void DFS(int v)
{//从图al的顶点v出发,递归地深度优先遍历图G
visited[v] = 1;
cout << vecNodes[v]->Alphabet << " ";
for (int i = 0; i < (vexLists[v]->size()); i++)
{
int nodeNum = vexLists[v]->at(i)->num;
if (visited[nodeNum] == 0)
{
DFS(nodeNum);
}
}
topologicalSequence.push_front(v);
}
//对于有向无环图,也可以使用深度优先遍历来求其拓扑序列!
//最先退出DFS函数的的顶点即出度为0的顶点,是拓扑排序序列中的最后一个顶点,
//按最先退出DFS函数的先后顺序记录下来的序列就是拓扑排序的逆序序列。
//类似于有向图的强连通分量时的finish数组,用以记录退出DFS函数的先后顺序!
//用一个双端队列来存储,就可以顺序输出!
void DFSTraverse()
{
for (int i = 0; i < vexNum; i++)
{
if (visited[i] == 0)
{
DFS(i);
}
}
/*
algraph是在堆中分配的结点,每次范围后,其每一个结点的标志位都设置为1了,退出时,
下次再遍历前要清一下标志位。
*/
for (int i = 0; i < vexNum; i++)
{
visited[i] = 0;
}
}
void printTopoSeq()
{
cout << endl;
cout << "拓扑序列为:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < topologicalSequence.size(); i++)
{
cout << vecNodes[topologicalSequence[i]]->Alphabet << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
};
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
//UDGALGraph udg;
//if (udg.hasLoop())
//{
// cout << "有环" << endl;
//}
//else
//{
// cout << "无环" << endl;
//}
//DGALGraph dg;
//dg.hasLoop();
DGALGraph dg2;
dg2.DFSTraverse();
dg2.printTopoSeq();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
/*
无向有环图1:
A-B
A-D
B-C
C-A
4 4
A B
A D
B C
C A
请输入无向图的顶点个数和边数目,然后依次输入各条边的两个顶点信息:
4 4
A B
A D
B C
C A
A B C D 有环
请按任意键继续. . .
无向无环图2:
4 3
A B
A D
B C
请输入无向图的顶点个数和边数目,然后依次输入各条边的两个顶点信息:
4 3
A B
A D
B C
A B C D 无环
请按任意键继续. . .
*/
/*
有向无环图:
6 8
A B
A C
A D
C B
C E
D E
F D
F E
请输入无向图的顶点个数和边数目,然后依次输入各条边的两个顶点信息:
6 8
A B
A C
A D
C B
C E
D E
F D
F E
有向图的拓扑排序:
6 1 4 3 5 2
该有向图无环!
请按任意键继续. . .
*/
数据结构有向图_拓扑排序_AOE关键路径 图判环