介绍
Xception是Google出品,属于2017年左右的东东。它在Google家的MobileNet v1之后,MobileNet v2之前。
它的主旨与MobileNet系列很像即推动Depthwise Conv + Pointwise Conv的使用。只是它直接以Inception v3为模子,将里面的基本inception module替换为使用Depthwise Conv + Pointwise Conv,又外加了residual connects,
最终模型在ImageNet等数据集上都取得了相比Inception v3与Resnet-152更好的结果。当然其模型大小与计算效率相对Inception v3也取得了较大提高。
从Inception module到Separable Conv的演变之路
下图1为一个典型的Inception module,它的实现的基本assumption就是feature在经conv处理时可分别学习feature channels间的关联关系与feature单个channel内部空间上的关联关系,为此inception module中使用了大量的1x1 conv来重视学习
channels之间的关联,然后再分别使用3x3/5x5(两个3x3)等去学习其不同维度上的单个channel内的空间上的关联;若我们基于以上inception中用到的关联关系分离假设而只使用3x3 convs来表示单个channel内的空间关联关系,那么就可以得到出下图2表示的
简化后了的inception module。
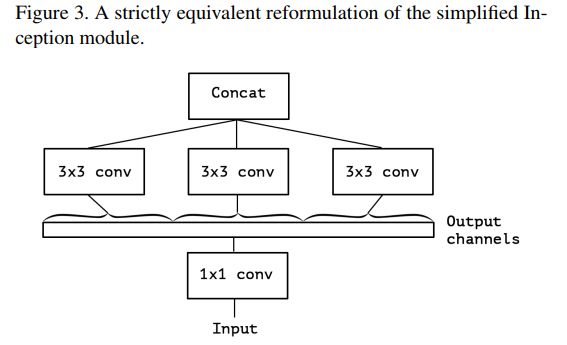
而本质上上图2中表示的简化版Inception模块又可被表示为下图3中的形式。可以看出实质上它等价于先使用一个1x1 conv来学习input feature maps之上channels间特征的关联关系,然后再将1x1 conv输出的feature maps进行分割,分别交由下面的若干个3x3
conv来处理其内的空间上元素的关联关系。
更进一步,何不做事做绝将每个channel上的空间关联分别使用一个相应的conv 3x3来单独处理呢。如此就得到了下图4中所示的Separable conv。
Xception架构
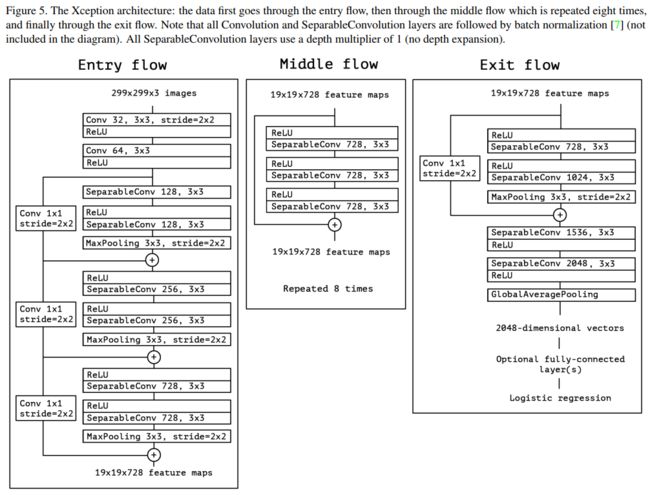
下图中为Xception结构的表示。它就是由Inception v3直接演变而来。其中引入了Residual learning的结构(已经有多项工作,同时在本文中作者也有相关实验表明Residual learning在CNN模型中的使用可带来收敛速度的加快。)。
同一向复杂的Inception系列模型一样,它也引入了Entry/Middle/Exit三个flow,每个flow内部使用不同的重复模块,当然最最核心的属于中间不断分析、过滤特征的Middel flow。
Entry flow主要是用来不断下采样,减小空间维度;中间则是不断学习关联关系,优化特征;最终则是汇总、整理特征,用于交由FC来进行表达。
实验结果
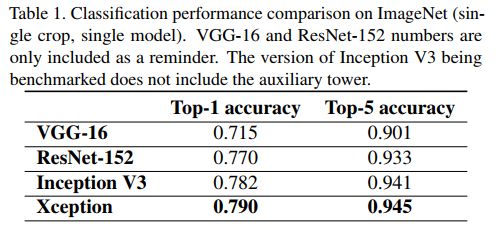
下表为Xception与其它模型在Imagenet上分类精度的结果比较。
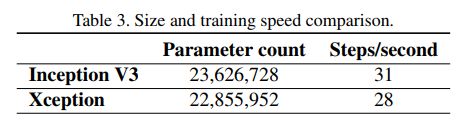
然后下表则为Xception与Inception v3在模型参数大小与计算速度上的比较。
代码分析
在TF的官方实现中,他们对Xception的模型结构做了些改变,主要如下两块。一是使用stride为2的conv来代替使用Maxpooling进行feature降维;二则是在depthwise conv之后同样使用ReLu与BN。
We made a few more changes on top of MSRA's modifications:
1. Fully convolutional: All the max-pooling layers are replaced with separable
conv2d with stride = 2. This allows us to use atrous convolution to extract
feature maps at any resolution.
2. We support adding ReLU and BatchNorm after depthwise convolution, motivated
by the design of MobileNetv1.
以下为Xception的模型构建入口函数。
def xception(inputs,
blocks,
num_classes=None,
is_training=True,
global_pool=True,
keep_prob=0.5,
output_stride=None,
reuse=None,
scope=None):
"""Generator for Xception models.
This function generates a family of Xception models. See the xception_*()
methods for specific model instantiations, obtained by selecting different
block instantiations that produce Xception of various depths.
Args:
inputs: A tensor of size [batch, height_in, width_in, channels]. Must be
floating point. If a pretrained checkpoint is used, pixel values should be
the same as during training (see go/slim-classification-models for
specifics).
blocks: A list of length equal to the number of Xception blocks. Each
element is an Xception Block object describing the units in the block.
num_classes: Number of predicted classes for classification tasks.
If 0 or None, we return the features before the logit layer.
is_training: whether batch_norm layers are in training mode.
global_pool: If True, we perform global average pooling before computing the
logits. Set to True for image classification, False for dense prediction.
keep_prob: Keep probability used in the pre-logits dropout layer.
output_stride: If None, then the output will be computed at the nominal
network stride. If output_stride is not None, it specifies the requested
ratio of input to output spatial resolution.
reuse: whether or not the network and its variables should be reused. To be
able to reuse 'scope' must be given.
scope: Optional variable_scope.
Returns:
net: A rank-4 tensor of size [batch, height_out, width_out, channels_out].
If global_pool is False, then height_out and width_out are reduced by a
factor of output_stride compared to the respective height_in and width_in,
else both height_out and width_out equal one. If num_classes is 0 or None,
then net is the output of the last Xception block, potentially after
global average pooling. If num_classes is a non-zero integer, net contains
the pre-softmax activations.
end_points: A dictionary from components of the network to the corresponding
activation.
Raises:
ValueError: If the target output_stride is not valid.
"""
with tf.variable_scope(
scope, 'xception', [inputs], reuse=reuse) as sc:
end_points_collection = sc.original_name_scope + 'end_points'
with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d,
slim.separable_conv2d,
xception_module,
stack_blocks_dense],
outputs_collections=end_points_collection):
with slim.arg_scope([slim.batch_norm], is_training=is_training):
net = inputs
if output_stride is not None:
if output_stride % 2 != 0:
raise ValueError('The output_stride needs to be a multiple of 2.')
output_stride /= 2
# Root block function operated on inputs.
net = resnet_utils.conv2d_same(net, 32, 3, stride=2,
scope='entry_flow/conv1_1')
net = resnet_utils.conv2d_same(net, 64, 3, stride=1,
scope='entry_flow/conv1_2')
# Extract features for entry_flow, middle_flow, and exit_flow.
net = stack_blocks_dense(net, blocks, output_stride)
# Convert end_points_collection into a dictionary of end_points.
end_points = slim.utils.convert_collection_to_dict(
end_points_collection, clear_collection=True)
if global_pool:
# Global average pooling.
net = tf.reduce_mean(net, [1, 2], name='global_pool', keepdims=True)
end_points['global_pool'] = net
if num_classes:
net = slim.dropout(net, keep_prob=keep_prob, is_training=is_training,
scope='prelogits_dropout')
net = slim.conv2d(net, num_classes, [1, 1], activation_fn=None,
normalizer_fn=None, scope='logits')
end_points[sc.name + '/logits'] = net
end_points['predictions'] = slim.softmax(net, scope='predictions')
return net, end_points
以下函数则是构建具体的blocks。。感觉Google有过度设计的嫌疑,非得将一个简单模型构得那么多层次,即使是slim这样已经高级了些的model让人看起来仍然要追着看很久。。推荐大家使用Pytorch啊。。:)。
就到这了,再向下不追了,还想进一步探究的朋友可以直接去翻参考文献里标明的code file。
@slim.add_arg_scope
def stack_blocks_dense(net,
blocks,
output_stride=None,
outputs_collections=None):
"""Stacks Xception blocks and controls output feature density.
First, this function creates scopes for the Xception in the form of
'block_name/unit_1', 'block_name/unit_2', etc.
Second, this function allows the user to explicitly control the output
stride, which is the ratio of the input to output spatial resolution. This
is useful for dense prediction tasks such as semantic segmentation or
object detection.
Control of the output feature density is implemented by atrous convolution.
Args:
net: A tensor of size [batch, height, width, channels].
blocks: A list of length equal to the number of Xception blocks. Each
element is an Xception Block object describing the units in the block.
output_stride: If None, then the output will be computed at the nominal
network stride. If output_stride is not None, it specifies the requested
ratio of input to output spatial resolution, which needs to be equal to
the product of unit strides from the start up to some level of Xception.
For example, if the Xception employs units with strides 1, 2, 1, 3, 4, 1,
then valid values for the output_stride are 1, 2, 6, 24 or None (which
is equivalent to output_stride=24).
outputs_collections: Collection to add the Xception block outputs.
Returns:
net: Output tensor with stride equal to the specified output_stride.
Raises:
ValueError: If the target output_stride is not valid.
"""
# The current_stride variable keeps track of the effective stride of the
# activations. This allows us to invoke atrous convolution whenever applying
# the next residual unit would result in the activations having stride larger
# than the target output_stride.
current_stride = 1
# The atrous convolution rate parameter.
rate = 1
for block in blocks:
with tf.variable_scope(block.scope, 'block', [net]) as sc:
for i, unit in enumerate(block.args):
if output_stride is not None and current_stride > output_stride:
raise ValueError('The target output_stride cannot be reached.')
with tf.variable_scope('unit_%d' % (i + 1), values=[net]):
# If we have reached the target output_stride, then we need to employ
# atrous convolution with stride=1 and multiply the atrous rate by the
# current unit's stride for use in subsequent layers.
if output_stride is not None and current_stride == output_stride:
net = block.unit_fn(net, rate=rate, **dict(unit, stride=1))
rate *= unit.get('stride', 1)
else:
net = block.unit_fn(net, rate=1, **unit)
current_stride *= unit.get('stride', 1)
# Collect activations at the block's end before performing subsampling.
net = slim.utils.collect_named_outputs(outputs_collections, sc.name, net)
if output_stride is not None and current_stride != output_stride:
raise ValueError('The target output_stride cannot be reached.')
return net
参考文献
- Xception: Deep Learning with Depthwise Separable Convolutions, Franc¸ois-Chollet, 2017
- https://github.com/tensorflow/models/blob/master/research/deeplab/core/xception.py