Torch - 官方例子
From:Torch7官网
1 Define a positive definite quadratic form
- rand() - creates tensor drawn from uniform distribution
- t() - transposes a tensor (note it returns a new view)
- dot() - performs a dot product between two tensors
- eye() - returns a identity matrix
- * - operator over matrices (which performs a matrix-vector or matrix-matrix multiplication)
例子:
require 'torch'
torch.manualSeed(1234) -- make sure the random seed is the same for everyone
N = 5 -- choose a dimension
A = torch.rand(N, N) -- create a random NxN matrix
A = A*A:t() -- make it symmetric positive
A:add(0.001, torch.eye(N)) -- make it definite
b = torch.rand(N) -- add a linear term
function J(x) -- create the quadratic form
return 0.5*x:dot(A*x)-b:dot(x)
end
print(J(torch.rand(N))) -- print the function value2. Find the exact minimum
xs = torch.inverse(A)*b -- inverse the matrix
print(string.format('J(x^*) = %g', J(xs)))3. Search the minimum by gradient descent
function dJ(x) -- define the gradient w.r.t. x of J(x)
return A*x-b
end
x = torch.rand(N) -- define some current solution
lr = 0.01 -- given learning rate lr
for i=1,20000 do
x = x - dJ(x)*lr
print(string.format('at iter %d J(x) = %f', i, J(x))) -- print the value of the objective function at each iteration
endoutput:
...
at iter 19995 J(x) = -3.135664
at iter 19996 J(x) = -3.135664
at iter 19997 J(x) = -3.135665
at iter 19998 J(x) = -3.135665
at iter 19999 J(x) = -3.135665
at iter 20000 J(x) = -3.1356664. Using the optim package
luarocks install optimTraining with optim:
require 'optim'
state = { -- define a state for conjugate gradient
verbose = true,
maxIter = 100
}
x = torch.rand(N)
optim.cg(JdJ, x, state)output:
after 120 evaluation J(x) = -3.136835
after 121 evaluation J(x) = -3.136836
after 122 evaluation J(x) = -3.136837
after 123 evaluation J(x) = -3.136838
after 124 evaluation J(x) = -3.136840
after 125 evaluation J(x) = -3.1368385. Plot
luarocks install gnuplot5.1 Store intermediate function evaluations
evaluations = {}
time = {}
timer = torch.Timer()
neval = 0
function JdJ(x)
local Jx = J(x)
neval = neval + 1
print(string.format('after %d evaluations, J(x) = %f', neval, Jx))
table.insert(evaluations, Jx)
table.insert(time, timer:time().real)
return Jx, dJ(x)
end
-- trian
state = {
verbose = true,
maxIter = 100
}
x0 = torch.rand(N)
cgx = x0:clone() -- make a copy of x0
timer:reset()
optim.cg(JdJ, cgx, state)
-- convert the evaluations and time tables to tensors for plotting:
cgtime = torch.Tensor(time)
cgevaluations = torch.Tensor(evaluations)5.2 Add support for stochastic gradient descent
-- add the training with stochastic gradient, using optim
evaluations = {}
time = {}
neval = 0
state = {
lr = 0.1
}
-- start from the same starting point than for CG
x = x0:clone()
-- reset the timer!
timer:reset()
-- note that SGD optimizer requires to do the loop
for i=1,1000 do
optim.sgd(JdJ, x, state)
table.insert(evaluations, Jx)
end
sgdtime = torch.Tensor(time)
sgdevaluations = torch.Tensor(evaluations)5.3 Final plot
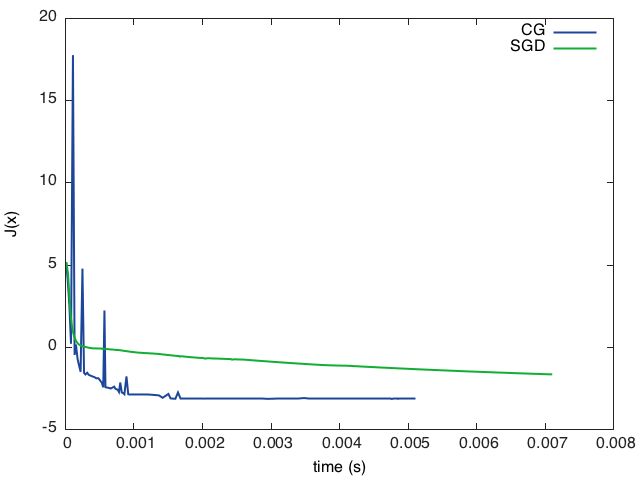
require 'gnuplot'
gnuplot.figure(1)
gnuplot.title('CG loss minimisation over time')
gnuplot.plot(cgtime, cgevaluations)
gnuplot.figure(2)
gnuplot.title('SGD loss minimisation over time')
gnuplot.plot(sgdtime, sgdevaluations)
或
require 'gnuplot'
gnuplot.pngfigure('plot.png')
gnuplot.plot(
{'CG', cgtime, cgevaluations, '-'},
{'SGD', sgdtime, sgdevaluations, '-'})
gnuplot.xlabel('time (s)')
gnuplot.ylabel('J(x)')
gnuplot.plotflush()