unix/linux ls命令的实现
Understanding Unix/Linux Programming(Unix/Linux编程实践教程)
学习模式:
(1)它能做什么?
(2)它是如何实现的?
(3)能不能自己编写一个?
(实验环境:gcc version 5.4.0 20160609 (Ubuntu 5.4.0-6ubuntu1~16.04.4) )
ls命令学习(1)ls命令能做什么
查看联机帮助:ls
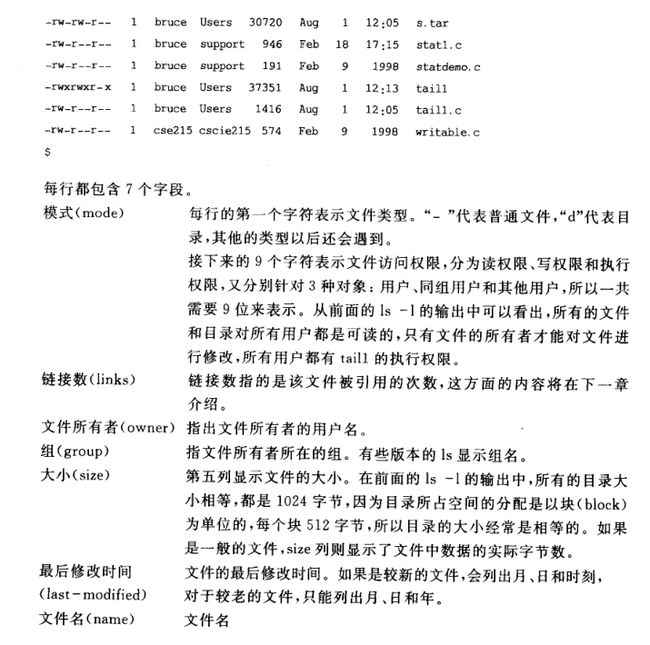
可知ls默认列出当前目录的文件夹跟文件。按字典序排序。
ls还可以跟其他参数:ls -l
cong@ubantu:/$ ls -l
total 100
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Mar 8 03:48 bin
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Mar 10 02:39 boot
drwxrwxr-x 2 root root 4096 Aug 22 2016 cdrom
drwxr-xr-x 19 root root 4320 Mar 10 22:09 dev
drwxr-xr-x 132 root root 12288 Mar 10 22:09 etc
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Aug 22 2016 home
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 32 Mar 8 03:56 initrd.img -> boot/initrd.img-4.4.0-66-generic
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 32 Oct 24 23:51 initrd.img.old -> boot/initrd.img-4.4.0-45-generic
drwxr-xr-x 22 root root 4096 Aug 22 2016 lib
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jul 19 2016 lib64
drwx------ 2 root root 16384 Aug 22 2016 lost+found
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Aug 22 2016 media
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Oct 15 04:39 mnt
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jul 19 2016 opt
dr-xr-xr-x 223 root root 0 Mar 10 22:08 proc
drwx------ 4 root root 4096 Oct 14 09:10 root
drwxr-xr-x 27 root root 860 Mar 11 00:45 run
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 12288 Mar 8 03:48 sbin
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jun 29 2016 snap
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jul 19 2016 srv
dr-xr-xr-x 13 root root 0 Mar 10 22:08 sys
drwxrwxrwt 12 root root 4096 Mar 11 00:45 tmp
drwxr-xr-x 11 root root 4096 Jul 19 2016 usr
drwxr-xr-x 14 root root 4096 Jul 19 2016 var
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 29 Mar 8 03:56 vmlinuz -> boot/vmlinuz-4.4.0-66-generic
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 29 Oct 24 23:51 vmlinuz.old -> boot/vmlinuz-4.4.0-45-generic(2)ls是如何实现的?
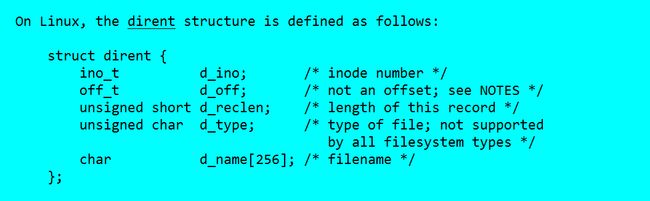
目录是一种特殊的文件,目录是文件的列表。每个目录都至少包含两个特殊的项。“.”(当前目录),“..”(上一级目录)。
如何读取目录的信息?如何获取文件的信息?
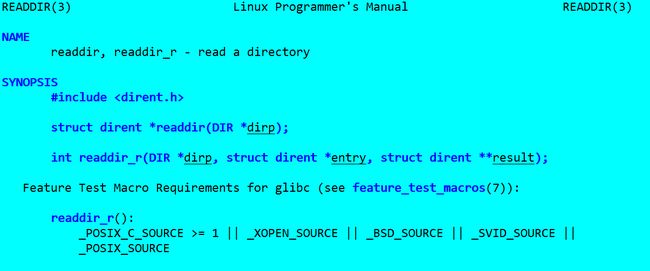
struct dirent结构
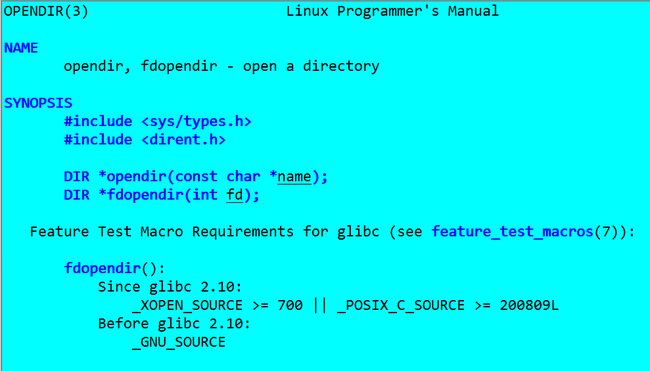
man 3 opendir
有了上面的信息,我们很容易编写自己的ls命令。
(3)如何编写ls
#include
#include
#include
void show_ls(char filename[]);
int main(int argc,char* argv[])
{
if(argc == 1)
show_ls(".");
while(--argc)
{
printf("%s: \n",*++argv);
show_ls(*argv);
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
void show_ls(char filename[])
{
DIR* dir_ptr; //the directory
struct dirent* direntp; //each entry
if((dir_ptr = opendir(filename)) == NULL)
fprintf(stderr,"ls1: cannot open%s \n",filename);
while((direntp = readdir(dir_ptr)) != NULL)
printf("%-10s",direntp->d_name);
closedir(dir_ptr);
} 
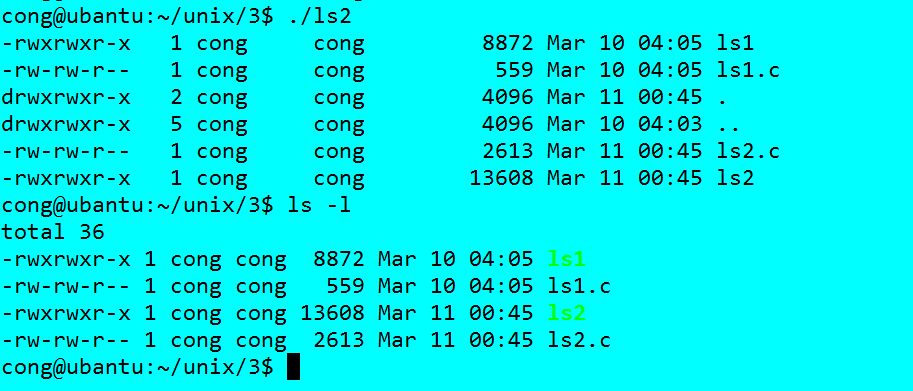
我们已经把当前目录文件的名称打印出来了。(默认打印“.”,"..",这完成可以通过程序过滤,字典序可以通过qsort)
接下来实现ls -l命令
ls -l命令需要文件的当前信息。
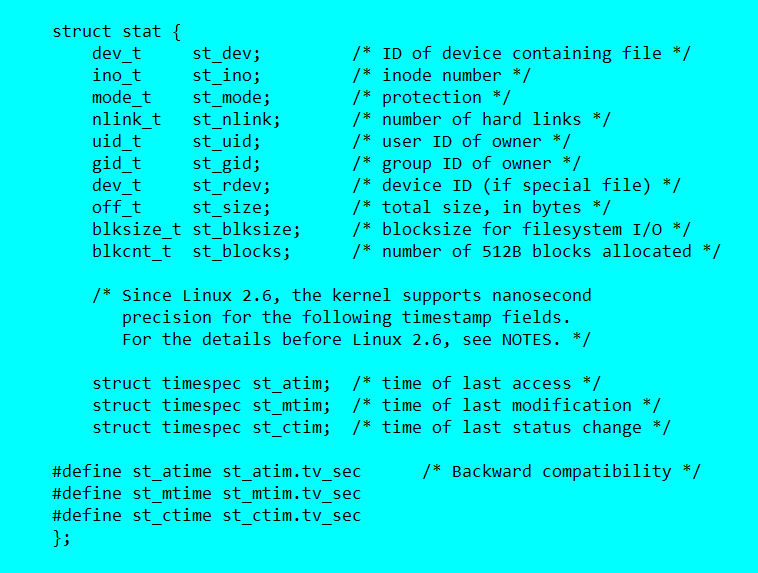
使用stat获得文件信息。
stat结构体
现在我们基本已经获得我们需要所有信息了,但是有些信息需要转换一下。才能跟shell标准下ls -l一致。
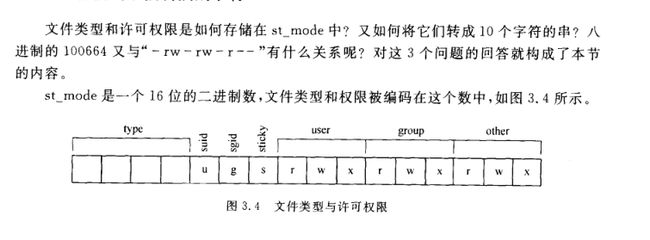
1.将模式串转为字符串。
在stat.h文件下可以看到很多关于模式判断的宏定义。这只是一部分, 可自行查阅。
#define S_IRUSR __S_IREAD /* Read by owner. */
#define S_IWUSR __S_IWRITE /* Write by owner. */
#define S_IXUSR __S_IEXEC /* Execute by owner. */
/* Read, write, and execute by owner. */
#define S_IRWXU (__S_IREAD|__S_IWRITE|__S_IEXEC)
#ifdef __USE_MISC
# define S_IREAD S_IRUSR
# define S_IWRITE S_IWUSR
# define S_IEXEC S_IXUSR
#endif
#define S_IRGRP (S_IRUSR >> 3) /* Read by group. */
#define S_IWGRP (S_IWUSR >> 3) /* Write by group. */
#define S_IXGRP (S_IXUSR >> 3) /* Execute by group. */
/* Read, write, and execute by group. */
#define S_IRWXG (S_IRWXU >> 3)
#define S_IROTH (S_IRGRP >> 3) /* Read by others. */2.用用户ID/组ID转成字符串。
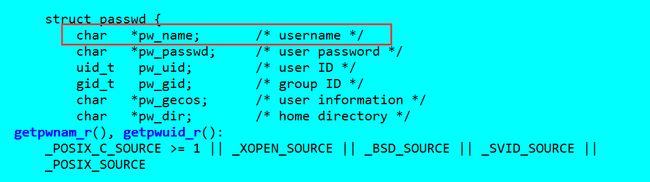
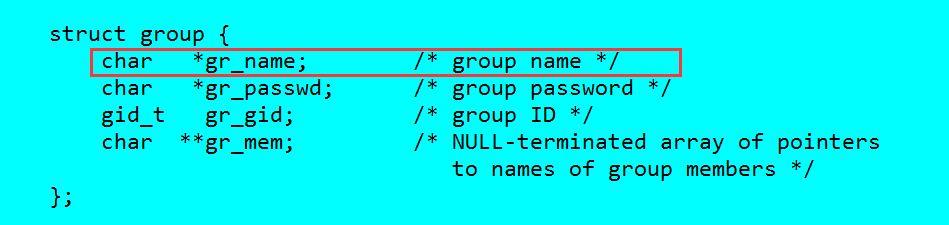
在struct stat中,文件所有者都是以ID形式存在的,然而ls要求输出用户名和组名。
(1)用户名: man 3 getpwuid
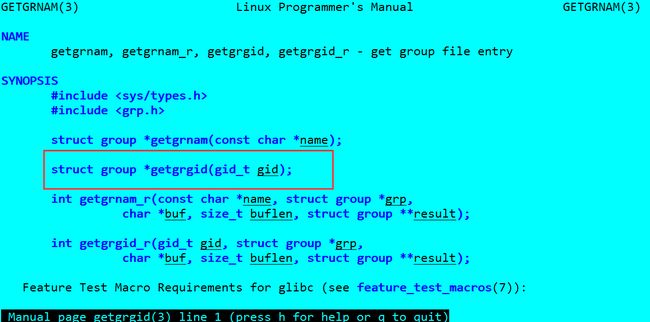
(2)组名: man 3 getgrgid
有了上面的信息之后,编码实现ls - l
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
void do_ls(char []);
void do_stat(char* );
void show_file_info(char* ,struct stat*);
void mode_to_letters(int ,char[]);
char* uid_to_name(uid_t);
char* gid_to_name(gid_t);
int main(int argc,char*argv[])
{
if(argc == 1)
do_ls(".");
else
{
while(--argc)
printf("%s:\n",*++argv);
do_ls(*argv);
}
return 0;
}
void do_ls(char dirname[])
{
/*list files in directory called dirname*/
DIR* dir_ptr;
struct dirent * direntp; /*each entry*/
if((dir_ptr = opendir(dirname)) == NULL)
perror("opendir fails");
while((direntp = readdir(dir_ptr)) !=NULL)
do_stat(direntp->d_name);
closedir(dir_ptr);
}
void do_stat(char* filename)
{
struct stat info;
if((stat(filename,&info)) == -1)
perror(filename);
else
show_file_info(filename,&info);
}
void show_file_info(char* filename,struct stat * info_p)
{
/*display the info about filename . the info is stored in struct at * info_p*/
char modestr[11];
mode_to_letters(info_p->st_mode,modestr);
printf("%s",modestr);
printf("%4d ",(int)info_p->st_nlink);
printf("%-8s ",uid_to_name(info_p->st_uid));
printf("%-8s ",gid_to_name(info_p->st_gid));
printf("%8ld ",(long)info_p->st_size);
printf("%.12s ",ctime(&info_p->st_mtime)+4);
printf("%s\n",filename);
}
void mode_to_letters(int mode,char str[])
{
strcpy(str,"----------");
if(S_ISDIR(mode)) str[0] = 'd'; //"directory ?"
if(S_ISCHR(mode)) str[0] = 'c'; //"char decices"?
if(S_ISBLK(mode)) str[0] = 'b'; //block device?
//3 bits for user
if(mode&S_IRUSR) str[1] = 'r';
if(mode&S_IWUSR) str[2] = 'w';
if(mode&S_IXUSR) str[3] = 'x';
//3 bits for group
if(mode&S_IRGRP) str[4] = 'r';
if(mode&S_IWGRP) str[5] = 'w';
if(mode&S_IXGRP) str[6] = 'x';
//3 bits for other
if(mode&S_IROTH) str[7] = 'r';
if(mode&S_IWOTH) str[8] = 'w';
if(mode&S_IXOTH) str[9] = 'x';
}
char* uid_to_name(uid_t uid)
{
struct passwd* pw_ptr;
static char numstr[10];
if((pw_ptr =getpwuid(uid)) == NULL)
{
sprintf(numstr,"%d",uid);
printf("world");
return numstr;
}
return pw_ptr->pw_name;
}
char* gid_to_name(gid_t gid)
{
/*returns pointer to group number gid, used getgrgid*/
struct group* grp_ptr;
static char numstr[10];
if((grp_ptr =getgrgid(gid)) == NULL)
{
printf("hello wofjl");
sprintf(numstr,"%d",gid);
return numstr;
}
else
return grp_ptr->gr_name;
} /** sol03.18.c
** ------------------------------------------------------------
sol03.18.c is a version
of ls2.c that supports the -R option. This program also
supports the suid, sgid, and sticky bit handling from solution
3.12.
** ------------------------------------------------------------
*
* ls2.c - supports -R option,
* handles suid, sgid, sticky bits, also fixes bug,
*
* purpose list contents of directory or directories
* action if no args, use . else list files in args
* note uses lstat and pwd.h and grp.h
* NOTE uses lstat to avoid chasing symlink loops
*
* build: cc sol03.18.c -o sol03.18
*/
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
void do_ls(char[],int);
void dostat(char *,char *);
void show_file_info( char *, struct stat *);
void mode_to_letters( int , char [] );
char *uid_to_name( uid_t );
char *gid_to_name( gid_t );
main(int ac, char *av[])
{
int R_flag = 0;
int anyfiles = 0;
while ( --ac ){
if ( strcmp("-R", *++av) == 0 )
R_flag = 1;
else {
do_ls( *av , R_flag );
anyfiles = 1;
}
}
if ( !anyfiles )
do_ls(".", R_flag);
}
void do_ls( char dirname[] , int subdirs )
/*
* list files in directory called dirname
* lists subdirs if `subdirs' is true
* First: list contents of dirname, then
* recurse to call each of the subdirs
*/
{
DIR *dir_ptr; /* the directory */
struct dirent *direntp; /* each entry */
char *fullpath;
/*
* get the problem case out of the way up front
*/
if ( ( dir_ptr = opendir( dirname ) ) == NULL ){
fprintf(stderr,"ls2: cannot open %s\n", dirname);
return;
}
/*
* ok, we can read the directory, make two passes through it
*/
printf("%s:\n", dirname);
fullpath = (char *)malloc(strlen(dirname) + 1 + MAXNAMLEN + 1);
/*
* pass 1: list the contents
*/
while ( ( direntp = readdir( dir_ptr ) ) != NULL ){
sprintf(fullpath,"%s/%s",dirname,direntp->d_name);
dostat( fullpath, direntp->d_name );
}
/*
* pass 2: rewind, traverse, and for each subdir, recurse
*/
/*The rewinddir() function resets the position of the directory stream dirp to the
beginning of the directory*/
if ( subdirs ){
rewinddir(dir_ptr);
while ( ( direntp = readdir( dir_ptr ) ) != NULL ){
/* skip . and .. */
if ( strcmp(".",direntp->d_name) == 0 ||
strcmp("..",direntp->d_name) == 0 )
continue;
sprintf(fullpath,"%s/%s",dirname,direntp->d_name);
if ( isadir(fullpath) ){
putchar('\n');
do_ls( fullpath, subdirs );
}
}
}
/* all done with this dir, close up and go */
closedir(dir_ptr);
free(fullpath);
}
void dostat( char *fullpath, char *filename )
{
struct stat info;
if ( lstat(fullpath, &info) == -1 ) /* cannot stat */
perror(filename); /* say why */
else /* else show info */
show_file_info(filename, &info);
}
void show_file_info( char *filename, struct stat *info_p )
/*
* display the info about 'filename'. The info is stored in struct at *info_p
*/
{
char *uid_to_name(), *ctime(), *gid_to_name(), *filemode();
void mode_to_letters();
char modestr[11];
mode_to_letters( info_p->st_mode, modestr );
printf( "%s" , modestr );
printf( "%4d " , (int) info_p->st_nlink);
printf( "%-8s " , uid_to_name(info_p->st_uid) );
printf( "%-8s " , gid_to_name(info_p->st_gid) );
printf( "%8ld " , (long)info_p->st_size);
printf( "%.12s ", 4+ctime(&info_p->st_mtime));
printf( "%s\n" , filename );
}
/*
* utility functions
*/
/*
* This function takes a mode value and a char array
* and puts into the char array the file type and the
* nine letters that correspond to the bits in mode.
* NOTE: It now codes suid, sgid, and sticky bits
* see manual for details.
*/
void mode_to_letters( int mode, char str[] )
{
strcpy( str, "----------" ); /* default=no perms */
if ( S_ISDIR(mode) ) str[0] = 'd'; /* directory? */
if ( S_ISCHR(mode) ) str[0] = 'c'; /* char devices */
if ( S_ISBLK(mode) ) str[0] = 'b'; /* block device */
if ( mode & S_IRUSR ) str[1] = 'r'; /* 3 bits for user */
if ( mode & S_IWUSR ) str[2] = 'w';
if ( (mode & S_ISUID) && (mode & S_IXUSR) )
str[3] = 's';
else if ( (mode & S_ISUID) && !(mode & S_IXUSR) )
str[3] = 'S';
else if ( mode & S_IXUSR )
str[3] = 'x';
if ( mode & S_IRGRP ) str[4] = 'r'; /* 3 bits for group */
if ( mode & S_IWGRP ) str[5] = 'w';
if ( (mode & S_ISGID) && (mode & S_IXGRP) )
str[6] = 's';
else if ( (mode & S_ISGID) && !(mode & S_IXGRP) )
str[6] = 'S';
else if ( mode & S_IXGRP )
str[6] = 'x';
if ( mode & S_IROTH ) str[7] = 'r'; /* 3 bits for other */
if ( mode & S_IWOTH ) str[8] = 'w';
if ( (mode & S_ISVTX) && (mode & S_IXOTH) )
str[9] = 't';
else if ( (mode & S_ISVTX) && !(mode & S_IXOTH) )
str[9] = 'T';
else if ( mode & S_IXOTH )
str[9] = 'x';
}
#include
char *uid_to_name( uid_t uid )
/*
* returns pointer to username associated with uid, uses getpw()
*/
{
struct passwd *getpwuid(), *pw_ptr;
static char numstr[10];
if ( ( pw_ptr = getpwuid( uid ) ) == NULL ){
sprintf(numstr,"%d", uid);
return numstr;
}
else
return pw_ptr->pw_name ;
}
#include
char *gid_to_name( gid_t gid )
/*
* returns pointer to group number gid. used getgrgid(3)
*/
{
struct group *getgrgid(), *grp_ptr;
static char numstr[10];
if ( ( grp_ptr = getgrgid(gid) ) == NULL ){
sprintf(numstr,"%d", gid);
return numstr;
}
else
return grp_ptr->gr_name;
}
/*
* boolean: tells if arg names a directory
*/
isadir(char *str)
{
struct stat info;
return ( lstat(str,&info) != -1 && S_ISDIR(info.st_mode) );
}