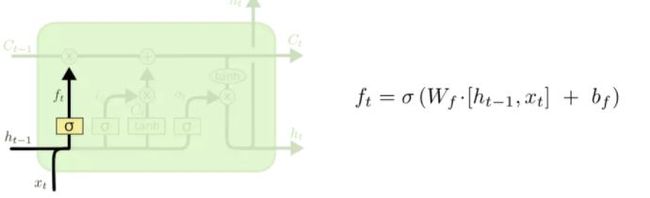Tensorflow与keras学习 (3)——循环神经网络RNN
循环神经网络RNN
3.1 RNN与LSTM介绍:
循环神经网络中的神经单元类似于模拟数字电路技术中的门电路,具有很多控制门来控制输入输出。
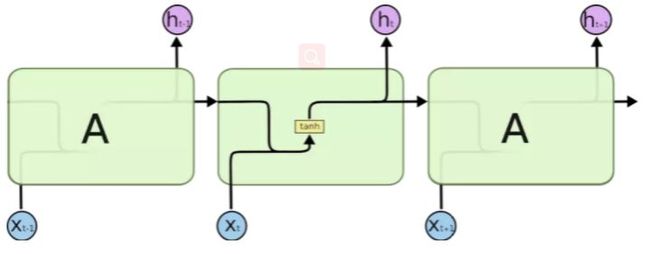
RNN结构:
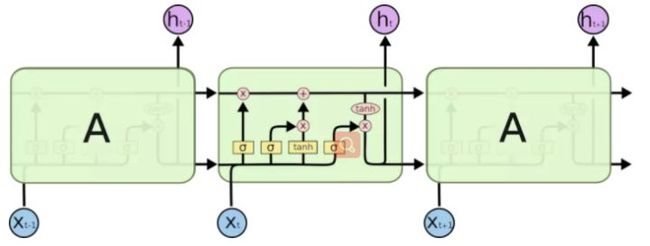
LSTM结构:
相比与传统的神经网络,RNN在上一层输入的基础上加入了一个x(该时刻)的输入,但是并不能解决长时间依赖。LSTM设计加入了忘记门,输入门,输出门,除了此时的输出还有一个该时刻的转态值,并独立传出到下一层。
忘记门:决定是否忘记上一级的状态
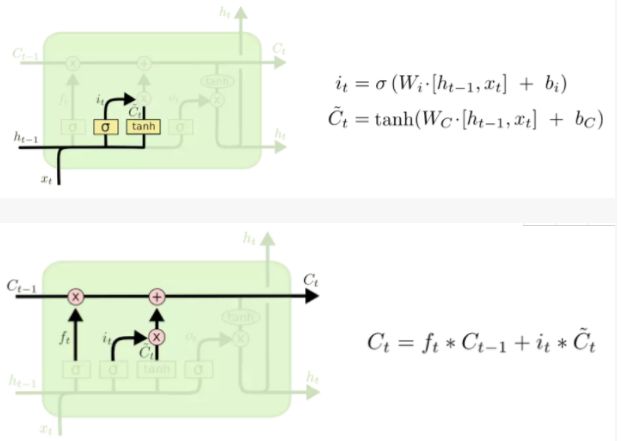
输入门:更新一个状态值
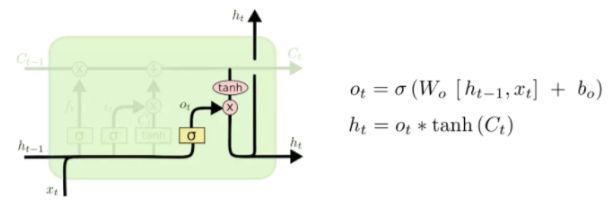
输出门:基于状态值决定当前门的输出
LSTM的变体不再赘述,参考:http://colah.github.io/posts/2015-08-Understanding-LSTMs/
3.2 RNN与LSTM函数接口介绍:
(1)tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell:
__init__(
num_units,
forget_bias=1.0,
state_is_tuple=True,
activation=None,
reuse=None,
name=None
)
num_units:int类型,LSTM 中单元个数(LSTM中包含memory blocks,也就是我们看到的图示的一个小长方形,memory block中有cell和gate,标准LSTM中一个memory block只有一个cell和三个gate,但可以包含多个cell及相应的gate,num_units就是一个memory block包含多少个cell及其相应的gate)
forget_bias:float,0.0或1.0(默认),
state_is_tuple:bool,默认True,即得到(cell,hidden_state)二元组。False的话是把(cell,hidden_state)连接起来,不过要deprecated了
activation:内部状态的激活函数,默认tanh
reuse; name
(2)tf.nn.rnn_cell.LSTMCell:
__init__(
num_units,
use_peepholes=False,
cell_clip=None,
initializer=None,
num_proj=None,
proj_clip=None,
num_unit_shards=None,
num_proj_shards=None,
forget_bias=1.0,
state_is_tuple=True,
activation=None,
reuse=None,
name=None
)
num_units:int, LSTM cell中单元个数
use_peepholes: bool, 如果为True,LSTM内部的cells与gates的连接以掌握精确的输出时机
cell_clip: float, 可选,如果cell state超过这个值,则在cell输出到激活之前被截断
initializer:权重(weights)及映射(projection)矩阵的初始化
num_proj:(可选),int,映射矩阵的输出维度
proj_clip:(可选),float,如果num_proj大于0,并且提供了cell_clip,则映射值截断于[-proj_clip, proj_clip]
num_unit_shards;num_proj_shards: deprecated
forget_bias:默认1.0
(3)tf.nn.rnn_cell.MultiRNNCell:
由多个简单cell顺序组成的RNN
__init__(
cells,
state_is_tuple=True
)
cells:RNN cell的一个列表,由这个顺序组成RNN
state_is_tuple: bool,如果为True(默认),接受并返回一个n-元组的状态,n=len(cells),为False的时候已经deprecated了。
(4)tf.nn.rnn_cell.GRUCell:
num_units: GRU cell中单元个数
activation:非线性函数,默认tanh
reuse
kernel_initializer:(可选),用于权重和映射矩阵的初始化
biase_initializer:(可选),用于偏置项的初始化
name:层的名字,相同的名称共享相同的权重,为避免错误,需要reuse=True
参考文献:Learning Phrase Representations using RNN Encoder-Decoder for Statistical Machine Translation
(5)tf.nn.rnn_cell.DropoutWrapper:
对给定cell的输入输出加上dropout
__init__(
cell,
input_keep_prob=1.0,
output_keep_prob=1.0,
state_keep_prob=1.0,
variational_recurrent=False,
input_size=None,
dtype=None,
seed=None,
dropout_state_filter_visitor=None
)
cell:一个RNNcell
input_keep_prob:0-1之间的float值,如果为1,对输入不添加dropout
output_keep_prob: 0-1之间的float值,如果为1,对输出不添加dropout
state_keep_prob: 0-1之间的float值,如果为1,想要dropout其中的cell,还需要设置dropout_state_filter_visitor(默认的是不会dropout cell的)
variation_recurrent:如果True,相同的dropout模式应用于所有的时间步,如果设置了这个参数,那么input_size也必须设置
input_size:嵌套的tensorshape,只有variation_recurrent为True并且input_keep_prob < 1才能用dtype; seed可选dropout_state_filter_visitor:默认除了cell外可以dropout任何项默认地,dropout应用层与层之间,variation_recurrent设置为True的时候不单可以应用于层层之间,还可用于时间步之间
(6)tf.nn.dynamic_rnn:
dynamic_rnn(
cell,
inputs,
sequence_length=None,
initial_state=None,
dtype=None,
parallel_iterations=None,
swap_memory=False,
time_major=False,
scope=None
)
cell:一个RNNcell
inputs:输入,每一个batch有相同的输入长度大小,不同的batch可以不同的输入大小
sequence_length:列表,一个batch中序列的真实长度
输出为记录lstm每个输出节点的结果,final_states是最后一个cell的结果,例如:output_rnn,final_states=tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(cell, input_rnn,initial_state=init_state, dtype=tf.float32)
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/littlely_ll/article/details/79671393
3.3 RNN预测股票代码示例:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf
#——————————————————导入数据——————————————————————
f=open('stock_dataset.csv')
df=pd.read_csv(f) #读入股票数据
data=np.array(df['最高价']) #获取最高价序列
data=data[::-1] #反转,使数据按照日期先后顺序排列
#以折线图展示data
plt.figure()
plt.plot(data)
plt.show()
normalize_data=(data-np.mean(data))/np.std(data) #标准化
normalize_data=normalize_data[:,np.newaxis] #增加维度
#生成训练集
#设置常量
time_step=20 #时间步
rnn_unit=10 #hidden layer units
batch_size=60 #每一批次训练多少个样例
input_size=1 #输入层维度
output_size=1 #输出层维度
lr=0.0006 #学习率
train_x,train_y=[],[] #训练集
for i in range(len(normalize_data)-time_step-1):
x=normalize_data[i:i+time_step]
y=normalize_data[i+1:i+time_step+1]
train_x.append(x.tolist())
train_y.append(y.tolist())
#——————————————————定义神经网络变量——————————————————
X=tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None,time_step,input_size]) #每批次输入网络的tensor
Y=tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None,time_step,output_size]) #每批次tensor对应的标签
#输入层、输出层权重、偏置
weights={
'in':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([input_size,rnn_unit])),
'out':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([rnn_unit,1]))
}
biases={
'in':tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1,shape=[rnn_unit,])),
'out':tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1,shape=[1,]))
}
#——————————————————定义神经网络变量——————————————————
def lstm(batch): #参数:输入网络批次数目
w_in=weights['in']
b_in=biases['in']
input=tf.reshape(X,[-1,input_size]) #需要将tensor转成2维进行计算,计算后的结果作为隐藏层的输入
input_rnn=tf.matmul(input,w_in)+b_in
input_rnn=tf.reshape(input_rnn,[-1,time_step,rnn_unit]) #将tensor转成3维,作为lstm cell的输入
cell=tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell(rnn_unit)
init_state=cell.zero_state(batch,dtype=tf.float32)
output_rnn,final_states=tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(cell, input_rnn,initial_state=init_state, dtype=tf.float32) #output_rnn是记录lstm每个输出节点的结果,final_states是最后一个cell的结果
output=tf.reshape(output_rnn,[-1,rnn_unit]) #作为输出层的输入
w_out=weights['out']
b_out=biases['out']
pred=tf.matmul(output,w_out)+b_out
return pred,final_states
#——————————————————训练模型——————————————————
def train_lstm():
global batch_size
pred,_=lstm(batch_size)
#损失函数
loss=tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(tf.reshape(pred,[-1])-tf.reshape(Y, [-1])))
train_op=tf.train.AdamOptimizer(lr).minimize(loss)
saver=tf.train.Saver(tf.global_variables())
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
#重复训练10000次
for i in range(10000):
step=0
start=0
end=start+batch_size
while(end更多内容关注微信公众号:ML_Study