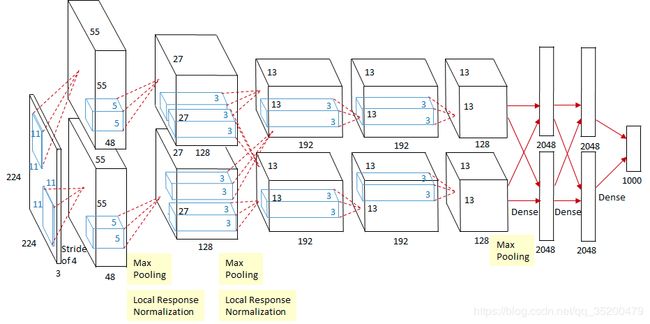
TensorFlow 实现 AlexNet 网络模型
模型特性:
- 所有卷积层都是使用ReLU 作为非线性映射函数,使模型收敛速度更快
- 在多个GPU 上进行模型的训练,不但可以提高模型的训练速度,还能提升数据的使用规模
- 使用 dropout 而不是正则化来处理过度拟合。当然,这也导致了训练时间加长。
- 重叠最大池化(overlapping max pooling) , 即池化范围 z 与步长 s 存在关系 z > s, 避免平均池化的平均效应。
- 使用 LRN 对局部特征进行归一化,增强了模型的泛化能力
AlexNet是由 Alex Krizhevsky 提出的首个应用于图像分类的深层卷积神经网络,该网络在2012年ILSVRC(ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Competition)图像分类竞赛中以15.3%的top-5测试错误率赢得第一名。AlexNet使用GPU代替CPU进行运算,使得在可接受的时间范围内模型结构能够更加复杂,它的出现证明了深层卷积神经网络在复杂模型下的有效性。
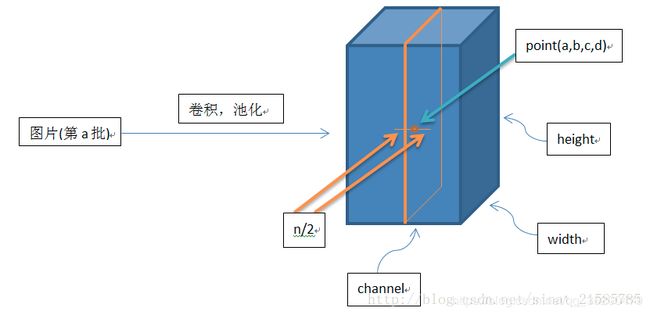
LRN (Local Response Normalization) : 局部特征归一化
公式:
b x , y i = a x , y i / ( k + α ∑ j = max ( 0 , i − n / 2 ) min ( N − 1 , i + n / 2 ) ( a x , y j ) 2 ) β b_{x, y}^{i}=a_{x, y}^{i} /\left(k+\alpha \sum_{j=\max (0, i-n / 2)}^{\min (N-1, i+n / 2)}\left(a_{x, y}^{j}\right)^{2}\right)^{\beta} bx,yi=ax,yi/⎝⎛k+αj=max(0,i−n/2)∑min(N−1,i+n/2)(ax,yj)2⎠⎞β
主要 a x , y i a_{x, y}^{i} ax,yi 为 [a, b, c, d] = [batch_size, height, width, channel] 看图解释。
sqr_sum[a, b, c, d] =
sum(input[a, b, c, d - depth_radius : d + depth_radius + 1] ** 2)
output = input / (bias + alpha * sqr_sum) ** beta
tensorflow :lrn参数解释:
def lrn(input, depth_radius=5, bias=1, alpha=1, beta=0.5, name=None):
r"""Local Response Normalization.
The 4-D `input` tensor is treated as a 3-D array of 1-D vectors (along the last
dimension), and each vector is normalized independently. Within a given vector,
each component is divided by the weighted, squared sum of inputs within
`depth_radius`. In detail,
sqr_sum[a, b, c, d] =
sum(input[a, b, c, d - depth_radius : d + depth_radius + 1] ** 2)
output = input / (bias + alpha * sqr_sum) ** beta
For details, see [Krizhevsky et al., ImageNet classification with deep
convolutional neural networks (NIPS 2012)](http://papers.nips.cc/paper/4824-imagenet-classification-with-deep-convolutional-neural-networks).
Args:
input: A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `half`, `bfloat16`, `float32`.
4-D.
depth_radius: An optional `int`. Defaults to `5`.
0-D. Half-width of the 1-D normalization window.
bias: An optional `float`. Defaults to `1`.
An offset (usually positive to avoid dividing by 0).
alpha: An optional `float`. Defaults to `1`.
A scale factor, usually positive.
beta: An optional `float`. Defaults to `0.5`. An exponent.
name: A name for the operation (optional).
Returns:
A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `input`.
"""
这里解释为什么 输入图片大小建议为 227 × 227 227\times 227 227×227
首先由计算公式
- VALID在 conv2d 的过程中对input以及filter数据不加任何pad不做任何处理:
o u t p u t = i − k s + 1 output = \frac{i - k}{s} + 1 output=si−k+1
- SAME 模式 加入 padding 之后, 输出长度或者宽度 与输入的长度或宽度在 stride 下保持一致:
o u t p u t = i s output = \frac{i}{s} output=si
假设左右两边需要补的总 padding 为 P a P_a Pa 那么:
o u t p u t = i − k + P a s + 1 output = \frac{i-k+P_a}{s} + 1 output=si−k+Pa+1
反过来计算:
P a = ( o u t p u t − 1 ) × s + k − i P_a = (output - 1) \times s + k - i Pa=(output−1)×s+k−i
左边需要补 padding 为 P l = P a 2 P_l = \frac{P_a}{2} Pl=2Pa, 右边需要补padding 为 P r = P a − P l P_r = P_a - P_l Pr=Pa−Pl 即 P r = P a 2 P_r = \frac{P_a}{2} Pr=2Pa
整体公式可为:
o u t p u t = ( i − k + 2 p ) s + 1 output = \frac {(i-k+2p)}{s} + 1 output=s(i−k+2p)+1
AlexNet 的第二层 输出维度为 55 × 55 55 \times 55 55×55
步长stride: s = 4
卷积核 kernel (filter) 大小 : k = 11 × 11 11 \times 11 11×11
假设 输入 为: i = 224 × 224 224 \times 224 224×224
如果是 224 的话,会出现小数,当计算 $ P_r$ 时,
P a = ( o u t p u t − 1 ) × s + k − i = ( 55 − 1 ) × 4 + 11 − 224 = 3 P_a = (output - 1) \times s + k - i = (55 - 1)\times 4 + 11 - 224 = 3 Pa=(output−1)×s+k−i=(55−1)×4+11−224=3
P r = 3 2 = 1.5 ( 向 上 取 整 ) = 2 P_r = \frac{3}{2} = 1.5 (向上取整) = 2 Pr=23=1.5(向上取整)=2
o u t p u t = ( i − k + 2 p ) s + 1 = ( 224 − 11 + 2 ∗ 2 ) 4 + 1 = 55.25 output = \frac{(i-k+2p)}{s} + 1 = \frac{(224 - 11 + 2 * 2)}{4} + 1 = 55.25 output=s(i−k+2p)+1=4(224−11+2∗2)+1=55.25
上式会出现 55.25 出现小数点。不方便处理后续调整
如果是 227 的话
P a = ( 55 − 1 ) × 4 + 11 − 227 = 0 P_a = (55 - 1) \times 4 + 11 - 227 = 0 Pa=(55−1)×4+11−227=0
会刚刚好,选择 ‘VALID’ , 对input以及filter数据不加任何pad不做任何处理。
把 AlexNet 解析成一个 GPU 来处理
使用一个GPU时,把他们串联,把 输入224 替换为 227
| Size / Operation | Filter | Depth | Stride | Padding | Number of Parameters | Forward Computation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3* 227 * 227 | ||||||
| Conv1 + Relu | 11 * 11 | 96 | 4 | (11 * 11 * 3 + 1) * 96=34944 | (11 * 11 * 3 + 1) * 96 * 55 * 55=105705600 | |
| 96 * 55 * 55 | ||||||
| Max Pooling | 3 * 3 | 2 | ||||
| 96 * 27 * 27 | ||||||
| Norm | ||||||
| Conv2 + Relu | 5 * 5 | 256 | 1 | 2 | (5 * 5 * 96 + 1) * 256=614656 | (5 * 5 * 96 + 1) * 256 * 27 * 27=448084224 |
| 256 * 27 * 27 | ||||||
| Max Pooling | 3 * 3 | 2 | ||||
| 256 * 13 * 13 | ||||||
| Norm | ||||||
| Conv3 + Relu | 3 * 3 | 384 | 1 | 1 | (3 * 3 * 256 + 1) * 384=885120 | (3 * 3 * 256 + 1) * 384 * 13 * 13=149585280 |
| 384 * 13 * 13 | ||||||
| Conv4 + Relu | 3 * 3 | 384 | 1 | 1 | (3 * 3 * 384 + 1) * 384=1327488 | (3 * 3 * 384 + 1) * 384 * 13 * 13=224345472 |
| 384 * 13 * 13 | ||||||
| Conv5 + Relu | 3 * 3 | 256 | 1 | 1 | (3 * 3 * 384 + 1) * 256=884992 | (3 * 3 * 384 + 1) * 256 * 13 * 13=149563648 |
| 256 * 13 * 13 | ||||||
| Max Pooling | 3 * 3 | 2 | ||||
| 256 * 6 * 6 | ||||||
| Dropout (rate 0.5) | ||||||
| FC6 + Relu | 256 * 6 * 6 * 4096=37748736 | 256 * 6 * 6 * 4096=37748736 | ||||
| 4096 | ||||||
| Dropout (rate 0.5) | ||||||
| FC7 + Relu | 4096 * 4096=16777216 | 4096 * 4096=16777216 | ||||
| 4096 | ||||||
| FC8 + Relu | 4096 * 1000=4096000 | 4096 * 1000=4096000 | ||||
| 1000 classes | ||||||
| Overall | 62369152=62.3 million | 1135906176=1.1 billion | ||||
| Conv VS FC | Conv:3.7million (6%) , FC: 58.6 million (94% ) | Conv: 1.08 billion (95%) , FC: 58.6 million (5%) |
TensorFlow 代码实现:
先解释Conv , fc 等辅助函数:
- 计算卷积 Conv + ReLU:
# Conv RelU
def conv(x
, filter_height
, filter_width
, num_filters
, stride_y
, stride_x
, name
, padding='SAME', groups=1):
# 输入通道数量
input_channels = int(x.get_shape()[-1])
# 利用 tf.nn.conv2d 卷积计算
convolve = lambda i, k: tf.nn.conv2d(i, k,
strides = [1, stride_y, stride_x, 1],
padding = padding)
with tf.variable_scope(name) as scope:
# 创建 权重和偏差值
weights = tf.get_variable('weights',
shape = [filter_height, filter_width,
input_channels/groups, num_filters])
biases = tf.get_variable('biases', shape=[num_filters])
if groups == 1:
conv = convolve(x, weights)
# 在多个组的情况下,拆分输入和权重
else:
# 拆分输入和权重并分别对其进行卷积
input_groups = tf.split(axis = 3, num_or_size_splits=groups, value=x)
weight_groups = tf.split(axis = 3, num_or_size_splits=groups, value=weights)
output_groups = [convolve(i, k) for i,k in zip(input_groups, weight_groups)]
conv = tf.concat(axis = 3, values = output_groups)
bias = tf.reshape(tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases), conv.get_shape().as_list())
relu = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope.name)
return relu
- 计算 最大池化层
def max_pool(x, filter_height, filter_width, stride_y, stride_x
, name, padding='SAME'):
return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, filter_height, filter_width, 1]
, strides = [1, stride_y, stride_x, 1],
padding = padding, name = name)
- 计算 局部特征归一化 LRN(Local Response Normalization)
def lrn(x, radius, alpha, beta, name, bias=1.0):
return tf.nn.local_response_normalization(x, depth_radius = radius,
alpha = alpha, beta = beta,
bias = bias, name = name)
- 计算 dropout 正则化
def dropout(x, keep_prob):
return tf.nn.dropout(x, keep_prob)
- 计算全连接层 fc + ReLU
def fc(x, num_in, num_out, name, relu=True):
with tf.variable_scope(name) as scope:
weights = tf.get_variable('weights', shape=[num_in, num_out], trainable=True)
biases = tf.get_variable('biases', [num_out], trainable=True)
act = tf.nn.xw_plus_b(x, weights, biases, name=scope.name)
if relu == True:
relu = tf.nn.relu(act)
return relu
else:
return act
- TensorFlow 实现AlexNet 网络,全部代码,github地址: alexnet.py
import tensorflow as tf
def AlexNet(x, keep_prob, num_classes):
# 第一层: Conv (w ReLu) -> Lrn -> Pool
conv1 = conv(x, 11, 11, 96, 4, 4, padding='VALID', name='conv1')
norm1 = lrn(conv1, 2, 2e-05, 0.75, name='norm1')
pool1 = max_pool(norm1, 3, 3, 2, 2, padding='VALID', name='pool1')
# 第二层: Conv (w ReLu) -> Lrn -> Pool with 2 groups
conv2 = conv(pool1, 5, 5, 256, 1, 1, groups=2, name='conv2')
norm2 = lrn(conv2, 2, 2e-05, 0.75, name='norm2')
pool2 = max_pool(norm2, 3, 3, 2, 2, padding='VALID', name='pool2')
# 第三层: Conv (w ReLu)
conv3 = conv(pool2, 3, 3, 384, 1, 1, name='conv3')
# 第四层: Conv (w ReLu)
conv4 = conv(conv3, 3, 3, 384, 1, 1, groups=2, name='conv4')
# 第五层: Conv (w ReLu) -> Pool 拆分两组
conv5 = conv(conv4, 3, 3, 256, 1, 1, groups=2, name='conv5')
pool5 = max_pool(conv5, 3, 3, 2, 2, padding='VALID', name='pool5')
# 第六层: Flatten -> FC (w ReLu) -> Dropout
flattened = tf.reshape(pool5, [-1, 6*6*256])
fc6 = fc(flattened, 6*6*256, 4096, name='fc6')
dropout6 = dropout(fc6, keep_prob)
# 第七层: FC (w ReLu) -> Dropout
fc7 = fc(dropout6, 4096, 4096, name='fc7')
dropout7 = dropout(fc7, keep_prob)
# 第八层全连接层没有 relu激活层: FC
fc8 = fc(dropout7, 4096, num_classes, relu = False, name='fc8')
return fc8
def conv(x, filter_height, filter_width, num_filters, stride_y, stride_x, name,
padding='SAME', groups=1):
# 输入通道数数量
input_channels = int(x.get_shape()[-1])
# 创建权重和偏差值
with tf.variable_scope(name) as scope:
weights = tf.get_variable('weights', shape=[filter_height,
filter_width,
input_channels/groups,
num_filters])
biases = tf.get_variable('biases', shape=[num_filters])
if groups == 1:
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(x, weights,
strides=[1, stride_y, stride_x, 1],
padding=padding)
# 在有多组的情况下,拆分输入权重
else:
# 拆分输入和权重并进行卷积
input_x = tf.split(axis=3, num_or_size_splits=groups, value=x)
weight_w = tf.split(axis=3, num_or_size_splits=groups,
value=weights)
output_groups = []
for i, k in zip(input_x, weight_w):
output_conv2d = tf.nn.conv2d(i, k,
strides=[1, stride_y, stride_x, 1],
padding=padding)
output_groups.append(output_conv2d)
# 创建连接
conv = tf.concat(axis=3, values=output_groups)
# 偏差值
bias = tf.reshape(tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases), tf.shape(conv))
# 激活函数Relu
relu = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope.name)
return relu
# 创建全连接层
def fc(x, num_in, num_out, name, relu=True):
with tf.variable_scope(name) as scope:
# 创建权重和偏差值
weights = tf.get_variable('weights', shape=[num_in, num_out],
trainable=True)
biases = tf.get_variable('biases', [num_out], trainable=True)
# 计算多个输入,权重,偏差值
act = tf.nn.xw_plus_b(x, weights, biases, name=scope.name)
if relu == True:
return tf.nn.relu(act)
else:
return act
# 创建max_pool最大池化层
def max_pool(x, filter_height, filter_width, stride_y, stride_x, name,
padding='SAME'):
return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, filter_height, filter_width, 1],
strides=[1, stride_y, stride_x, 1],
padding=padding, name=name)
# 创建 LRN 层
def lrn(x, radius, alpha, beta, name, bias=1.0):
return tf.nn.local_response_normalization(x, depth_radius=radius,
alpha=alpha, beta=beta,
bias=bias, name=name)
# 创建dropout层
def dropout(x, keep_prob):
return tf.nn.dropout(x, rate=1-keep_prob)
具体训练github 的地址: https://github.com/BillyLearn/paper/tree/master/tensorflow_alexnet
训练: python train.py
图片测试: jupyter notebook 运行 image_validate.ipynb
参考资料:
深度学习500问经典网络 AlexNet模型
论文AlexNet
深度学习局部响应归一化LRN
python - What is the difference between ‘SAME’ and ‘VALID’ padding in tf.nn.max_pool of tensorflow? - Stack Overflow
padding方式SAME和VALID有什么区别
alexnet-with-tensorflow