莫烦PYTHON 模型保存和提取
文章目录
- 已知神经网络net1:
- 保存整个模型并调用
- 保存模型参数并调用
- 可视化三个模型
- 完整代码
已知神经网络net1:
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = torch.unsqueeze(torch.linspace(-1, 1, 100), dim=1) # x data (tensor), shape=(100, 1)
y = x.pow(2) + 0.2*torch.rand(x.size()) # noisy y data (tensor), shape=(100, 1)
net1 = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Linear(1,10),
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.Linear(10,1)
)
print(net1)
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net1.parameters(), lr=0.2)
loss_func = torch.nn.MSELoss() # this is for regression mean squared loss
for t in range(200):
prediction = net1(x) # input x and predict based on x
loss = loss_func(prediction, y) # must be (1. nn output, 2. target)
optimizer.zero_grad() # clear gradients for next train
loss.backward() # backpropagation, compute gradients
optimizer.step() # apply gradients
保存整个模型并调用
先保存整个模型为.pkl,torch.save(net, ‘net.pkl’),
然后加载这个保存的模型net.pkl: torch.load(net.pkl)
torch.save(net1, 'net.pkl') # save entire net
net2 = torch.load('net.pkl')
prediction2 = net2(x)
保存模型参数并调用
先保存模型参数torch.save(net1.state_dict(), ‘net_params.pkl’)
然后重建整个模型结构,与保存模型的结构一致net3
最后将保存的模型参数传入新建的模型中:net3.load_state_dict(torch.load(‘net_params.pkl’))
torch.save(net1.state_dict(), 'net_params.pkl') # save only the parameters
net3 = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Linear(1, 10),
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.Linear(10, 1)
)
# copy net1's parameters into net3
net3.load_state_dict(torch.load('net_params.pkl'))
prediction3 = net3(x)
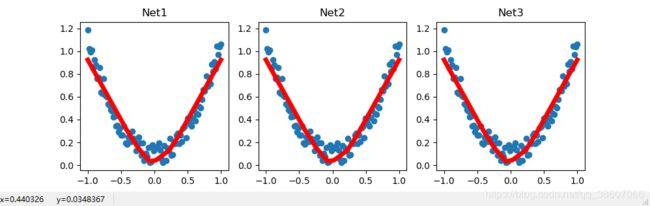
可视化三个模型
# plot net1
plt.figure(1, figsize=(10, 3))
plt.subplot(131)
plt.title('Net1')
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(), y.data.numpy())
plt.plot(x.data.numpy(), prediction.data.numpy(), 'r-', lw=5)
# plot net2
plt.subplot(132)
plt.title('Net2')
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(), y.data.numpy())
plt.plot(x.data.numpy(), prediction2.data.numpy(), 'r-', lw=5)
# plot net3
plt.subplot(133)
plt.title('Net3')
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(), y.data.numpy())
plt.plot(x.data.numpy(), prediction3.data.numpy(), 'r-', lw=5)
plt.show()
完整代码
"""
View more, visit my tutorial page: https://morvanzhou.github.io/tutorials/
My Youtube Channel: https://www.youtube.com/user/MorvanZhou
Dependencies:
torch: 0.4
matplotlib
"""
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# torch.manual_seed(1) # reproducible
x = torch.unsqueeze(torch.linspace(-1, 1, 100), dim=1) # x data (tensor), shape=(100, 1)
y = x.pow(2) + 0.2*torch.rand(x.size()) # noisy y data (tensor), shape=(100, 1)
# print(x.dtype)
# print(type(x))
# print(x.size())
# print(y.dtype)
# print(type(y))
# print(y.size())
# torch can only train on Variable, so convert them to Variable
# The code below is deprecated in Pytorch 0.4. Now, autograd directly supports tensors
# x, y = Variable(x), Variable(y)
# plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(), y.data.numpy())
# plt.show()
net1 = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Linear(1,10),
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.Linear(10,1)
)
print(net1)
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net1.parameters(), lr=0.2)
loss_func = torch.nn.MSELoss() # this is for regression mean squared loss
for t in range(200):
prediction = net1(x) # input x and predict based on x
loss = loss_func(prediction, y) # must be (1. nn output, 2. target)
optimizer.zero_grad() # clear gradients for next train
loss.backward() # backpropagation, compute gradients
optimizer.step() # apply gradients
# 2 ways to save the net
torch.save(net1, 'net.pkl') # save entire net
net2 = torch.load('net.pkl')
prediction2 = net2(x)
torch.save(net1.state_dict(), 'net_params.pkl') # save only the parameters
# restore only the parameters in net1 to net3
net3 = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Linear(1, 10),
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.Linear(10, 1)
)
# copy net1's parameters into net3
net3.load_state_dict(torch.load('net_params.pkl'))
prediction3 = net3(x)
#可视化三个模型
# plot net1
plt.figure(1, figsize=(10, 3))
plt.subplot(131)
plt.title('Net1')
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(), y.data.numpy())
plt.plot(x.data.numpy(), prediction.data.numpy(), 'r-', lw=5)
# plot net2
plt.subplot(132)
plt.title('Net2')
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(), y.data.numpy())
plt.plot(x.data.numpy(), prediction2.data.numpy(), 'r-', lw=5)
# plot net3
plt.subplot(133)
plt.title('Net3')
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(), y.data.numpy())
plt.plot(x.data.numpy(), prediction3.data.numpy(), 'r-', lw=5)
plt.show()