关于字体有两种描述方式,一种是UIFont或者CTFont(在IOS7之后两者可直接进行桥接),另外一个方式使用UIFontDescriptor或CTFontDescriptor(二者可进行桥接)。
Fonts
用字体名称以及字体大小通过调用init(name:size:)来初始化一个UIFont对象。每个字体的属性(Bold,italic)都会被当做一个不同的字体,最终组合成字体族(font families).
你可以通过UIFont的familyNames()类方法来列举相关字体,具体的用法可参考以下的例子
//显示系统中所有的字体名称
UIFont.familyNames().map {
UIFont.fontNamesForFamilyName($0)
}.forEach {
(n:[String]) in n.forEach
{
print($0)
}
系统字体 (System Font)
系统字体就是IOS界面系统预设好的字体集,当一个UILabel对象实例化后,它本身font属性会默认使用系统字体。获取系统字体可通过调用systemFontOfSize:或systemFontOfSize:weight,其中后者中weight是IOS9系统中新加入的参数,表示字体的粗细程度,具体参数如下:
UIFontWeightUltraLightUIFontWeightThinUIFontWeightLightUIFontWeightRegularUIFontWeightMediumUIFontWeightSemiboldUIFontWeightBoldUIFontWeightHeavyUIFontWeightBlack
UIButton中并没有有关font属性,因此你不能直接进行对其中的文字进行字体设置,而应该设置setAttributeTitle属性,该属性是一个属性字符串,在该属性字符串中你可以设置字体类型。
IOS9系统总,系统字体是San Franciso,该系统字体是以.SF开始,在实际应用中不能直接使用改字体.相比系统字体,Apple帮助文档建议优先使用动态字体。
动态字体(Dynamic Type Fonts)
动态字体是自IOS7引入的,它主要有以下两个用途:
- 可自定义字体大小,
在IOS设备上可通过设置->显示与亮度->"字体大小"来进行字体大小的调节 - 可指定特殊的字体样式(如标题样式、页脚样式、子标题栏样式等)
使用动态字体可不需要指定字体的大小,根据实际需要确定字体的样式即可,相关函数为preferredFontForTextStyle:,有关样式的相关参数如下:
-
UIFontTextStyleTitle1,标题1字体样式 -
UIFontTextStyleTitle2,标题2字体样式 -
UIFontTextStyleTitle3,标题3字体样式 -
UIFontTextStyleHeadline,大标题字体样式 -
UIFontTextStyleSubheadline,小标题字体样式 -
UIFontTextStyleCallout,插图字体样式 -
UIFontTextStyleFootnote,脚注字体样式 -
UIFontTextStyleCaption1,说明1字体样式 -
UIFontTextStyleCaption2,说明2字体样式
注意:preferredFontForTextStyle返回的字体大小是按照“字体大小”中设置字体值的进行缩放的。如果用户更改了系统中的字体大小,必须再次调用perferredFontForTextStyle以匹配调整后的字体大小。为了响应系统字体大小改变的事件,必须监听UIContentSizeCategoryDidChaneNotification消息。
override func viewDidLoad()
{
super.viewDidLoad()
// Do any additional setup after loading the view, typically from a nib.
NSNotificationCenter.defaultCenter().addObserver(self, selector: #selector(ViewController.changeFont(_:)), name: UIContentSizeCategoryDidChangeNotification, object: nil)
}
func changeFont(n:NSNotification)
{
let style = self.lb.font.fontDescriptor().objectForKey(UIFontDescriptorNameAttribute) as! String
print(style)
self.lb.font = UIFont.preferredFontForTextStyle(style)
}
自IOS8之后,
UITableViewCell中的label自动监听UIContentSizeCategoryDidChangeNotification消息,根据设置中字体大小而自动调整lable中的字体。
UIFont常用相关属性方法
-
fontWithSize(_:),重新设置基于当前字体的大小并返回该字体 -
preferredFontForTextStyle(_ sytle:String),返回基于特定样式的字体 -
systemFontOfSize(_:),systemFontOfSize:weight,返回标准IOS界面所需的字体 -
boldSystemFontOfSize:,italicSystemFontOfSize:,返回加粗或倾斜的标准界面所需的字体 -
familyName:,类函数,返回系统上所有的字体族 -
fontNamesForFamilyName:,类函数,返回特定的字体族中所有字体的名称 -
labelFontSize:,类函数,返回label中字体的标准尺寸 -
buttonFontSize:,类函数,返回button中字体的标准尺寸 -
systemFontSize:,类函数,返回系统中的字体的标准尺寸 -
fontDescriptor:,返回字体对应的字体描述符
字体描述符(Font Descriptor)
UIFontDescriptor(可与CTFontDescriptor进行桥接)提供了一个使用属性字典来描述字体的机制,可用于新建或修改UIFont对象。对UIFontDescriptor相关属性的修改实质上是针对其内部属性字典的修改。通常用来进行字体间互相转化的一种方法,例如:
let desc2 = desc.fontDescriptorWithSymbolicTraits(.TraitItalic)
上述代码是在字体描述符desc对应的字体进行斜体格式化后生成desc2字体描述符.请注意字体描述符并非字体,而且是不同的概念,但是二者可进行相互转化。一个UIFont对象通过其fontDescriptor获得其对应的字体描述符,而UIFont通过初始化函数init(descriptor:size:)可根据字体描述符获取对应的字体,二者之间的转化可参考如下代码:
let font = UIFont(name: "Helvetica", size: 20)!
let desc = font.fontDescriptor()
let desc2 = desc.fontDescriptorWithSymbolicTraits(.TraitItalic)
let font2 = UIFont(descriptor: desc2, size: 0)
self.lb.font = font2
同样的,字体描述也可以应用于动态字体中,UIFontDescriptor类方法preferredFontDescriptorWithTextStyle:可将动态字体转化为字体描述符。
UIFontDescriptor相关属性与方法
-
创建字体描述方法
-
class func preferredFontDescriptor(withTextStyle: String),基于动态字体来创建字体描述符 init(name: String, size: CGFloat)-
func addingAttributes([String : AnyObject] = [:]),基于现有字体描述符的基础上,增加指定的属性并返回新的字体描述符 -
withFace:,withFamily:,withMatric:,withSize:,withSymbolicTraits:,基于现有字体描述符的基础上,设置对应的属性后并返回新的字体描述符 init(fontAttributes: [String : AnyObject] = [:])
-
-
查找字体
-
func matchingFontDescriptors(withMandatoryKeys: Set,返回系统上所有匹配特定属性的字体?)
-
-
查询属性
-
func fontAttributes(),返回属性字典 -
func object(forKey: String),返回特定Key值得属性,其中有关Key的参数如下:
-
UIFontDescriptorFamilyAttributeUIFontDescriptorNameAttributeUIFontDescriptorFaceAttributeUIFontDescriptorSizeAttributeUIFontDescriptorVisibleNameAttributeUIFontDescriptorMatrixAttributeUIFontDescriptorCharacterSetAttributeUIFontDescriptorCascadeListAttributeUIFontDescriptorTraitsAttributeUIFontDescriptorFixedAdvanceAttributeUIFontDescriptorFeatureSettingsAttribute-
UIFontDescriptorTextStyleAttribute: String-
pointSize、matrix、postscriptName,symbolicTraits
-
添加字体
可通过以下2中方式添加字体:
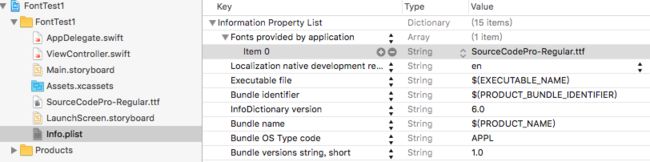
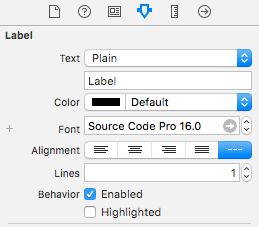
- 从app的文件环境中加载,如果Info.plist中设置了Fonts provided by application,字体在程序运行时会自动加载。
若以上的步骤添加字体成功后,你可在 Attribute Inspector中使用改字体,也可以通过代码来创建该字体。
- 在程序运行时下载所需字体。首先先提供一个字体描述符,然后调用Core Text库中的
CTFontDescriptorMatchFontDescriptorsWithProgressHandler,该方法接受一个回调方法作为参数,
该方法将在下载的每个阶段调用,并且针对该方法的调用都是后台进行的,不会阻塞主进程,具体过程可参见以下代码:
override func viewDidLoad()
{
super.viewDidLoad()
// Do any additional setup after loading the view, typically from a nib.\
let name="NanumBrush"
let size:CGFloat=24
let f:UIFont!=UIFont(name: name, size: size)
if f != nil
{
self.lb.font=f
print("already installed")
return
}
print("attemping to download font")
let desc = UIFontDescriptor(name: name, size: size)
CTFontDescriptorMatchFontDescriptorsWithProgressHandler([desc], nil)
{
(state:CTFontDescriptorMatchingState, prog:CFDictionary) -> Bool in
switch state
{
case .DidBegin:
NSLog("%@", "matching did begin")
case .WillBeginDownloading:
NSLog("%@", "downloading will begin")
case .Downloading:
let d = prog as NSDictionary
let key=kCTFontDescriptorMatchingPercentage
let cur:AnyObject? = d[key as NSString]
if let cur = cur as? NSNumber
{
NSLog("Progress:%@", cur)
}
case .DidFinishDownloading:
NSLog("%@", "Downloading did finish")
case .DidFailWithError:
NSLog("%@", "Download failed")
case .DidFinish:
NSLog("%@","Matching did finish")
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), {
let f = UIFont(name: name, size: size)
//self.lb.font=f
if f != nil
{
self.lb.font=f
NSLog("%@","Got the font!")
}
})
default:
break
}
return true
}
}