在同时使用RAC和Aspects的时候,遇到了一个Crash,栈溢出了。
看了一下,是之前在项目中使用了RAC的rac_singalForSelector
@weakify(self);
[[viewController rac_signalForSelector:@selector(viewDidAppear:)] subscribeNext
:^(id x) {
@strongify(self);
self.shouldIgnorePushingViewControllers = NO;
}];
后来他又使用了Aspects库中的aspect_hookSelector
[UIViewController aspect_hookSelector:@selector(viewDidAppear:) withOptions
:AspectPositionAfter usingBlock:^(id info, BOOL animated) {
NSLog(@"AOP: %@ - %d", [info.instance class], animated);
} error:NULL];
后来就仔细看了一下两者的实现,从接口上来说,RAC的rac_singalForSelector的实例对象方法Aspects的aspect_hookSelector类对象方法。
第一感觉是前者针对是实例对象,后者针对的是类对象。主要涉及的其实还是对象模型里的一些知识,操作了类对象和实例对象中的数据如果对对象模型不太熟悉,可以看一下我之前写的一篇Blog:对象模型
现在来分析下原因,从源码入手,先来大致看RAC相关的源码:
static RACSignal *NSObjectRACSignalForSelector(NSObject *self, SEL selector,
Protocol *protocol) {
//aliasSelector是为了区分原Selector,RAC加了自己的前缀
SEL aliasSelector = RACAliasForSelector(selector);
@synchronized (self) {
//这里是根据aliasSelector获得相应的热信号,这个热信号主要是用于通知业务层的回调
//也就是subscribeNext后面那一段block
RACSubject *subject = objc_getAssociatedObject(self
, aliasSelector);
if (subject != nil) return subject;
//这个地方是基于当前self类创建了一个新类型,有很多hook的逻辑都放在这个类型中
//具体逻辑在RACSwizzleClass函数中再分析
Class class = RACSwizzleClass(self);
NSCAssert(class != nil, @"Could not swizzle class of %@", self);
//创建一个用于通知的热信号
subject = [[RACSubject subject] setNameWithFormat:@"%@
-rac_signalForSelector: %s",
self.rac_description,
sel_getName(selector)];
//通过关联对象的方式存储热信号
objc_setAssociatedObject(self,
aliasSelector,
subject,
OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN);
[self.rac_deallocDisposable addDisposable:
[RACDisposable disposableWithBlock:^{
[subject sendCompleted];
}]];
//targetMethod是"viewDidApear"这个Selector的方法对象
Method targetMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(class, selector);
if (targetMethod == NULL) {
//按照现有逻辑,这里应该是走不到的,先不去看它
const char *typeEncoding;
if (protocol == NULL) {
typeEncoding = RACSignatureForUndefinedSelector(selector);
} else {
// Look for the selector as an optional instance method.
struct objc_method_description methodDescription =
protocol_getMethodDescription(protocol, selector, NO, YES);
if (methodDescription.name == NULL) {
// Then fall back to looking for a required
//instance method.
methodDescription =
protocol_getMethodDescription(protocol
, selector
, YES
, YES);
NSCAssert(methodDescription.name != NULL
, @"Selector %@ does not exist in <%s>"
,NSStringFromSelector(selector)
, protocol_getName(protocol));
}
typeEncoding = methodDescription.types;
}
RACCheckTypeEncoding(typeEncoding);
// Define the selector to call -forwardInvocation:.
if (!class_addMethod(class,
selector,
_objc_msgForward,
typeEncoding)) {
NSDictionary *userInfo = @{
NSLocalizedDescriptionKey:
[NSString stringWithFormat:
NSLocalizedString(
@"A race condition occurred
implementing %@ on class %@"
, nil)
,NSStringFromSelector(selector)
, class],
NSLocalizedRecoverySuggestionErrorKey:
NSLocalizedString(@"Invoke -rac_signalForSelector:
again to override the implementation.", nil)
};
return [RACSignal error:[NSError errorWithDomain:
RACSelectorSignalErrorDomain
code:RACSelectorSignalErrorMethodSwizzlingRace
userInfo:userInfo]];
}
//_objc_msgForward是消息进行转发的开始,这里主要是判断原始的
//方法对象有没有被hook成_objc_msgForward,因为下面要开始进行方法实现的替换了
} else if (method_getImplementation(targetMethod) !=
_objc_msgForward) {
// Make a method alias for the existing
//method implementation.
const char *typeEncoding =
method_getTypeEncoding(targetMethod);
RACCheckTypeEncoding(typeEncoding);
//class_addMethod只是在当前类型对象(不会去基类中查找)中
//去找有没有aliasSelector的方法,如果有就直接返回原来的方法实现
//如果没有就添加一个
BOOL addedAlias __attribute__((unused)) =
class_addMethod(class, aliasSelector,
method_getImplementation(targetMethod),
typeEncoding);
NSCAssert(addedAlias, @"Original implementation
for %@ is already copied to %@ on %@",
NSStringFromSelector(selector),
NSStringFromSelector(aliasSelector), class);
// Redefine the selector to call -forwardInvocation:.
// 这里相当于对原始方法进行方法实现的替换,
//只要调用原始方法,直接会开始方法转发的过程
class_replaceMethod(class
, selector
, _objc_msgForward,
method_getTypeEncoding(targetMethod));
}
return subject;
}
}
通过原始英文注释加上后来的中文注释应该能比较好的理解大致的过程了
分为2部分
1是创建用于通知业务层回调的热信号
2是Hook了当前类,创建了新的子类型,并将这个子类型的原始selector进行了方法实现的替换
既将原始selector实现替换成_objc_msgForward,增加了一个新的selector prefix_selector,
并将其实现为原始selector。另外个人觉得命名上最好是不要叫class了,可以改为subClass或者
swizzleClass,容易跟原始class搞混
接着就是RACSwizzleCalss函数了:
static Class RACSwizzleClass(NSObject *self) {
//self.class和object_getClass返回的都是当前实例的类对象,好像没什么区别???
Class statedClass = self.class;
Class baseClass = object_getClass(self);
// The "known dynamic subclass" is the subclass generated by RAC.
// It's stored as an associated object on every instance that's already
// been swizzled, so that even if something else swizzles the class of
// this instance, we can still access the RAC generated subclass.
//这里官方说明了子类的用途,如果有其他地方swizzle了当前类对象,那也不太影响RAC自己的逻辑
//因为它所有的信息都保存在自己创建的子类中。
Class knownDynamicSubclass =
objc_getAssociatedObject(self, RACSubclassAssociationKey);
if (knownDynamicSubclass != Nil) return knownDynamicSubclass;
NSString *className = NSStringFromClass(baseClass);
if (statedClass != baseClass) {
//这部分逻辑没走到,先不看
@synchronized (swizzledClasses()) {
if (![swizzledClasses() containsObject:className]) {
RACSwizzleForwardInvocation(baseClass);
RACSwizzleRespondsToSelector(baseClass);
RACSwizzleGetClass(baseClass, statedClass);
RACSwizzleGetClass(object_getClass(baseClass),
statedClass);
RACSwizzleMethodSignatureForSelector(baseClass);
[swizzledClasses() addObject:className];
}
}
return baseClass;
}
//加上RAC自己的前缀,给新的子类命名
const char *subclassName = [className stringByAppendingString:
RACSubclassSuffix].UTF8String;
Class subclass = objc_getClass(subclassName);
if (subclass == nil) {
//createClass里面调用的是objc_allocateClassPair函数用于创建新的类型对象,
//它和下面的objc_registerClassPair函数是配对使用的
subclass = [RACObjCRuntime createClass:subclassName
inheritingFromClass:baseClass];
if (subclass == nil) return nil;
//这里是对新的子类的forwardInvocation方法hook
RACSwizzleForwardInvocation(subclass);
//hookRespondsToSelector方法
RACSwizzleRespondsToSelector(subclass);
//hook了Class方法
RACSwizzleGetClass(subclass, statedClass);
//这里object_getClass得到的还是statedClass,既原始的类。
RACSwizzleGetClass(object_getClass(subclass), statedClass);
//hook了方法签名
RACSwizzleMethodSignatureForSelector(subclass);
//结束子类的创建
objc_registerClassPair(subclass);
}
//这里是将当前实例对象的类型信息改写成新的子类
object_setClass(self, subclass);
//保存子类信息
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, RACSubclassAssociationKey, subclass,
OBJC_ASSOCIATION_ASSIGN);
return subclass;
}
RACSwizzleCalss函数里主要干的事情就是创建子类型:
1.给新的子类型命名
2.hook几个重要的消息转发方法,1是为了得到方法调用的入口 2是将子类伪装成原始的类型
3.改变了实例对象的isa指针为新的子类,当前实例对象的类型信息为新的子类信息
这里有必要看一下RACSwizzleGetClass函数的实现:
static void RACSwizzleGetClass(Class class, Class statedClass) {
SEL selector = @selector(class);
Method method = class_getInstanceMethod(class, selector);
IMP newIMP = imp_implementationWithBlock(^(id self) {
//当调用子类的class方法的时候,返回的还是原始类型对象
return statedClass;
});
class_replaceMethod(class
, selector
, newIMP
, method_getTypeEncoding(method));
}
这样一来,使用者感觉不到有什么异样,不知道hook的存在了
最后重点看一下RACSwizzleForwardInvocation函数:
static void RACSwizzleForwardInvocation(Class class) {
SEL forwardInvocationSEL = @selector(forwardInvocation:);
Method forwardInvocationMethod =
class_getInstanceMethod(class
, forwardInvocationSEL);
// Preserve any existing implementation of -forwardInvocation:.
void (*originalForwardInvocation)(id, SEL, NSInvocation *) = NULL;
if (forwardInvocationMethod != NULL) {
originalForwardInvocation =
(__typeof__(originalForwardInvocation))method_getImplementation(
forwardInvocationMethod);
}
// Set up a new version of -forwardInvocation:.
//
// If the selector has been passed to -rac_signalForSelector:, invoke
// the aliased method, and forward the arguments to any attached signals.
//
// If the selector has not been passed to -rac_signalForSelector:,
// invoke any existing implementation of -forwardInvocation:. If there
// was no existing implementation, throw an unrecognized selector
// exception.
id newForwardInvocation = ^(id self, NSInvocation *invocation) {
BOOL matched = RACForwardInvocation(self, invocation);
if (matched) return;
if (originalForwardInvocation == NULL) {
[self doesNotRecognizeSelector:invocation.selector];
} else {
//如果走到这里,基本上也要抛出异常了,一搬hook的都是必有的方法,已经绕过了
//原来的方法查找的过程到了消息转发这一步
originalForwardInvocation(self, forwardInvocationSEL,
invocation);
}
};
class_replaceMethod(class, forwardInvocationSEL,
imp_implementationWithBlock(newForwardInvocation)
, "v@:@");
}
用newForwardInvocation替换了原来的forwardInvocation实现,里面又调用了RACForwardInvocation函数:
static BOOL RACForwardInvocation(id self, NSInvocation *invocation) {
//这里的invocation还是原始的方法调用信息,手动改成了带前缀的selector
SEL aliasSelector = RACAliasForSelector(invocation.selector);
//获取一下之前存储的热信号
RACSubject *subject = objc_getAssociatedObject(self, aliasSelector);
//这里的class得到的是RAC创建的子类,因为之前已经改写了实例对象的ISA指针
Class class = object_getClass(invocation.target);
BOOL respondsToAlias = [class instancesRespondToSelector:aliasSelector];
if (respondsToAlias) {
//去改变selector为hook的新的selector,不然要死循环了
invocation.selector = aliasSelector;
//这一步就是真正原始的方法调用了,还记得之前已经把aliasSelector的实现改为
//原始Selector的实现了吧
[invocation invoke];
}
if (subject == nil) return respondsToAlias;
//通知业务层,要监听的selector已经被调用了,这个发生在原始方法调用之后
[subject sendNext:invocation.rac_argumentsTuple];
return YES;
}
前面几个函数都是为这一步打基础的,到了真正方法调用的时候,原始方法的调用以及通知业务层回调都在这里完成。
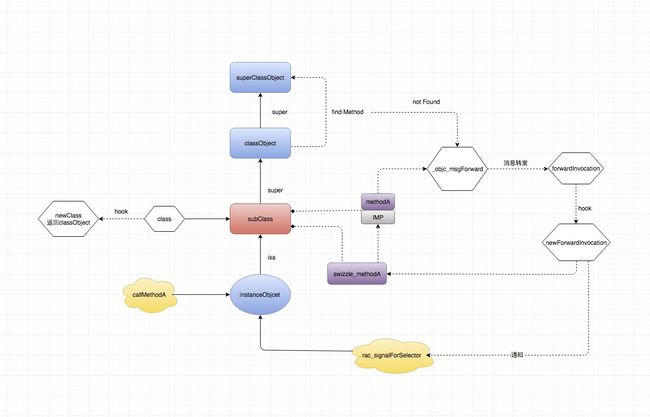
通过以上分析,现在通过一张图总结一下:
现在看一下Aspectsaspect_hookSelector的实现,主要是aspect_prepareClassAndHookSelector函数
static void aspect_prepareClassAndHookSelector(NSObject *self, SEL selector
, NSError **error) {
NSCParameterAssert(selector);
//这里等看aspect_hookClass具体分析其过程,暂时来看是生成了新子类
Class klass = aspect_hookClass(self, error);
//获得原始方法对象
Method targetMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(klass, selector);
IMP targetMethodIMP = method_getImplementation(targetMethod);
if (!aspect_isMsgForwardIMP(targetMethodIMP)) {
// Make a method alias for the existing method implementation,
//it not already copied.
const char *typeEncoding = method_getTypeEncoding(targetMethod);
SEL aliasSelector = aspect_aliasForSelector(selector);
if (![klass instancesRespondToSelector:aliasSelector]) {
//添加alias方法,实现为原方法实现
__unused BOOL addedAlias =
class_addMethod(klass
, aliasSelector
,method_getImplementation(targetMethod)
,typeEncoding);
NSCAssert(addedAlias, @"Original implementation for %@ is already
copied to %@ on %@", NSStringFromSelector(selector),
NSStringFromSelector(aliasSelector), klass);
}
// We use forwardInvocation to hook in.
//这里跟RAC一样的做法,把原方法实现换成了_objc_msgForward
//调原方法会直接开始消息转发的过程
class_replaceMethod(klass
, selector
, aspect_getMsgForwardIMP(self, selector)
,typeEncoding);
AspectLog(@"Aspects: Installed hook for -[%@ %@].", klass,
NSStringFromSelector(selector));
}
}
大致上来看,在方法实现的层面的处理和RAC很类似.实际调试过程中,aspect_hookClass最终只是调用了aspect_swizzleClassInPlace,然后aspect_swizzleClassInPlace其实调用了aspect_swizzleForwardInvocation现在来看一下aspect_swizzleForwardInvocation函数:
static void aspect_swizzleForwardInvocation(Class klass) {
NSCParameterAssert(klass);
// If there is no method, replace will act like class_addMethod.
//将forwardInvocation方法实现替换成了__ASPECTS_ARE_BEING_CALLED__
IMP originalImplementation = class_replaceMethod(klass
,@selector(forwardInvocation:)
,(IMP)__ASPECTS_ARE_BEING_CALLED__
,"v@:@");
if (originalImplementation) {
//alias的forwardInvocation换成了原始实现
class_addMethod(klass,
NSSelectorFromString(AspectsForwardInvocationSelectorName),
originalImplementation, "v@:@");
}
AspectLog(@"Aspects: %@ is now aspect aware.", NSStringFromClass(klass));
}
在消息转发的最后关头,调用ASPECTS_ARE_BEING_CALLED
static void __ASPECTS_ARE_BEING_CALLED__(__unsafe_unretained NSObject *self,
SEL selector,
NSInvocation *invocation) {
NSCParameterAssert(self);
NSCParameterAssert(invocation);
SEL originalSelector = invocation.selector;
//得到相应的aliasSelector
SEL aliasSelector = aspect_aliasForSelector(invocation.selector);
//替换selector,因为invocation中的selector还是原始的selector
//不然递归死循环跟RAC一样
invocation.selector = aliasSelector;
//通过aliasSelector得到hook的用户回调
AspectsContainer *objectContainer = objc_getAssociatedObject(self,
aliasSelector);
AspectsContainer *classContainer = aspect_getContainerForClass(
object_getClass(self),
aliasSelector);
AspectInfo *info = [[AspectInfo alloc] initWithInstance:self
invocation:invocation];
NSArray *aspectsToRemove = nil;
// Before hooks.
//触发那些在原始逻辑调用之前的回调
aspect_invoke(classContainer.beforeAspects, info);
aspect_invoke(objectContainer.beforeAspects, info);
// Instead hooks.
BOOL respondsToAlias = YES;
if (objectContainer.insteadAspects.count ||
classContainer.insteadAspects.count) {
//直接是回调替换原始实现了
aspect_invoke(classContainer.insteadAspects, info);
aspect_invoke(objectContainer.insteadAspects, info);
}else {
Class klass = object_getClass(invocation.target);
do {
if ((respondsToAlias = [klass instancesRespondToSelector:
aliasSelector])) {
//这里是触发原始方法的实现
[invocation invoke];
break;
}
}while (!respondsToAlias && (klass = class_getSuperclass(klass)));
}
// After hooks.
//触发那些在原始方法调用之后的用户回调
aspect_invoke(classContainer.afterAspects, info);
aspect_invoke(objectContainer.afterAspects, info);
// If no hooks are installed, call original implementation (usually
//to throw an exception)
if (!respondsToAlias) {
invocation.selector = originalSelector;
SEL originalForwardInvocationSEL =
NSSelectorFromString(AspectsForwardInvocationSelectorName);
if ([self respondsToSelector:originalForwardInvocationSEL]) {
((void( *)(id, SEL, NSInvocation *))objc_msgSend)(self,
originalForwardInvocationSEL,
invocation);
}else {
[self doesNotRecognizeSelector:invocation.selector];
}
}
// Remove any hooks that are queued for deregistration.
[aspectsToRemove makeObjectsPerformSelector:@selector(remove)];
}
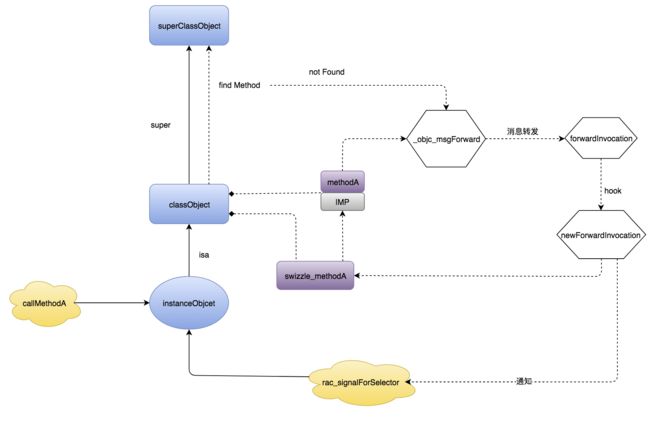
看样子,在这种情况下A并没有想RAC一样创建新的子类型,它是直接更改了原始类型的方法信息。
用图来表示一下它当前的实现:
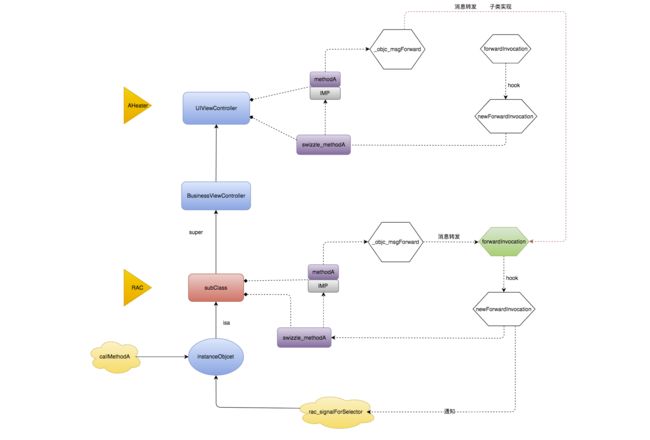
和RAC比要简单一些,那么当同时使用两个库Hook的时候会出现什么情况呢?按照文章开头的场景,RAC相当于Hook了某个继承自UIViewController的子类,并基于该子类创建了新的子类型Aspects相当于直接Hook了UIViewController,对UIViewController本身的方法实现进行了更改替换现在假设继承自UIViewController业务子类型叫做BusinessVieweController
还是用一张简略图来表示两个库Hook之后的场景吧:
在类的继承结构下,Hook之后的结果,Aspects在UIViewController这一层,RAC在subClass这一层当有外界调用A方法时,subClass会最终首先调用原始A方法的实现。如果说在BusisnessViewController类型中定义了A方法的实现,并且在A方法中调用了super的A方法,类似:
- (void)viewDidAppear:(BOOL)animated
{
[super viewDidAppear:animated];
//业务代码
//.....
}
那这个时候会继续调用到UIViewController这一层,这个时候就会开始走UIViewController这一层的Hook流程了,还是一样最终会调用到forwardInvocation这个方法,但是这个时候subClass已经实现了这个方法,所以调用流程会回到子类subClass的Hook流程中,见上图中右上角的红色虚线部分。后面的逻辑就是无限循环,在两个类对象中往返直到栈溢出。
通过上面的分析,如果说在BusinessViewController中没有调用super的方法,那么不会引起死循环的,因为不会触发UIViewController类对象的Hook流程。并且当触发了死循环之后,会发现RAC订阅的业务层的回调和BusinessViewController的A方法中除了Super那一句,剩下的业务代码也没有被执行。另外,RAC这种Hook相对来说会更安全一些(并不是说Aspects就没有Hook Class 的情况,只是当前是这样):它完全子类化了业务类,并且将Hook全都保留在了新建的子类型中,对其他类型包括原始业务类型没有干扰并且这种Hook只针对了某个具体的实例对象,其他势力对象如果没有通过调用rac_singalForSelector并不会受到任何影响。
如果是直接Hook原始类型,那么影响的面将是非常广的,包括所有的实例对象和所有的子类对象。