解决当应用内有多个进程时通讯问题
服务基本上分为两种形式:
启动
当应用组件(如 Activity)通过调用 startService() 启动服务时,服务即处于“启动”状态。一旦启动,服务即可在后台无限期运行,即使启动服务的组件已被销毁也不受影响。 已启动的服务通常是执行单一操作,而且不会将结果返回给调用方。例如,它可能通过网络下载或上传文件。 操作完成后,服务会自行停止运行。
绑定
当应用组件通过调用 bindService() 绑定到服务时,服务即处于“绑定”状态。绑定服务提供了一个客户端-服务器接口,允许组件与服务进行交互、发送请求、获取结果,甚至是利用进程间通信 (IPC) 跨进程执行这些操作。 仅当与另一个应用组件绑定时,绑定服务才会运行。 多个组件可以同时绑定到该服务,但全部取消绑定后,该服务即会被销毁。
所以 进程间通信需要 bindService();
bindService(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags)
service 的intent
ServiceConnection用于 服务端(理解远端的service)和本地(当前进程)的连接
flags 是绑定方式 普遍两种 0 或者 Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE
0 : 绑定service不启动service ,需要手动startService启动service
BIND_AUTO_CREATE : 绑定service后会自动启动service
首先创建一个ServiceConnection,里面两个方法断开和连接的接口
private ServiceConnection mConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName className, IBinder service) {
}
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName className) {
}
};
创建一个服务端service(远端的service)
public class MessengerService extends Service {
static final String TAG = "MessengerService";
/**
* Command to the service to display a message
*/
static final int MSG_SAY_HELLO = 1;
/**
* Handler of incoming messages from clients.
*/
class IncomingHandler extends Handler {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case MSG_SAY_HELLO:
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "hello!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
Log.e(TAG, "IncomingHandler-MSG_SAY_HELLO");
break;
default:
super.handleMessage(msg);
}
}
}
/**
* Target we publish for clients to send messages to IncomingHandler.
*/
final Messenger mMessenger = new Messenger(new IncomingHandler());
/**
* When binding to the service, we return an interface to our messenger
* for sending messages to the service.
*/
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "binding", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
Log.e(TAG, "onBind");
return mMessenger.getBinder();
}
}
xml新起一个进程,
发起通讯
public class ActivityMessenger extends Activity {
static final String TAG = "ActivityMessenger";
/**
* Messenger for communicating with the service.
*/
Messenger mService = null;
/**
* Flag indicating whether we have called bind on the service.
*/
boolean mBound;
/**
* Class for interacting with the main interface of the service.
*/
private ServiceConnection mConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName className, IBinder service) {
// This is called when the connection with the service has been
// established, giving us the object we can use to
// interact with the service. We are communicating with the
// service using a Messenger, so here we get a client-side
// representation of that from the raw IBinder object.
Log.e(TAG, "ServiceConnection-onServiceConnected");
mService = new Messenger(service);
mBound = true;
}
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName className) {
// This is called when the connection with the service has been
// unexpectedly disconnected -- that is, its process crashed.
Log.e(TAG, "ServiceConnection-onServiceDisconnected");
mService = null;
mBound = false;
}
};
public void sayHello() {
if (!mBound) return;
// Create and send a message to the service, using a supported 'what' value
Message msg = Message.obtain(null, MessengerService.MSG_SAY_HELLO, 0, 0);
try {
mService.send(msg);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
((Button) findViewById(R.id.test1)).setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
sayHello();
}
});
}
@Override
protected void onStart() {
super.onStart();
// Bind to the service
Intent intent = new Intent(this, MessengerService.class);
bindService(intent, mConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
@Override
protected void onStop() {
super.onStop();
// Unbind from the service
if (mBound) {
unbindService(mConnection);
mBound = false;
}
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
unbindService(mConnection);
Toast.makeText(ActivityMessenger.this, "Service Un-Binded", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
以上当前进程 就可以和服务端进行通讯了
发送了一条消息MSG_SAY_HELLO ,服务端service弹出hello
现在只是方面发送 而且还无法得到返回消息 .
怎么才能互相通讯呢
需要做一点改变
首先在发送msg时 携带当前service的messenger 并且收到消息后的handle
Handler handler = new Handler(new Handler.Callback() {
@Override
public boolean handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case MSG_REPLY:
Log.e(TAG, "handler-MSG_REPLY");
}
return false;
}
});
public void sayHello() {
Log.e(TAG, "sayHello()");
if (!mBound) return;
Message msg = Message.obtain();
msg.what = MessengerService.MSG_SAY_HELLO;
msg.replyTo = new Messenger(handler);
try {
mService.send(msg);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
服务端需要做的是
根据接收到的message 中的messenger 返回消息
服务端message只有messenger 才知道是哪个service发过来的
messenger理解为信使
class IncomingHandler extends Handler {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case MSG_SAY_HELLO:
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "hello!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
Log.e(TAG, "IncomingHandler-MSG_SAY_HELLO");
if (msg.replyTo == null) return;
Message message = Message.obtain();
message.what = ActivityMessenger.MSG_REPLY;
Messenger messenger = msg.replyTo;
try {
messenger.send(message);
Log.e(TAG, "IncomingHandler-send-MSG_REPLY");
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
break;
default:
super.handleMessage(msg);
}
}
}
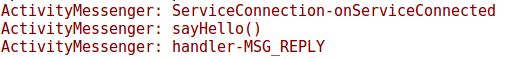
结果 log
两个class 完整code
public class ActivityMessenger extends Activity {
static final String TAG = "ActivityMessenger";
static final int MSG_REPLY = 2;
/**
* Messenger for communicating with the service.
*/
Messenger mService = null;
/**
* Flag indicating whether we have called bind on the service.
*/
boolean mBound;
Handler handler = new Handler(new Handler.Callback() {
@Override
public boolean handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case MSG_REPLY:
Log.e(TAG, "handler-MSG_REPLY");
}
return false;
}
});
;
/**
* Class for interacting with the main interface of the service.
*/
private ServiceConnection mConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName className, IBinder service) {
// This is called when the connection with the service has been
// established, giving us the object we can use to
// interact with the service. We are communicating with the
// service using a Messenger, so here we get a client-side
// representation of that from the raw IBinder object.
Log.e(TAG, "ServiceConnection-onServiceConnected");
mService = new Messenger(service);
mBound = true;
}
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName className) {
// This is called when the connection with the service has been
// unexpectedly disconnected -- that is, its process crashed.
Log.e(TAG, "ServiceConnection-onServiceDisconnected");
mService = null;
mBound = false;
}
};
public void sayHello() {
Log.e(TAG, "sayHello()");
if (!mBound) return;
Message msg = Message.obtain();
msg.what = MessengerService.MSG_SAY_HELLO;
msg.replyTo = new Messenger(handler);
try {
mService.send(msg);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
((Button) findViewById(R.id.test1)).setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
sayHello();
}
});
}
@Override
protected void onStart() {
super.onStart();
// Bind to the service
Intent intent = new Intent(this, MessengerService.class);
bindService(intent, mConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
@Override
protected void onStop() {
super.onStop();
// Unbind from the service
if (mBound) {
unbindService(mConnection);
mBound = false;
}
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
unbindService(mConnection);
Toast.makeText(ActivityMessenger.this, "Service Un-Binded", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
service
public class MessengerService extends Service {
static final String TAG = "MessengerService";
/**
* Command to the service to display a message
*/
static final int MSG_SAY_HELLO = 1;
/**
* Handler of incoming messages from clients.
*/
class IncomingHandler extends Handler {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case MSG_SAY_HELLO:
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "hello!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
Log.e(TAG, "IncomingHandler-MSG_SAY_HELLO");
if (msg.replyTo == null) return;
Message message = Message.obtain();
message.what = ActivityMessenger.MSG_REPLY;
Messenger messenger = msg.replyTo;
try {
messenger.send(message);
Log.e(TAG, "IncomingHandler-send-MSG_REPLY");
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
break;
default:
super.handleMessage(msg);
}
}
}
/**
* Target we publish for clients to send messages to IncomingHandler.
*/
final Messenger mMessenger = new Messenger(new IncomingHandler());
/**
* When binding to the service, we return an interface to our messenger
* for sending messages to the service.
*/
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "binding", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
Log.e(TAG, "onBind");
return mMessenger.getBinder();
}
}
参考 :
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/14746245/use-0-or-bind-auto-create-for-bindservices-flag
https://developer.android.com/guide/components/bound-services.html