File server and client
GENERAL USAGE
—————————————
Start server.java first by typing “java server” in a terminal window.
Start the client.java by typing “java client ‘host-name’ ‘file-name’” in a terminal
window where host-name is the host to use and file-name is the required file.这个是单线程处理,接受连接请求和处理连接是基本的业务逻辑。
多线程和线程池的解决方案
Server:
//*****************************************************************
// server.java
//
// Allows clients to connect and request files. If the file
// exists it sends the file to the client.
//*****************************************************************
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class server
{
private final static int PORT = 12345;
private final static int QUEUE_SIZE = 10;
private final static int BUF_SIZE = 4096;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try {
// Create the server socket
ServerSocket sSocket = new ServerSocket(PORT, QUEUE_SIZE);
// Socket is set up and will wait for connections
while (true) { //不用true会好一些
// Listen for a connection to be made to this socket and accept it
Socket cSocket = sSocket.accept();
byte[] byteArray = new byte[BUF_SIZE];
// Get the name of the file from the client
Scanner scn = new Scanner(cSocket.getInputStream());
String fileName = scn.next();
// Send the contents of the file
BufferedInputStream bis = new
BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(fileName));
OutputStream outStream = cSocket.getOutputStream();
while(bis.available() > 0) {
bis.read(byteArray, 0, byteArray.length);
outStream.write(byteArray, 0, byteArray.length);
}
// Close
bis.close();
cSocket.close();
}
}
catch(EOFException eofe) {
eofe.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
catch(FileNotFoundException fnfe) {
fnfe.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
catch(IllegalArgumentException iae) {
iae.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("Bind failed");
System.exit(1);
}
catch(IOException ioe) {
ioe.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("Could not complete request");
System.exit(1);
}
}
}
Client:
//*****************************************************************
// client.java
//
// Connects to the server and sends a request for a file by
// the file name. Prints the file contents to standard output.
//*****************************************************************
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
public class client
{
private final static int PORT = 12345;
private final static int BUF_SIZE = 4096;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Set up socket using host name and port number
try {
// Get host name and file name from command line arguments
String host = args[0];
String fileName = args[1];
Socket s = new Socket(host, PORT);
byte[] byteArray = new byte[BUF_SIZE];
// Send filename to the server
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(s.getOutputStream(), true);
pw.println (fileName);
// Get the file from the server and print to command line
DataInputStream fromServer = new DataInputStream(s.getInputStream());
while(fromServer.read(byteArray) > 0) {
System.out.println(new String(byteArray, "UTF-8"));
}
fromServer.close();
s.close();
}
catch(IndexOutOfBoundsException iobe) {
System.out.println("Usage: client host-name file-name");
System.exit(1);
}
catch(UnknownHostException unhe) {
unhe.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("Unknown Host, Socket");
System.exit(1);
}
catch(IOException ioe) {
ioe.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
}
}
注意:
Server进入Socket cSocket = sSocket.accept();的时候,判断语句内容其实不是很重要,有的地方写成 if ( !serverSocket.close( )){ 假设我们一定要进入accept(),那含义是一样的。ServerSocket的accept()本身是个当前线程阻塞方法(一个线程在执行过程中暂停,以等待某个条件的触发,或者说是等待所有资源到位),那么,当它只有接受一个客户端的链接时,才会往下执行,在此之前将一直等待,无限原地循环,如果直接关闭ServerSocket,那么会报socket异常,因为:
public Socket accept() throws IOException {
if (isClosed())
throw new SocketException("Socket is closed"); //here
if (!isBound())
throw new SocketException("Socket is not bound yet");
Socket s = new Socket((SocketImpl) null);
implAccept(s);
return s;
}
解决方案,可以创建一个新的socket链接,并且改变flag值:
public void stopThread(){
this.flag = false;
try {
new Socket("localhost",50001);
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
网上看到的另外一个版本:
Server:
package socket;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
public class TcpServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(9091);
try {
Socket client = server.accept();
try {
BufferedReader input =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(client.getInputStream()));
boolean flag = true;
int count = 1;
while (flag) {
System.out.println(客户端要开始说话了,这是第 + count + 次!);
count++;
String line = input.readLine();
System.out.println(客户端说: + line);
if (line.equals(exit)) {
flag = false;
System.out.println(客户端不想玩了!);
} else {
System.out.println(客户端说: + line);
}
}
} finally {
client.close();
}
} finally {
server.close();
}
}
}
Client:
package socket;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TcpClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Socket client = new Socket(127.0.0.1, 9091);
try {
PrintWriter output =
new PrintWriter(client.getOutputStream(), true);
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
String words;
while (cin.hasNext()) {
words = cin.nextLine();
output.println(words);
System.out.println(写出了数据: + words);
}
cin.close();
} finally {
client.close();
}
}
}
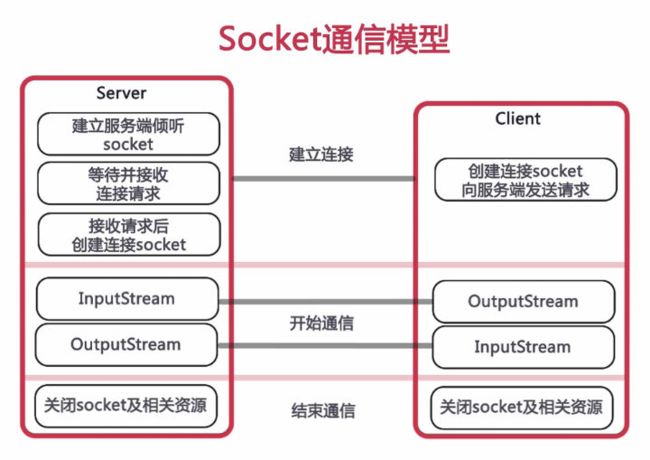
这是一个socket套接字通信的图: