学习资料:
Android群英传Android开发艺术探索- 刘望舒Android View体系系列
- 爱哥AigeStudio自定义控件其实很简单系列
感谢以上各位大神前辈们 :)
除了爱哥的自定义系列博客,再推荐一个非常不错的系列,GcsSloop的自定义系列,可以看完我写的再去看,我写的很基础,适合刚开始学习自定义View的同学来了解基础知识,原理及更深入的知识,可看两位大神的系列 : )
安利,安利,安利
扔物线大神的 HenCoder 自定义VIew系列
整个系列学习,记录的大概过程:
- 准备
- 开始了解Canvas和Paint
- Paint 绘制文字属性
- Paint 关于ColorMatrix学习
- Paint 关于PorterDuffXfermode学习
- Paint 关于Shader的学习
- 补充学习Bitmap
- Canvas 方法 以及属性学习
- Matrix学习
- Drawable补充学习
- 贝塞尔曲线入门学习
- SurfaceView学习
- Camera 图像处理入门学习
- View测量
- ViewGroup知识学习
- 注意事项和继承View知识点学习
- 触摸事件学习
- 滑动学习
- ViewDragHelper学习使用
- PathMeasure学习
- 学习总结
- 画图板练习
是一个长期的学习计划 : )
本篇就是个读书笔记而已
1.Android控件架构
Android中的每个控件都会在界面中占据一个矩形区域。控件大致分为View和ViewGroup。ViewGroup控件作为父类控件可以包含多个View控件。
通过ViewGroup,整个界面控件形成树形结构,也即是控件树。上层控件负责下层控件的测量和绘制,并传递交互事件。在一个Activity中,findViewById()就是在控件树中以树的深度优先遍历来查找对应的元素。
在每棵树的顶部,都有一个ViewParent对象,所有的交互管理事件都有这个ViewParent对象调度和分配
通常情况下,在Activity中使用setContent()方法设置一个布局在调用本方法后,布局内容才会真正显示出来。
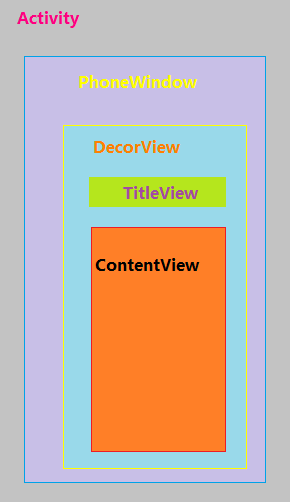
每个Activity都包含有一个Window对象,通常是PhoneWindow。PhoneWindow将一个DecorView设置为整个应用的窗口的根View。DecorView作为窗口界面顶层视图,里面封装了一些窗口操作的通用方法。
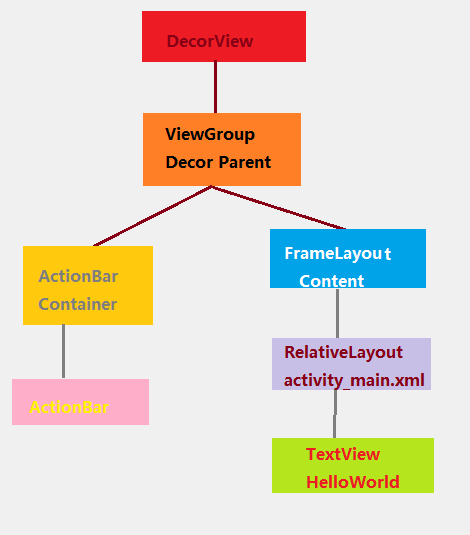
DecorView将内容显示在PhoneWindow上,并通过WindowManagerService来进行接收,并通过Activity对象来回调对应的onClickListener。显示时,将屏幕分成两个部分,TitleView和ContentView。Content是一个id为content的FrameLayout,activity_main.xml就在其中。
通过以上就可以得到下面的标准视图树:
视图树的第二层加载一个LinearLayout作为ViewGroup。这一层布局结构会根据对应的参数设置不同的布局。
最常用的布局,上面显示TitleBar下面是Content。如果用户通过设置requestWindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE)来设置全屏显示,视图树就只有Content。这也是为什么requestWindowFeature()要在setContent()之前生效的原因。
当程序在onCreate()方法中调用了setContentView()方法后,ActivityManagerService会回调onResume()方法,系统会把整个DecorView添加进PhoneWindow中,显示出来后,完成界面的绘制。
2.坐标体系
View的位置只要由它的四个顶点来决定。分别对应于View的四个属性:
-
top,getTop()左上角的纵坐标 -
left,getLeft()左上角的横坐标 -
right,getRight()右下角的横坐标 -
bottom,getBottom()右下角的纵坐标
View的这些坐标都是相对于View的父容器来说。
在Android 3.0 后,
View增加了:x,y,tranlastionX和translationY。x,y是View左上角的坐标,tranlastionX和translationY是View左上角相对于父容器的偏移量。
换算关系:
x = left + translationX
y = top + translationY
需要注意的是,View在平移过程中,top和left表示的原始左上角的位置信息,其值并不会发生改变,此时发生改变的是x,y,tranlastionX和translationY
图颜色配的有点多。 :)
3.View的测量
一个View显示在屏幕上需要经历三个流程:测量,布局,绘制
测量的目的在于告诉系统绘制一个多大的,位置在哪里。这个过程在onMeasure()方法中进行。
测量主要依赖MeasureSppec类。MeasureSpec是一个32位的int值,高2位为测量的模式,低30位为测量的大小。
测量的模式共有三种:
-
EXACTLY精确模式,两种情况
控件的layout_width,layout_height
- 指定数值时,例如
layout_width="100dp" - 指定为
match_parent
-
AT_MOST最大值模式
控件的layout_width,layout_height指定为wrap_content
控件大小一般会随着子空间的或内容的变化而变化,此时要求控件的尺寸只要不超过父类控件允许的最大尺寸即可
-
UNSPECIFIED未指明模式
不指定控件大小,View想多大就多大。
View类默认的onMeasure()方法只支持EXACTLY模式。自定义View时,需要重写onMeasure()方法后,才可以支持其他的模式。假如想要自定义的控件支持wrap_content,就要在onMeasure()中告诉系统自定义控件wrap_content时的大小。
3.1 最基础的实现
用来测试onMeasure()方法。
public class MeasureView extends View {
public MeasureView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
在布局中使用:
运行之后,wrap_content在此时和match_parent效果是一样的。都是沾满全屏。此时在Acitivity中拿到的MeasureView的大小和match_parent是一样的。
3.2 修改onMeasure()方法
重写onMeasure()方法后
public class MeasureView extends View {
public MeasureView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(measureWidth(widthMeasureSpec),measuredHeight(heightMeasureSpec));
}
/**
* 测量宽
* @param widthMeasureSpec
*/
private int measureWidth(int widthMeasureSpec) {
int result ;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
if (specMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY){
result = specSize;
}else {
result = 200;
if (specMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
result = Math.min(result,specSize);
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* 测量高
* @param heightMeasureSpec
*/
private int measuredHeight(int heightMeasureSpec) {
int result ;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
if (specMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY){
result = specSize;
}else{
result = 200;
if(specMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
result = Math.min(result,specSize);
}
}
return result;
}
}
加入了利用MeasureSpec来判断模式。根据不同模式,进行对宽高赋值。在AT_MOST也就是wrap_content时,默认最大的宽高都是200px
3.3 涉及的部分源码
getMode()
/**
* Extracts the mode from the supplied measure specification.
*
* @param measureSpec the measure specification to extract the mode from
* @return {@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#UNSPECIFIED},
* {@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#AT_MOST} or
* {@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#EXACTLY}
*/
@MeasureSpecMode
public static int getMode(int measureSpec) {
//noinspection ResourceType
return (measureSpec & MODE_MASK);
}
由@return可知,返回结果就是MeasureSpec的三种模式
getSize()
/**
* Extracts the size from the supplied measure specification.
*
* @param measureSpec the measure specification to extract the size from
* @return the size in pixels defined in the supplied measure specification
*/
public static int getSize(int measureSpec) {
return (measureSpec & ~MODE_MASK);
}
返回的是在布局文件中声明的值,结果是px
onMeasure()
/**
*
* Measure the view and its content to determine the measured width and the
* measured height. This method is invoked by {@link #measure(int, int)} and
* should be overridden by subclasses to provide accurate and efficient
* measurement of their contents.
*
*
*
* CONTRACT: When overriding this method, you
* must call {@link #setMeasuredDimension(int, int)} to store the
* measured width and height of this view. Failure to do so will trigger an
* IllegalStateException, thrown by
* {@link #measure(int, int)}. Calling the superclass'
* {@link #onMeasure(int, int)} is a valid use.
*
*
*
* The base class implementation of measure defaults to the background size,
* unless a larger size is allowed by the MeasureSpec. Subclasses should
* override {@link #onMeasure(int, int)} to provide better measurements of
* their content.
*
*
*
* If this method is overridden, it is the subclass's responsibility to make
* sure the measured height and width are at least the view's minimum height
* and width ({@link #getSuggestedMinimumHeight()} and
* {@link #getSuggestedMinimumWidth()}).
*
*
* @param widthMeasureSpec horizontal space requirements as imposed by the parent.
* The requirements are encoded with
* {@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec}.
* @param heightMeasureSpec vertical space requirements as imposed by the parent.
* The requirements are encoded with
* {@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec}.
*
* @see #getMeasuredWidth()
* @see #getMeasuredHeight()
* @see #setMeasuredDimension(int, int)
* @see #getSuggestedMinimumHeight()
* @see #getSuggestedMinimumWidth()
* @see android.view.View.MeasureSpec#getMode(int)
* @see android.view.View.MeasureSpec#getSize(int)
*/
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}
在View的onMeasure()方法源码中,调用了setMeasuredDimension()方法来确定View的宽和高
View的源码23000行。 : )
4.最后
写的都比较表面,目前深入不了,基本就是看Android 群英传第三章的读写笔记。也不晓得能不能对学习自定义View有些帮助。后面学习,遇到一些知识点也会再补充。
下一篇学习了解一下Canvas和Paint都是干嘛的。