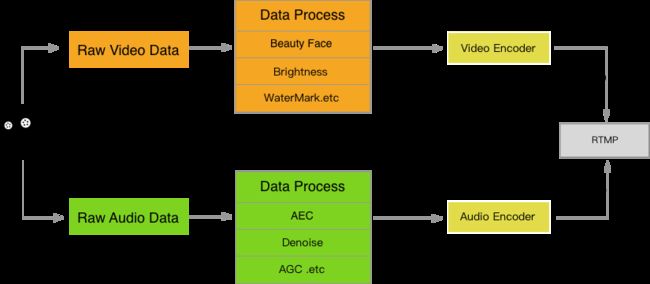
学习过音视频的都知道,不常用的话就会容易忘记。因此,记下以前学些的点滴。(这不是入门贴)
主要分为以下主题做学习记录:
- 视频采集与编码
- 音频采集与编码
视频采集与编码
视频采集
- 获取输入设备
NSError *deviceError;
AVCaptureDeviceInput *inputDevice;
for (AVCaptureDevice *device in [AVCaptureDevice devicesWithMediaType:AVMediaTypeVideo])
{
if ([device position] == AVCaptureDevicePositionFront)
{
inputDevice = [AVCaptureDeviceInput deviceInputWithDevice:device error:&deviceError];
}
}
- 输出设备
AVCaptureVideoDataOutput *outputDevice = [[AVCaptureVideoDataOutput alloc]init];
NSString *key = (NSString *)kCVPixelBufferPixelFormatTypeKey;
NSNumber *val = [NSNumber numberWithUnsignedInt:kCVPixelFormatType_420YpCbCr8BiPlanarFullRange];
NSDictionary *videoSettings = [NSDictionary dictionaryWithObject:val forKey:key];
outputDevice.videoSettings = videoSettings;
[outputDevice setSampleBufferDelegate:self queue:dispatch_get_main_queue()];
- 启动相机
AVCaptureSession *captureSession = [[AVCaptureSession alloc]init];
[captureSession addInput:inputDevice];
[captureSession addOutput:outputDevice];
[captureSession beginConfiguration];
captureSession.sessionPreset = AVCaptureSessionPreset640x480;
[outputDevice connectionWithMediaType:AVMediaTypeVideo];
[captureSession commitConfiguration];
AVCaptureVideoPreviewLayer *previewLayer = [[AVCaptureVideoPreviewLayer alloc]initWithSession:captureSession];
previewLayer.videoGravity = AVLayerVideoGravityResizeAspectFill;
[self.view.layer addSublayer:previewLayer];
previewLayer.frame = self.view.bounds;
[captureSession startRunning];
- 获取输出的CMSampleBufferRef
-(void) captureOutput:(AVCaptureOutput*)captureOutput
didOutputSampleBuffer:(CMSampleBufferRef)sampleBuffer
fromConnection:(AVCaptureConnection*)connection
{
CVImageBufferRef imageBuffer = (CVImageBufferRef)CMSampleBufferGetImageBuffer(sampleBuffer);
//TODO : Send to server
}
基于现在是颜值的社会,美颜什么的功能必须要有。因此需要在视频录制的时候直接做处理 。GPUImage是不二之选。下面的Demo code 创建了一个摄像机,并把美化后的图像显示在屏幕上。
//Camera configuration
GPUImageVideoCamera *videoCamera = [[GPUImageVideoCamera alloc] initWithSessionPreset:AVCaptureSessionPreset640x480 cameraPosition:AVCaptureDevicePositionBack];
videoCamera.outputImageOrientation = UIInterfaceOrientationPortrait;
videoCamera.frameRate = 24;
//Filter
GPUImageFilter *brightnessFilter = [[GPUImageBrightnessFilter alloc] init];
GPUImageWhiteBalanceFilter *whiteBalanceFilter = [[GPUImageWhiteBalanceFilter alloc] init];
GPUImageOutput *output = [[GPUImageFilter alloc] init];
//Display
GPUImageView *filteredVideoView = [[GPUImageView alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(0.0, 0.0, viewWidth, viewHeight)];
//Targets
[videoCamera addTarget: brightnessFilter];
[brightnessFilter addTarget: whiteBalanceFilter];
[whiteBalanceFilter addTarget: output];
[whiteBalanceFilter addTarget:filteredVideoView];
//Get the render output
[output setFrameProcessingCompletionBlock:^(GPUImageOutput *output, CMTime time) {
GPUImageFramebuffer *imageFramebuffer = output.framebufferForOutput;
CVPixelBufferRef pixelBuffer = [imageFramebuffer pixelBuffer];
//TODO : Send to server
}];
[videoCamera startCameraCapture];
在GPUImage 里面,Filter是非常重要的。理解它也很简单。首先是原图输入,然后是一系列的filter处理(duang ~~~加各种特效)。最后就是输出。
从上面的demo code可以看到,使用系统库拿到的是CVImageBufferRef ,GPUImage 拿到的是CVPixelBufferRef ,其实它们是同个东西。
typedef CVImageBufferRef CVPixelBufferRef;
视频数据有了,接下来就是编码了。
视频编码
视频编码有硬编码和软编码。
- 区别:
软编码:使用CPU进行编码
硬编码:使用非CPU进行编码,如显卡GPU、专用的DSP、FPGA、ASIC芯片等
- 比较
软编码:实现直接、简单,参数调整方便,升级易,但CPU负载重,性能较硬编码低,低码率下质量通常比硬编码要好一点。
硬编码:性能高,低码率下通常质量低于软编码器,但部分产品在GPU硬件平台移植了优秀的软编码算法(如X264)的,质量基本等同于软编码。
下面主要讲iOS 的硬编码。配置编码器,不熟悉的请自行google。
VTCompressionSessionRef compressionSession = NULL;
OSStatus status = VTCompressionSessionCreate(NULL,width,height, kCMVideoCodecType_H264, NULL, NULL, NULL, VideoCompressonOutputCallback, (__bridge void *)self, &compressionSession);
CGFloat videoBitRate = 800*1024;
CGFloat videoFrameRate = 24;
CGFloat videoMaxKeyframeInterval = 48;
VTSessionSetProperty(compressionSession, kVTCompressionPropertyKey_MaxKeyFrameInterval, (__bridge CFTypeRef)@(videoMaxKeyframeInterval));
VTSessionSetProperty(compressionSession, kVTCompressionPropertyKey_MaxKeyFrameIntervalDuration, (__bridge CFTypeRef)@(videoMaxKeyframeInterval/videoFrameRate));
VTSessionSetProperty(compressionSession, kVTCompressionPropertyKey_ExpectedFrameRate, (__bridge CFTypeRef)@(videoFrameRate));
VTSessionSetProperty(compressionSession, kVTCompressionPropertyKey_AverageBitRate, (__bridge CFTypeRef)@(videoBitRate));
NSArray *limit = @[@(videoBitRate * 1.5/8), @(1)];
VTSessionSetProperty(compressionSession, kVTCompressionPropertyKey_DataRateLimits, (__bridge CFArrayRef)limit);
VTSessionSetProperty(compressionSession, kVTCompressionPropertyKey_RealTime, kCFBooleanTrue);
VTSessionSetProperty(compressionSession, kVTCompressionPropertyKey_ProfileLevel, kVTProfileLevel_H264_Main_AutoLevel);
VTSessionSetProperty(compressionSession, kVTCompressionPropertyKey_AllowFrameReordering, kCFBooleanTrue);
VTSessionSetProperty(compressionSession, kVTCompressionPropertyKey_H264EntropyMode, kVTH264EntropyMode_CABAC);
VTCompressionSessionPrepareToEncodeFrames(compressionSession);
有几个概念比较重要:
- 码率
简单来说就是指在压缩视频的时候给这个视频指定一个参数,用以告诉压缩软件期望的压缩后视频的大小。码率的英文名为bps(bit per second),就是用平均每秒多少bit来衡量一个视频大小。更多请点击查看 - 帧率
用于测量显示帧数的量度。所谓的测量单位为每秒显示帧数(Frames per Second,简称:FPS)或“赫兹”(Hz)
代码中配置的码率是800 * 1024 bit/s ,帧率是24。还有一个叫最大关键帧间隔,可设置为帧率的两倍。
VideoCompressonOutputCallback 是硬编码后的回调,
static void VideoCompressonOutputCallback(void *VTref, void *VTFrameRef, OSStatus status, VTEncodeInfoFlags infoFlags, CMSampleBufferRef sampleBuffer){
if (!sampleBuffer) return;
CFArrayRef array = CMSampleBufferGetSampleAttachmentsArray(sampleBuffer, true);
if (!array) return;
CFDictionaryRef dic = (CFDictionaryRef)CFArrayGetValueAtIndex(array, 0);
if (!dic) return;
BOOL keyframe = !CFDictionaryContainsKey(dic, kCMSampleAttachmentKey_NotSync);
uint64_t timeStamp = [((__bridge_transfer NSNumber *)VTFrameRef) longLongValue];
HardwareVideoEncoder *videoEncoder = (__bridge HardwareVideoEncoder *)VTref;
if (status != noErr) {
return;
}
if (keyframe && !videoEncoder->sps) {
CMFormatDescriptionRef format = CMSampleBufferGetFormatDescription(sampleBuffer);
size_t sparameterSetSize, sparameterSetCount;
const uint8_t *sparameterSet;
OSStatus statusCode = CMVideoFormatDescriptionGetH264ParameterSetAtIndex(format, 0, &sparameterSet, &sparameterSetSize, &sparameterSetCount, 0);
if (statusCode == noErr) {
size_t pparameterSetSize, pparameterSetCount;
const uint8_t *pparameterSet;
OSStatus statusCode = CMVideoFormatDescriptionGetH264ParameterSetAtIndex(format, 1, &pparameterSet, &pparameterSetSize, &pparameterSetCount, 0);
if (statusCode == noErr) {
videoEncoder->sps = [NSData dataWithBytes:sparameterSet length:sparameterSetSize];
videoEncoder->pps = [NSData dataWithBytes:pparameterSet length:pparameterSetSize];
}
}
}
CMBlockBufferRef dataBuffer = CMSampleBufferGetDataBuffer(sampleBuffer);
size_t length, totalLength;
char *dataPointer;
OSStatus statusCodeRet = CMBlockBufferGetDataPointer(dataBuffer, 0, &length, &totalLength, &dataPointer);
if (statusCodeRet == noErr) {
size_t bufferOffset = 0;
static const int AVCCHeaderLength = 4;
while (bufferOffset < totalLength - AVCCHeaderLength) {
uint32_t NALUnitLength = 0;
memcpy(&NALUnitLength, dataPointer + bufferOffset, AVCCHeaderLength);
NALUnitLength = CFSwapInt32BigToHost(NALUnitLength);
VideoFrame *videoFrame = [VideoFrame new];
videoFrame.timestamp = timeStamp;
videoFrame.data = [[NSData alloc] initWithBytes:(dataPointer + bufferOffset + AVCCHeaderLength) length:NALUnitLength];
videoFrame.isKeyFrame = keyframe;
videoFrame.sps = videoEncoder->sps;
videoFrame.pps = videoEncoder->pps;
if (videoEncoder.h264Delegate && [videoEncoder.h264Delegate respondsToSelector:@selector(videoEncoder:videoFrame:)]) {
[videoEncoder.h264Delegate videoEncoder:videoEncoder videoFrame:videoFrame];
}
bufferOffset += AVCCHeaderLength + NALUnitLength;
}
}
}
程序调用:encodeVideoData:timeStamp 进行硬编码,数据处理完之后会从VideoCompressonOutputCallback输出。
- (void)encodeVideoData:(CVPixelBufferRef)pixelBuffer timeStamp:(uint64_t)timeStamp {
if(_isBackGround) return;
frameCount++;
CMTime presentationTimeStamp = CMTimeMake(frameCount, (int32_t)videoFrameRate);
VTEncodeInfoFlags flags;
CMTime duration = CMTimeMake(1, (int32_t)videoFrameRate);
NSDictionary *properties = nil;
if (frameCount % (int32_t)_configuration.videoMaxKeyframeInterval == 0) {
properties = @{(__bridge NSString *)kVTEncodeFrameOptionKey_ForceKeyFrame: @YES};
}
NSNumber *timeNumber = @(timeStamp);
OSStatus status = VTCompressionSessionEncodeFrame(compressionSession, pixelBuffer, presentationTimeStamp, duration, (__bridge CFDictionaryRef)properties, (__bridge_retained void *)timeNumber, &flags);
if(status != noErr){
[self resetCompressionSession];
}
}
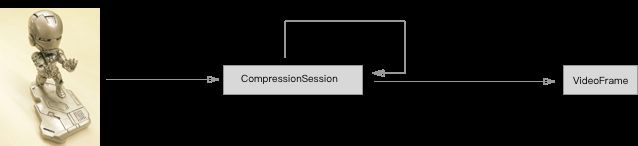
整个过程如下图 ,从摄像机拿到的视频数据,使用CompressionSession进行硬编码,最后输出准备用于传输的videoFrame。
在硬编码这个过程中,有一点需要注意的。当手机遇到电量较低、充电时,必然会导致手机电池严重发热发烫;此种情况下iPhone手机的h264硬编码性能有相当大概率的性能衰减,编码输出帧率严重下降;
手机H264编码器编码统计得到的实际输出帧率低于预期帧率,如摄像头采集帧率30fps、H264硬编码预期帧率20fps、实际输出帧率小于15fps;手机发热后性能H264硬编码器性能下降,二输入帧率30fps加剧编码器的能耗压力;
解决:采取主动平滑丢帧的策略,将输入帧率降低到编码器实际输出帧率以上,如实际输出帧率15fps,输入帧率调整成18fps,以降低编码器压力;待编码器实际编码输出帧率逐渐升高到18fps后,再提高输入帧率使编码实际输出帧率符合设计预期。
音频采集与编码
音频采集
- 获得输入设备
AudioComponentDescription acd;
acd.componentType = kAudioUnitType_Output;
acd.componentSubType = kAudioUnitSubType_RemoteIO;
acd.componentManufacturer = kAudioUnitManufacturer_Apple;
acd.componentFlags = 0;
acd.componentFlagsMask = 0;
AudioComponent *component = AudioComponentFindNext(NULL, &acd);
- 创建AudioUnit
AudioComponentInstance componetInstance;
OSStatus status = noErr;
status = AudioComponentInstanceNew(self.component, &_componetInstance);
if (noErr != status) {
[self handleAudioInitializeError];
}
UInt32 flagOne = 1;
AudioUnitSetProperty(self.componetInstance, kAudioOutputUnitProperty_EnableIO, kAudioUnitScope_Input, 1, &flagOne, sizeof(flagOne));
AudioStreamBasicDescription desc = {0};
desc.mSampleRate = 44100;
desc.mFormatID = kAudioFormatLinearPCM;
desc.mFormatFlags = kAudioFormatFlagIsSignedInteger | kAudioFormatFlagsNativeEndian | kAudioFormatFlagIsPacked;
desc.mChannelsPerFrame = 2;
desc.mFramesPerPacket = 1;
desc.mBitsPerChannel = 16;
desc.mBytesPerFrame = desc.mBitsPerChannel / 8 * desc.mChannelsPerFrame;
desc.mBytesPerPacket = desc.mBytesPerFrame * desc.mFramesPerPacket;
AURenderCallbackStruct cb;
cb.inputProcRefCon = (__bridge void *)(self);
cb.inputProc = InputBufferCallback;
AudioUnitSetProperty(componetInstance, kAudioUnitProperty_StreamFormat, kAudioUnitScope_Output, 1, &desc, sizeof(desc));
AudioUnitSetProperty(componetInstance, kAudioOutputUnitProperty_SetInputCallback, kAudioUnitScope_Global, 1, &cb, sizeof(cb));
status = AudioUnitInitialize(componetInstance);
if (noErr != status) {
[self handleAudioInitializeError];
}
获取音频数据,其中handleInputBuffer为AudioUnit的输入回调。
static OSStatus handleInputBuffer(void *inRefCon,
AudioUnitRenderActionFlags *ioActionFlags,
const AudioTimeStamp *inTimeStamp,
UInt32 inBusNumber,
UInt32 inNumberFrames,
AudioBufferList *ioData) {
@autoreleasepool {
AudioCapture *source = (__bridge AudioCapture *)inRefCon;
if (!source) return -1;
AudioBuffer buffer;
buffer.mData = NULL;
buffer.mDataByteSize = 0;
buffer.mNumberChannels = 1;
AudioBufferList buffers;
buffers.mNumberBuffers = 1;
buffers.mBuffers[0] = buffer;
OSStatus status = AudioUnitRender(source.componetInstance,
ioActionFlags,
inTimeStamp,
inBusNumber,
inNumberFrames,
&buffers);
if (source.muted) {
for (int i = 0; i < buffers.mNumberBuffers; i++) {
AudioBuffer ab = buffers.mBuffers[i];
memset(ab.mData, 0, ab.mDataByteSize);
}
}
if (!status) {
if (source.delegate && [source.delegate respondsToSelector:@selector(captureOutput:audioData:)]) {
[source.delegate captureOutput:source audioData:[NSData dataWithBytes:buffers.mBuffers[0].mData length:buffers.mBuffers[0].mDataByteSize]];
}
}
return status;
}
}
至于音频的处理,主要是用到WebRTC,后面会有专门讲WebRTC 的文件,介绍如何消除回音等。
音频编码
- 创建编码器
AudioConverterRef m_converter;
AudioStreamBasicDescription inputFormat = {0};
inputFormat.mSampleRate = 44100;
inputFormat.mFormatID = kAudioFormatLinearPCM;
inputFormat.mFormatFlags = kAudioFormatFlagIsSignedInteger | kAudioFormatFlagsNativeEndian | kAudioFormatFlagIsPacked;
inputFormat.mChannelsPerFrame = (UInt32)2;
inputFormat.mFramesPerPacket = 1;
inputFormat.mBitsPerChannel = 16;
inputFormat.mBytesPerFrame = inputFormat.mBitsPerChannel / 8 * inputFormat.mChannelsPerFrame;
inputFormat.mBytesPerPacket = inputFormat.mBytesPerFrame * inputFormat.mFramesPerPacket;
AudioStreamBasicDescription outputFormat; // 这里开始是输出音频格式
memset(&outputFormat, 0, sizeof(outputFormat));
outputFormat.mSampleRate =44100; // 采样率保持一致
outputFormat.mFormatID = kAudioFormatMPEG4AAC; // AAC编码 kAudioFormatMPEG4AAC kAudioFormatMPEG4AAC_HE_V2
outputFormat.mChannelsPerFrame = 2;
outputFormat.mFramesPerPacket = 1024; // AAC一帧是1024个字节
const OSType subtype = kAudioFormatMPEG4AAC;
AudioClassDescription requestedCodecs[2] = {
{
kAudioEncoderComponentType,
subtype,
kAppleSoftwareAudioCodecManufacturer
},
{
kAudioEncoderComponentType,
subtype,
kAppleHardwareAudioCodecManufacturer
}
};
OSStatus result = AudioConverterNewSpecific(&inputFormat, &outputFormat, 2, requestedCodecs, &m_converter);;
UInt32 outputBitrate = 96000;
UInt32 propSize = sizeof(outputBitrate);
if(result == noErr) {
result = AudioConverterSetProperty(m_converter, kAudioConverterEncodeBitRate, propSize, &outputBitrate);
}
编码器准备好了,可以对采集的PCM数据进行编码。这里会有两个缓冲区:AudioBuffe,AACBuffer,大小都是audioBufferSize。当PCM的数据和AudioBuffer中的数据大小超过AudioBuffer 的大小,才送到AAC Encoder。
- (void)encodeAudioData:(nullable NSData*)audioData timeStamp:(uint64_t)timeStamp {
if(leftLength + audioData.length >= audioBufferSize){
NSInteger totalSize = leftLength + audioData.length;
NSInteger encodeCount = totalSize / audioBufferSize;
char *totalBuf = malloc(totalSize);
char *p = totalBuf;
memset(totalBuf, (int)totalSize, 0);
memcpy(totalBuf, audioBuffer, leftLength);
memcpy(totalBuf + leftLength, audioData.bytes, audioData.length);
for(NSInteger index = 0;index < encodeCount;index++){
[self encodeBuffer:p timeStamp:timeStamp];
p += audioBufferSize;
}
leftLength = totalSize % audioBufferSize;
memset(audioBuffer, 0, audioBufferSize);
memcpy(audioBuffer, totalBuf + (totalSize -leftLength), leftLength);
free(totalBuf);
}else{
memcpy(audioBuffer+leftLength, audioData.bytes, audioData.length);
leftLength = leftLength + audioData.length;
}
}
接下来就是编码从AudioBuffer中送过来的数据。其中inputDataProc 为编码器转化数据时的回调。
- (void)encodeBuffer:(char*)buf timeStamp:(uint64_t)timeStamp{
AudioBuffer inBuffer;
inBuffer.mNumberChannels = 1;
inBuffer.mData = buf;
inBuffer.mDataByteSize = audioBufferSize;
AudioBufferList buffers;
buffers.mNumberBuffers = 1;
buffers.mBuffers[0] = inBuffer;
// 初始化一个输出缓冲列表
AudioBufferList outBufferList;
outBufferList.mNumberBuffers = 1;
outBufferList.mBuffers[0].mNumberChannels = inBuffer.mNumberChannels;
outBufferList.mBuffers[0].mDataByteSize = inBuffer.mDataByteSize; // 设置缓冲区大小
outBufferList.mBuffers[0].mData = aacBuffer; // 设置AAC缓冲区
UInt32 outputDataPacketSize = 1;
if (AudioConverterFillComplexBuffer(m_converter, inputDataProc, &buffers, &outputDataPacketSize, &outBufferList, NULL) != noErr) {
return;
}
AudioFrame *audioFrame = [AudioFrame new];
audioFrame.timestamp = timeStamp;
audioFrame.data = [NSData dataWithBytes:aacBuffer length:outBufferList.mBuffers[0].mDataByteSize];
char exeData[2];
///// flv编码音频头 44100 为0x12 0x10
exeData[0] = 0x12;
exeData[1] = 0x10;
audioFrame.audioInfo = [NSData dataWithBytes:exeData length:2];
if (self.aacDeleage && [self.aacDeleage respondsToSelector:@selector(audioEncoder:audioFrame:)]) {
[self.aacDeleage audioEncoder:self audioFrame:audioFrame];
}
}
OSStatus inputDataProc(AudioConverterRef inConverter, UInt32 *ioNumberDataPackets, AudioBufferList *ioData, AudioStreamPacketDescription * *outDataPacketDescription, void *inUserData)
{
AudioBufferList bufferList = *(AudioBufferList *)inUserData;
ioData->mBuffers[0].mNumberChannels = 1;
ioData->mBuffers[0].mData = bufferList.mBuffers[0].mData;
ioData->mBuffers[0].mDataByteSize = bufferList.mBuffers[0].mDataByteSize;
return noErr;
}
那么44100 为0x12 0x10 ,这数据是怎么得出的?
- 获取sampleIndex
//https://wiki.multimedia.cx/index.php?title=MPEG-4_Audio
- (NSInteger)sampleRateIndex:(NSInteger)frequencyInHz {
NSInteger sampleRateIndex = 0;
switch (frequencyInHz) {
case 96000:
sampleRateIndex = 0;
break;
case 88200:
sampleRateIndex = 1;
break;
case 64000:
sampleRateIndex = 2;
break;
case 48000:
sampleRateIndex = 3;
break;
case 44100:
sampleRateIndex = 4;
break;
case 32000:
sampleRateIndex = 5;
break;
case 24000:
sampleRateIndex = 6;
break;
case 22050:
sampleRateIndex = 7;
break;
case 16000:
sampleRateIndex = 8;
break;
case 12000:
sampleRateIndex = 9;
break;
case 11025:
sampleRateIndex = 10;
break;
case 8000:
sampleRateIndex = 11;
break;
case 7350:
sampleRateIndex = 12;
break;
default:
sampleRateIndex = 15;
}
return sampleRateIndex;
}
根据公式就可以计算出44100的asc。
asc[0] = 0x10 | ((sampleRateIndex>>1) & 0x7);
asc[1] = ((sampleRateIndex & 0x1)<<7) | ((numberOfChannels & 0xF) << 3);
asc[0] = 0x10 | ((4>>1) & 0x7) = 0x12
asc[1] = ((4 & 0x1)<<7) | ((2 & 0xF) << 3) = 0x10
结论
经过音视频编码后,最终得到的VideoFrame和Video Frame ,它们包含了当前数据的时间戳和数据。
下一篇将会记录如何通过rtmp发送数据。