目录
- 学号 2019-2020-1823 《数据结构与面向对象程序设计》实验六报告
- 1.实验内容
- 3. 实验过程中遇到的问题和解决过程
- 其他(感悟、思考等)
学号 2019-2020-1823 《数据结构与面向对象程序设计》实验六报告
班级: 1823
姓名: 杨凯涵
学号:20182321
实验教师:王志强
实验日期:2019年11月13日
必修/选修: 必修
1.实验内容
实验一
要求:参考教材PP16.1,完成链树LinkedBinaryTree的实现(getRight,contains,toString,preorder,postorder)
用JUnit或自己编写驱动类对自己实现的LinkedBinaryTree进行测试,提交测试代码运行截图,要全屏,包含自己的学号信息
课下把代码推送到代码托管平台
首先,先把pp16.1的代码LinkedBinaryTree打下来
public BTNode root;
public LinkedBinaryTree()
{
root = null;
}
public LinkedBinaryTree(T element)
{
root = new BTNode(element);
}
public LinkedBinaryTree(T element,LinkedBinaryTree left,LinkedBinaryTree right)
{
root = new BTNode(element);
root.setLeft(left.root);
root.setRight(right.root);
}
public T getRootElement() {
if(root == null)
throw new EmptyCollectionException("Get root operation failed.The tree is empty" );
return root.getElement();
}
public LinkedBinaryTree getLeft()
{
if(root == null)
throw new EmptyCollectionException("Get left operation faild. The tree is empty");
LinkedBinaryTree result = new LinkedBinaryTree();
result.root=root.getLeft();
return result;
}
public T find (T target)
{
BTNode node = null;
if(root != null)
node = root.find(target);
if(node == null)
throw new ElementNotFoundException("Find operation faild. No such element in tree");
return node.getElement();
}
public int size()
{
int result =0;
if(root!= null)
result = root.count();
return result;
}
public ArrayList inorder()
{
ArrayList iter = new ArrayList();
if(root != null)
root.inorder(iter);
return iter;
}
public ArrayList levelorder() throws zhan.EmptyCollectionException {
CircularArrayQueue> queue = new CircularArrayQueue>();
ArrayList iter = new ArrayList();
if (root != null)
{
queue.enqueue(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty())
{
BTNode current = queue.dequeue();
iter.add(current.getElement());
if(current.getLeft()!= null)
queue.enqueue(current.getLeft());
if(current.getRight()!= null)
queue.enqueue(current.getRight());
}
}
return iter;
}
public ArrayList iterator()
{
return inorder();
} 接着按要求填充代码,首先是getright方法的
public LinkedBinaryTree getright()
{
if(root == null)
throw new EmptyCollectionException("Get left operation faild. The tree is empty");
LinkedBinaryTree result = new LinkedBinaryTree();
result.root=root.getRight();
return result;
} 与之前的getleft相同,接着我们补充contains代码
public boolean contains (T target)
{
BTNode now =null;
now =root.find(target);
if(root.getElement() == target)
return true;
else
return false;
} 然后是isEmpty和toString
public boolean isEmpty() {
if (root == null)
return true;
else
return false;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "LinkedBinaryTree{" +
"root=" + root +
'}';
}最后是前序遍历和后序遍历
public ArrayList preoder(){
ArrayList iter = new ArrayList();
if(root != null)
root.preorder(iter);
return iter;
}
public ArrayList postoder(){
ArrayList iter = new ArrayList();
if(root != null)
root.postorder(iter);
return iter;
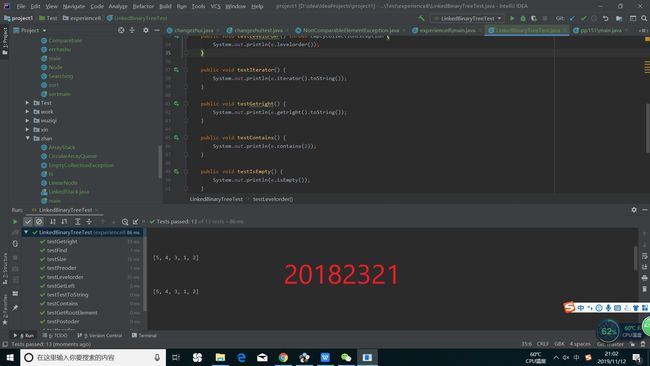
} 接着我们再继续编写Test类来测试这个程序,最后得出结果
实验二
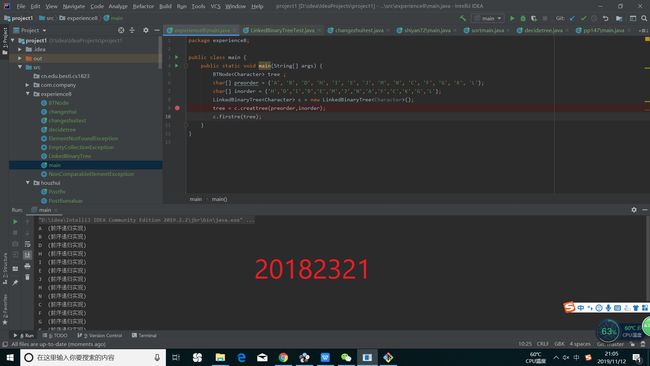
要求:基于LinkedBinaryTree,实现基于(中序,先序)序列构造唯一一棵二㕚树的功能,比如给出中序HDIBEMJNAFCKGL和后序ABDHIEJMNCFGKL,构造出附图中的树
用JUnit或自己编写驱动类对自己实现的功能进行测试,提交测试代码运行截图,要全屏,包含自己的学号信息
课下把代码推送到代码托管平台
根据题目要求,我们编写了基于中序和先序的构建二叉树的代码(具体什么算法,我们会在下面讲到)
public BTNode creattree(char[] preOrders, char[] inOrders)
{
if (preOrders.length == 0 || inOrders.length == 0) {
return null;
}
BTNode tree = new BTNode(preOrders[0]);
int index = search(0, inOrders.length, inOrders, tree.getElement());
tree.setLeft(creattree(Arrays.copyOfRange(preOrders, 1, index + 1), Arrays.copyOfRange(inOrders, 0, index)));
tree.setRight(creattree(Arrays.copyOfRange(preOrders, index + 1, preOrders.length),
Arrays.copyOfRange(inOrders, index + 1, inOrders.length)));
return tree;
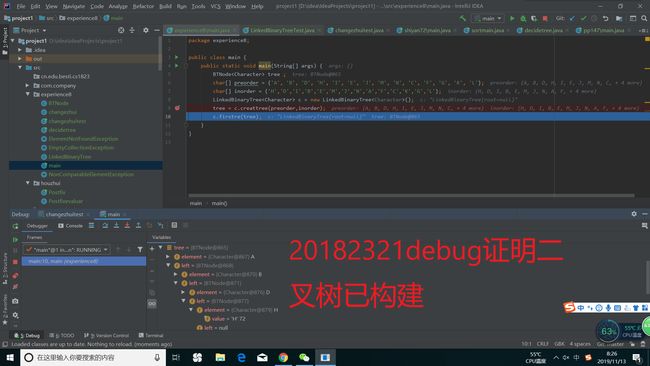
} 接着我们再通过dubug来验证是否二叉树已经构成
再用前序输出它
public void firstre(BTNode biTree)
{
System.out.println(biTree.getElement()+" (前序递归实现)");
BTNode leftTree = biTree.left;
if(leftTree != null)
{
firstre(leftTree);
}
BTNode rightTree = biTree.right;
if(rightTree != null)
{
firstre(rightTree);
}
} 实验三
要求:自己设计并实现一颗决策树
提交测试代码运行截图,要全屏,包含自己的学号信息
课下把代码推送到代码托管平台
根据教材上的提示,决策树就是以二叉树的形式建立其一颗“数”,通过问题的层层递进,最后输出结果。
然后按照以上的思路,我们构建二叉树,再运行输出
package experience8;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class decidetree {
private LinkedBinaryTree tree;
public decidetree()
{
String e1 = "你是中国人吗?";
String e2 = "你是电科院的吗?";
String e3 = "你是外国留学生吗?" ;
String e4 = "你太菜了";
String e5 = "欢迎";
String e6 = "给我滚!";
String e7 = "别来";
LinkedBinaryTree n1,n2,n3,n4,n5,n6,n7;
n4= new LinkedBinaryTree(e4);
n5=new LinkedBinaryTree(e5);
n2 = new LinkedBinaryTree(e2,n4,n5);
n6=new LinkedBinaryTree(e6);
n7 = new LinkedBinaryTree(e7);
n3 = new LinkedBinaryTree(e3,n6,n7);
n1=new LinkedBinaryTree(e1,n2,n3);
tree = n1;
}
public void diagnose()
{
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
LinkedBinaryTree current = tree;
System.out.println("请接收我的审判");
while (current.size()>1)
{
System.out.println(current.getRootElement());
if(scan.nextLine().equalsIgnoreCase("N"))
current = current.getLeft();
else
current = current.getright();
}
System.out.println(current.getRootElement());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
decidetree d = new decidetree();
d.diagnose();
}
} 最后的输出结果
实验四
要求 :输入中缀表达式,使用树将中缀表达式转换为后缀表达式,并输出后缀表达式和计算结果(如果没有用树,正常评分。如果用到了树,即使有小的问题,也酌情给满分)
我们编写了如下代码(算法思路会在下面问题处讲解)
static Stack op = new Stack<>();
public static Float getv(char op, Float f1, Float f2){
if(op == '+') return f2 + f1;
else if(op == '-') return f2 - f1;
else if(op == '*') return f2 * f1;
else if(op == '/') return f2 / f1;
else return Float.valueOf(-0);
}
public static float calrp(String rp){
Stack v = new Stack<>();
char[] arr = rp.toCharArray();
int len = arr.length;
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
Character ch = arr[i];
// if is operand, push to the stack
if(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') v.push(Float.valueOf(ch - '0'));
// if is operator, calculate the result
// with top 2 operands in the stack,
// push the result into the stack
else v.push(getv(ch, v.pop(), v.pop()));
}
return v.pop();
}
public static String getrp(String s) {
char[] arr = s.toCharArray();
int len = arr.length;
String out = "";
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
char ch = arr[i];
if (ch == ' ') continue;
// if is operand, add to
// the output stream directly
if (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
out += ch;
continue;
}
//if is '(', push to the stack directly
if (ch == '(') op.push(ch);
//if is '+' or '-', pop the operator
// from the stack until '(' and add to
// the output stream
//push the operator to the stack
if (ch == '+' || ch == '-') {
while (!op.empty() && (op.peek() != '('))
out += op.pop();
op.push(ch);
continue;
}
//if is '*' or '/', pop the operator stack and
// add to the output stream
// until lower priority or '('
//push the operator to the stack
if (ch == '*' || ch == '/') {
while (!op.empty() && (op.peek() == '*' || op.peek() == '/'))
out += op.pop();
op.push(ch);
continue; 输出如下所示
3. 实验过程中遇到的问题和解决过程
- 问题1:如何基于中序和先序来构建二叉树?
- 问题1解决方法:基本的算法如下
算法的思路是由先序来确定一个节点,而中序来确定左子树和右子数如
前序:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
中序:3 2 5 4 1 7 8 6 10 9
(1)第一次:
产生节点 1。(先序的第一个数肯定是节点)
生成左子树(在中序中找到1,左为左子树,右为右子树)
先序:2 3 4 5
中序:3 2 5 4
生成右子树
前序:6 7 8 9 10
中序:7 8 6 10 9
(2)第二次
产生节点 2(由左子树得来,故为第一次结点的左子树)。
生成左子树
前序:3
中序:3
生成右子树
先序:4 5
中序:5 4
以此类推,来完成构建二叉树。
- 问题2:如何来完成中缀转换成后缀
- 问题2解决方法:
算法思路:
我做的是用栈来实现,利用等式的运算优先级来完成
1.按次序读取中缀表达式的字符。
2.读到一个操作数的时候,立即放入到输出中。
3.读到操作符“+”,“-”,“*”,“/”,则从栈中弹出栈元素并输出,直到遇到优先级更低或者“(”的为止操作符为止(该元素不出栈)。
4.读到操作符“(”,则直接把“(”压入栈中。
5.读到操作符“)”,则从栈中弹出栈元素并输出,直到遇到第一个“(”为止。其中“(”不再添加到输出中,而是直接舍弃。
6.当输入为空时,把栈里的操作符全部依次弹出并输出。
例如输入:5+2(3(3-1*2+1))
其他(感悟、思考等)
- 对于学习数据结构来说,应该先想好算法再编写程序,否则上场就会相当懵逼
树其实只是多个链表的一个集合,所以在处理树为问题时,其实就是一个多条链表集合的问题
参考资料
《Java程序设计与数据结构教程(第二版)》
《Java程序设计与数据结构教程(第二版)》学习指导