目录
- 学号 2019-2020-1823 《数据结构与面向对象程序设计》实验六报告
- 1.实验内容
- 3. 实验过程中遇到的问题和解决过程
- 其他(感悟、思考等)
学号 2019-2020-1823 《数据结构与面向对象程序设计》实验六报告
班级: 1823
姓名: 杨凯涵
学号:20182321
实验教师:王志强
实验日期:2019年11月17日
必修/选修: 必修
1.实验内容
实验一
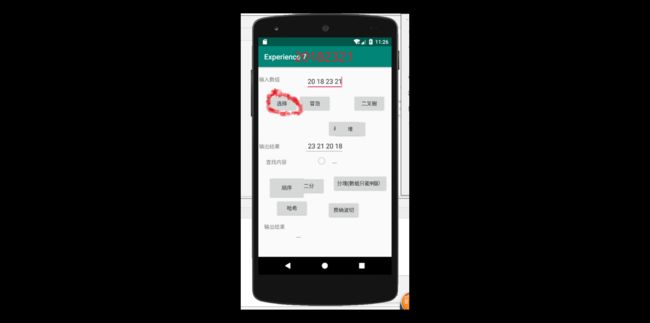
要求:定义一个Searching和Sorting类,并在类中实现linearSearch,SelectionSort方法,最后完成测试。
要求不少于10个测试用例,提交测试用例设计情况(正常,异常,边界,正序,逆序),用例数据中要包含自己学号的后四位
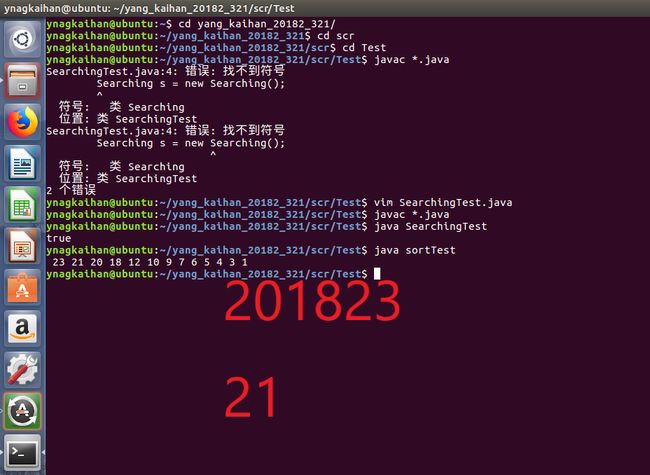
sorting类用的是选择排序,而searching类使用的是线性查找,这两个方法都是java算法里最最最最基本的算法了。代码如下
选择排序算法
public String selectionsort(String a)
{
String[] s = a.split("\\s");
int[] b = new int[s.length];
for(int i=0;i线性查找算法
public boolean linearSearch(String a, int target)
{
String[] s = a.split("\\s");
int data[]=new int[s.length];
for(int i=0;i选择排序和线性查找算法的核心就是一股劲的往前冲,基本上没有什么很特殊、很难的地方。
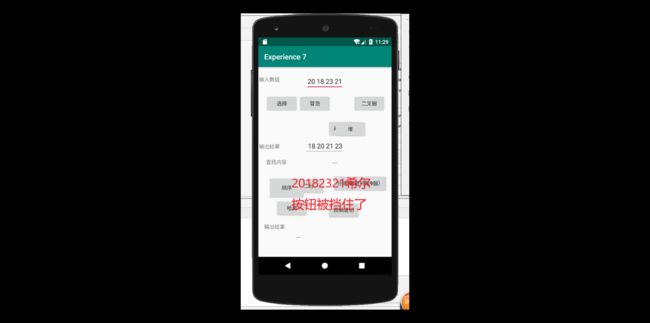
运行结果如下
而异常情况运行结果为
实验二
要求:重构你的代码
把Sorting.java Searching.java放入 cn.edu.besti.cs1823.(姓名首字母+四位学号) 包中(例如:cn.edu.besti.cs1823.G2301)
把测试代码放test包中
重新编译,运行代码,提交编译,运行的截图(IDEA,命令行两种)
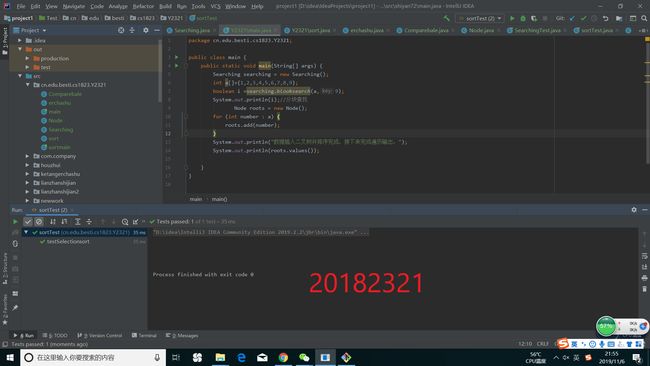
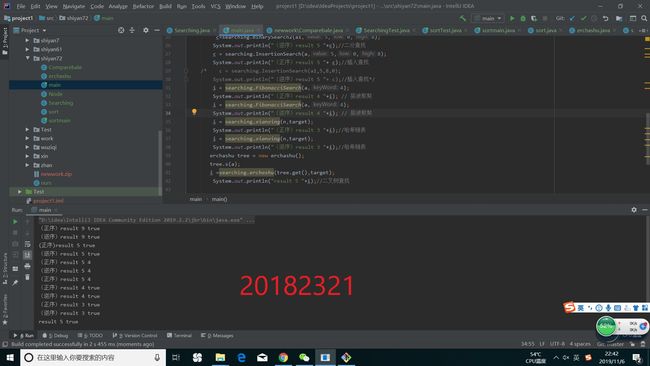
首先在idea上运行,先把之前的两个类放入到题目要求的包中,然后再重新穿建立一个Test类,用来对其进行测试,测试代码如下
测试查找
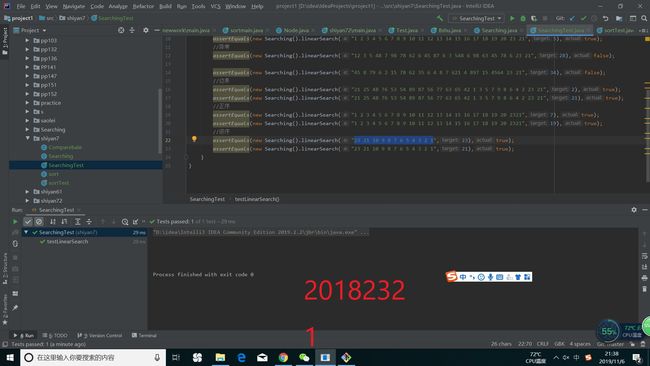
public void testLinearSearch() {
//正常
assertEquals(new shiyan7.Searching().linearSearch("21 25 48 76 53 54 89 87 56 77 63 65 42 1 3 5 7 9 8 6 4 2 23 21",54),true);
assertEquals(new shiyan7.Searching().linearSearch("1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 23 21",5),true);
//异常
assertEquals(new shiyan7.Searching().linearSearch("12 3 5 48 7 98 78 62 6 45 87 6 3 548 6 98 63 45 78 6 23 21",28),false);
assertEquals(new shiyan7.Searching().linearSearch("45 8 79 6 2 15 78 62 35 6 4 8 7 621 4 897 15 4564 23 21",34),false);
//边界
assertEquals(new shiyan7.Searching().linearSearch("21 25 48 76 53 54 89 87 56 77 63 65 42 1 3 5 7 9 8 6 4 2 23 21",2),true);
assertEquals(new shiyan7.Searching().linearSearch("21 25 48 76 53 54 89 87 56 77 63 65 42 1 3 5 7 9 8 6 4 2 23 21",21),true);
//正序
assertEquals(new shiyan7.Searching().linearSearch("1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 2321",7),true);
assertEquals(new shiyan7.Searching().linearSearch("1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 2321",19),true);
//逆序
assertEquals(new shiyan7.Searching().linearSearch("23 21 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1",23),true);
assertEquals(new Searching().linearSearch("23 21 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1",21),true);
} public void testSelectionsort() {
//正常
assertEquals(new shiyan7.sort().selectionsort("1 4 7 2 5 8 3 6 9 10")," 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1");
//逆序
assertEquals(new shiyan7.sort().selectionsort("1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10")," 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1");
//正序
assertEquals(new sort().selectionsort("10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1")," 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1");
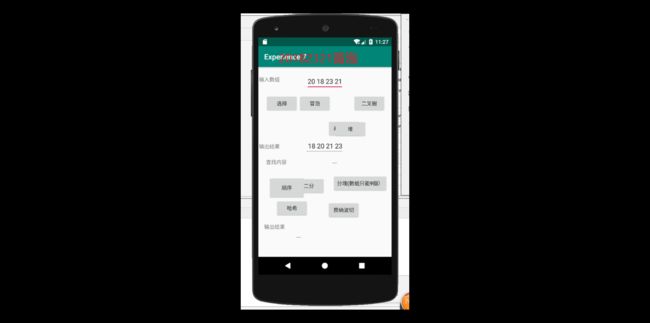
}然后我们的运行结果如下所示
在虚拟机中,我安装了junit
但是发现这个东西属实难用,和idea里面的简直就是一个天一个地,所以经过考虑,我决定使用驱动程序在虚拟机里面进行测试
实验三
要求:参考http://www.cnblogs.com/maybe2030/p/4715035.html ,学习各种查找算法并在Searching中补充查找算法并测试
我们按照里面的链接知道,编写相应的算法代码,并进行测试
二分查找
public int BinarySearch2(int a[], int value, int low, int high)
{
int mid = low+(high-low)/2;
if(a[mid]==value)
return mid;
if(a[mid]>value)
return BinarySearch2(a, value, low, mid-1);
if(a[mid]插入查找(其实和二分查找没什么区别)
public int InsertionSearch(int a[], int value, int low, int high)
{
int mid = low+(value-a[low])/(a[high]-a[low])*(high-low);
if(a[mid]==value)
return mid;
if(a[mid]>value)
return InsertionSearch(a, value, low, mid-1);
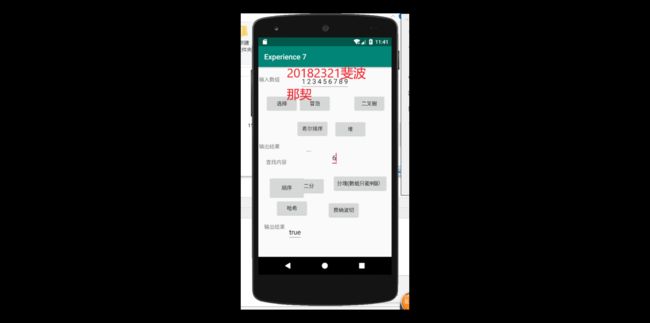
if(a[mid]斐波那契数列
public static boolean FibonacciSearch(int[] table, int keyWord) {
//确定需要的斐波那契数
int i = 0;
while (getFibonacci(i) - 1 == table.length) {
i++;
}
//开始查找
int low = 0;
int height = table.length - 1;
while (low <= height) {
int mid = low + getFibonacci(i - 1);
if (table[mid] == keyWord) {
return true;
} else if (table[mid] > keyWord) {
height = mid - 1;
i--;
} else if (table[mid] < keyWord) {
low = mid + 1;
i -= 2;
}
}
return false;
}
//得到第n个斐波那契数
public static int getFibonacci(int n) {
int res = 0;
if (n == 0) {
res = 0;
} else if (n == 1) {
res = 1;
} else {
int first = 0;
int second = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
res = first + second;
first = second;
second = res;
}
}
return res;
}哈希线性查找(需要先提前构造哈希函数)
public static boolean xianxing(Comparebale[] data , Comparebale target)
{
int num = target.geti()%9;
boolean i ;
while (data[num]!=null) {
if(data[num].geti()==target.geti())
return true;
else
num++;
}
return false;
}这里我的哈希函数设置为h%9,大家可以自行设定
二叉树查找
public static boolean erchashu(Comparebale tree, Comparebale target)
{
while (tree!=null)
{
if(tree.geti()target.geti())
{
tree = tree.secondnext;
}
else if(tree.geti()==target.geti())
return true;
}
return false;
} 二叉树之前也是要先构建
public class erchashu {
Comparebale tree = new Comparebale(-1);
Comparebale head = new Comparebale(-1);
int[] a = new int[12];
public erchashu()
{
head.setNext(tree);
}
public void s(int[] b)
{
tree.setI(b[0]);
for(int i=1;ib[i]&&tree.getSecondnext()!=null)
tree = tree.getSecondnext();
else if(tree.geti()>b[i]&&tree.getSecondnext()==null)
{
tree.setSecondnext(c);
tree = c;
}
}
}
}
public String toString( int[] a)
{
s(a);
String result = "";
for(int i=0;i 接着是分块查找
public static boolean blooksearch(int[] a ,int key)
{
int[] b = new int[3];
int n = a.length/3;
int max = a[0];
int j=0;
while (n<=9)
{
for(int i=n-3;i=key)
{
for(int l = (i+1)*3-1;l>=(i+1)*3-3;l--)
{
if(a[l]==key)
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
return false;
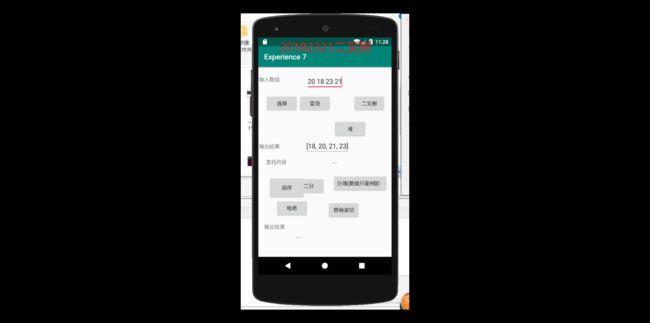
} 最后测试的运行截图为
实验四
要求:补充实现课上讲过的排序方法:希尔排序,堆排序,二叉树排序等(至少3个)
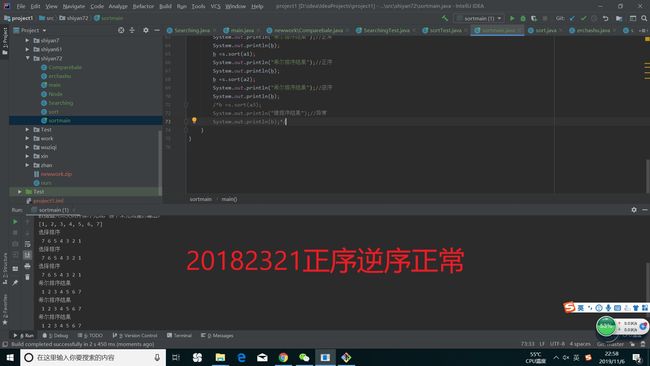
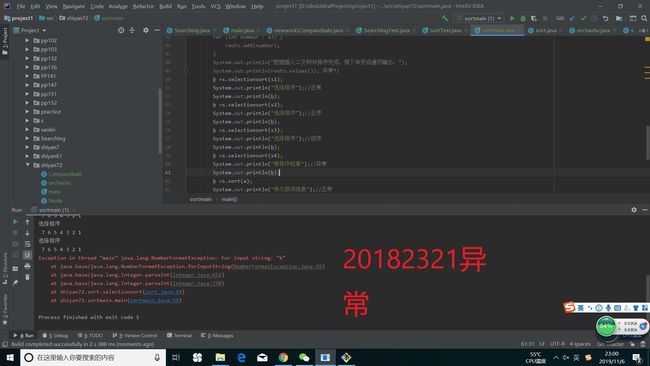
测试实现的算法(正常,异常,边界)
提交运行结果截图
希尔排序
public String sort (int[] arr)
{
for(int gap = arr.length/2;gap>0;gap/=2)
{
for(int i=gap;i=0&&arr[j] 堆排序
public static void heapify(int[] arrays, int currentRootNode, int size) {
if (currentRootNode < size) {
//左子树和右字数的位置
int left = 2 * currentRootNode + 1;
int right = 2 * currentRootNode + 2;
//把当前父节点位置看成是最大的
int max = currentRootNode;
if (left < size) {
//如果比当前根元素要大,记录它的位置
if (arrays[max] < arrays[left]) {
max = left;
}
}
if (right < size) {
//如果比当前根元素要大,记录它的位置
if (arrays[max] < arrays[right]) {
max = right;
}
}
//如果最大的不是根元素位置,那么就交换
if (max != currentRootNode) {
int temp = arrays[max];
arrays[max] = arrays[currentRootNode];
arrays[currentRootNode] = temp;
//继续比较,直到完成一次建堆
heapify(arrays, max, size);
}
}
}
public static void maxHeapify(int[] arrays, int size) {
// 从数组的尾部开始,直到第一个元素(角标为0)
for (int i = size - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
heapify(arrays, i, size);
}
}
public static String dui(int[] arrays)
{
for (int i = 0; i < arrays.length; i++) {
//每次建堆就可以排除一个元素了
maxHeapify(arrays, arrays.length - i);
//交换
int temp = arrays[0];
arrays[0] = arrays[(arrays.length - 1) - i];
arrays[(arrays.length - 1) - i] = temp;
}
String result="";
for(int i=0;i二叉树排序
public void s(int[] b)
{
tree.setI(b[0]);
for(int i=1;ib[i]&&tree.getSecondnext()!=null)
tree = tree.getSecondnext();
else if(tree.geti()>b[i]&&tree.getSecondnext()==null)
{
tree.setSecondnext(c);
tree = c;
}
}
}
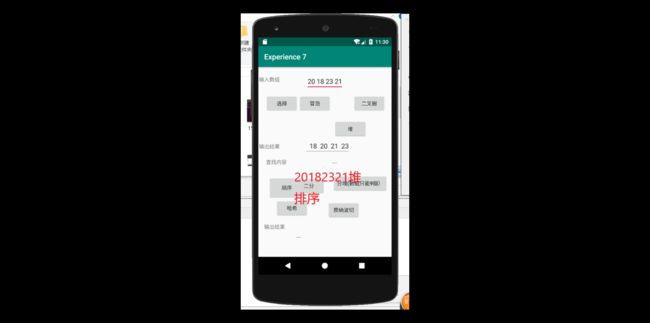
} 代码测试运行截图为
异常截图
实验五
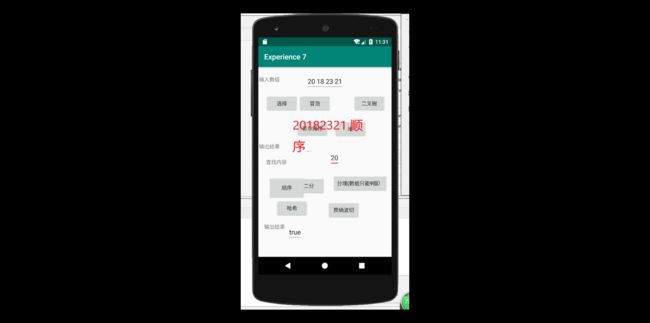
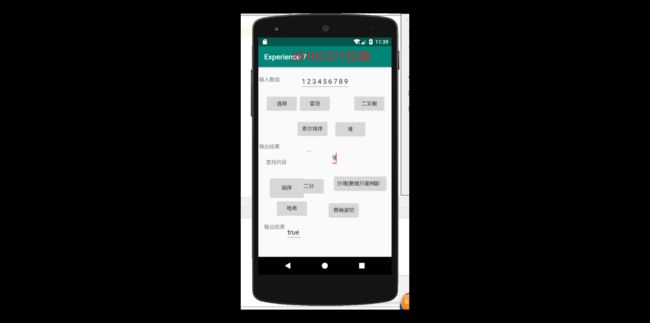
要求:编写Android程序对实现各种查找与排序算法进行测试
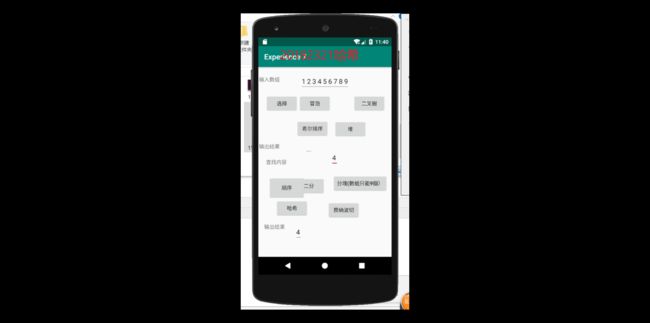
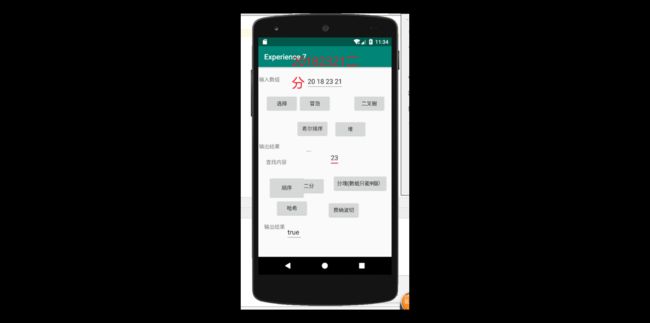
提交运行结果截图
推送代码到码云
进行布局并放入代码进去之后,结果如图
3. 实验过程中遇到的问题和解决过程
问题一:如何进行堆排序算法?
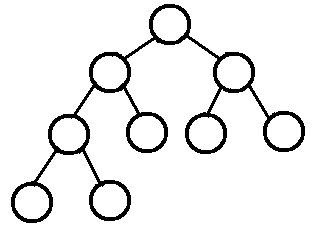
问题一解决方法:了解堆排序之前就必须要知道一个完全二叉树的概念,何为完全二叉树,如下图
即除了最后一层之外的其他每一层都被完全填充,并且所有结点都保持向左对齐。它和满二叉树这个概念是一定要区分开的。从总体来讲,堆排序就是讲数据看成是完全二叉树类型,然后用二叉树的特性来进行排序的一种算法。
如下图
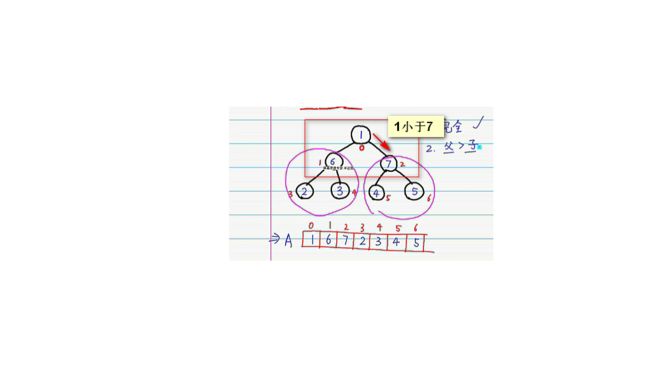
这是一个完全二叉树,而二叉树的数据其实都存储进了数组里面,左子树的序数其实是其父亲的2i+1,右子数的序数是其父亲的2i+2,可以按照这个特性将二叉树的值都依次附进数组里,接着我们发现左右子树都符合最大堆,但是父类子树不符合,则我们需要先对其父亲子树进行操作,让7在根节点上。
那这样右子数又不符合了,那我们又要对右子数进行调换,则
右子数变成了这样
这属于建堆成功,最后我们还需要进行调换,将最开头的元素与最末尾的元素进行调换,如下图
堆排序是通过不断的这样建堆的过程完成其排序的,详细我自己手写的下图
则这样我们就实现了堆排序,具体代码在我的实验过程里有了。
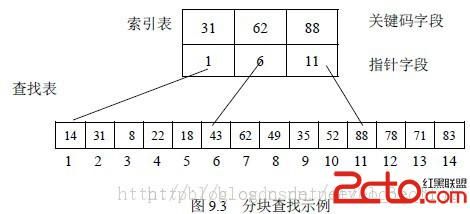
- 问题2:分块查找的算法是如何设计的?
- 问题2解决方法:分块查找其实是线性查找的改良版,它把一个线性集合的数组分成数个模块,每个模块有着的一个最大关键字作为索引
将所有的最大索引变成一个索引表,查找分为两部分,先对索引表进行二分查找或是顺序查找,以确定待查记录在哪一块中,然后,在已经确定的块中用顺序法进行查找。具体代码可看我的实验过程。
其他(感悟、思考等)
- 算法的排序查找是一个及其复杂的东西,让人掉发,关键在于设计算法出来后如何实现非常的困难,本人也只能上网去查阅他人资料学习。
只有在打下坚实的基础下,才能把这些排序算法打出来,否则会极易出现错误。
参考资料
《Java程序设计与数据结构教程(第二版)》
《Java程序设计与数据结构教程(第二版)》学习指导