mybatis的基本用法如下:
//根据配置文件创建SqlSessionFactory
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = new ClassPathResource(resource).getInputStream();
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//通过session.selectOne()的方式调用
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
Blog blog = session.selectOne("mybatis.dao.BlogMapper.selectBlog", 1);
System.out.println(blog.toString());
//通过BeanMapper的方式调用
BlogMapper blogMapper = session.getMapper(BlogMapper.class);
Blog blog1 = blogMapper.selectBlog(1L);
System.out.println(blog1.toString());
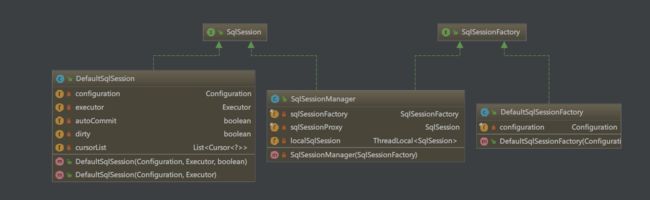
其中最重要的是SqlSessionFactory和SqlSession,下面对其进行具体分析。
其类继承结构如图:
上述例子中,我们通过加载mybatis-config.xml文件,配置完成了一个DefaultSessionFactory。
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
//读取xml配置文件中的配置信息,配置工厂类需要的各类配置信息
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
而后通过已配置好的SqlSessionFactory工厂类,获取一个SqlSession实例
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
通过SqlSession来执行mapper.xml中配置的sql语句,并执行数据库属性到对象的自动封装
Blog blog = session.selectOne("mybatis.dao.BlogMapper.selectBlog", 1);
其中selectOne源码如下:
public T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) {
// Popular vote was to return null on 0 results and throw exception on too many.
List list = this.selectList(statement, parameter);
if (list.size() == 1) {
return list.get(0);
} else if (list.size() > 1) {
throw new TooManyResultsException("Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: " + list.size());
} else {
return null;
}
}
selectList源码如下:
public List selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
//根据id获取sql语句
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
//将语句交给executor代理执行
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
这里详细分析一下mybatis是怎么根据id查找到对应的sql语句信息的:
configuration.getMappedStatement(statement)
public MappedStatement getMappedStatement(String id, boolean validateIncompleteStatements) {
if (validateIncompleteStatements) {
buildAllStatements();
}
return mappedStatements.get(id);
}
其中mappedStatements是Configuration的一个属性
protected final Map mappedStatements
= new StrictMap("Mapped Statements collection");
其中StrictMap是mybatis自定义的一个map对象,继承自HashMap,重载了map的get和set方法,以保证在插入重复mapper id时,能够得到相应通知,源码如下:
protected static class StrictMap extends HashMap {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -4950446264854982944L;
private final String name;
public StrictMap(String name, int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
this.name = name;
}
public StrictMap(String name, int initialCapacity) {
super(initialCapacity);
this.name = name;
}
public StrictMap(String name) {
super();
this.name = name;
}
public StrictMap(String name, Map m) {
super(m);
this.name = name;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public V put(String key, V value) {
if (containsKey(key)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(name + " already contains value for " + key);
}
if (key.contains(".")) {
//获取key的短名称,以 “.” 作为分隔符,得到的字符数组,取最后一个
final String shortKey = getShortName(key);
//如果短名称的key之前不存在,那么插入key-value
//如果存在,则插入Ambiguity对象,表示此短名称重复了
if (super.get(shortKey) == null) {
super.put(shortKey, value);
} else {
super.put(shortKey, (V) new Ambiguity(shortKey));
}
}
return super.put(key, value);
}
public V get(Object key) {
V value = super.get(key);
if (value == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(name + " does not contain value for " + key);
}
//如果根据key取出的为Ambiguity对象,表示存在重复配置的mapper语句,抛出异常
if (value instanceof Ambiguity) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(((Ambiguity) value).getSubject() + " is ambiguous in " + name
+ " (try using the full name including the namespace, or rename one of the entries)");
}
return value;
}
private String getShortName(String key) {
final String[] keyParts = key.split("\\.");
return keyParts[keyParts.length - 1];
}
protected static class Ambiguity {
final private String subject;
public Ambiguity(String subject) {
this.subject = subject;
}
public String getSubject() {
return subject;
}
}
}
通过分析源码,在new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream)时即对mapper.xml文件进行了解析,并将解析的结果put到了mappedStatements 中。
上面我们知道了通过session.selectOne(mapperKeyId, param)的方式执行具体的数据库操作,是在configuration加载的时候,读取mapper.xml相关配置,从而获取到了在加载配置时缓存的mapper sql语句信息。
那么,我们通过session.getMapper(BlogMapper.class);的方式,其中BlogMapper是一个接口,并没有其具体的实现类,mybatis是如何查找其具体的执行sql的呢?
通过查找session.getMapper()方法的调用栈,其源码为:
public T getMapper(Class type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
这里通过JDK动态代理的方法,生成了一个mapper的代理类
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
分析mapper代理类的代理处理方法源码如下:
public class MapperProxy implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -6424540398559729838L;
private final SqlSession sqlSession;
private final Class mapperInterface;
private final Map methodCache;
public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class mapperInterface, Map methodCache) {
this.sqlSession = sqlSession;
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
this.methodCache = methodCache;
}
//重点关注invoke方法,因为调用代理mapper类的具体方法时,会进入此方法执行具体逻辑,以实现对原方法的加强
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) {
return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
//查找mapper class对应的执行脚本
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
//具体执行sql操作
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) {
MapperMethod mapperMethod = methodCache.get(method);
if (mapperMethod == null) {
mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration());
methodCache.put(method, mapperMethod);
}
return mapperMethod;
}
@UsesJava7
private Object invokeDefaultMethod(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
throws Throwable {
final Constructor constructor = MethodHandles.Lookup.class
.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, int.class);
if (!constructor.isAccessible()) {
constructor.setAccessible(true);
}
final Class declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass();
return constructor
.newInstance(declaringClass,
MethodHandles.Lookup.PRIVATE | MethodHandles.Lookup.PROTECTED
| MethodHandles.Lookup.PACKAGE | MethodHandles.Lookup.PUBLIC)
.unreflectSpecial(method, declaringClass).bindTo(proxy).invokeWithArguments(args);
}
/**
* Backport of java.lang.reflect.Method#isDefault()
*/
private boolean isDefaultMethod(Method method) {
return ((method.getModifiers()
& (Modifier.ABSTRACT | Modifier.PUBLIC | Modifier.STATIC)) == Modifier.PUBLIC)
&& method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface();
}
}
mapper代理类对原mapper对象进行了增强,会首先根据mapper的Method作为key查找methodCache,如果没有找到,则将Method-mapperInterface.getName() + "." + methodName及其他配置属性,作为键值对插入缓存中。
而后,进行具体的执行过程mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args)
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {…… }
case DELETE: {…… }
case SELECT:……
case FLUSH:……
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
具体进行sql操作的方法为sqlSession.insert | delete | update | select