版本记录
| 版本号 | 时间 |
|---|---|
| V1.0 | 2019.02.11 星期一 |
前言
quartz是一个通用的术语,用于描述在iOS和MAC OS X中整个媒体层用到的多种技术 包括图形、动画、音频、适配。Quart 2D是一组二维绘图和渲染API,Core Graphic会使用到这组API,Quartz Core专指Core Animation用到的动画相关的库、API和类。CoreGraphics是UIKit下的主要绘图系统,频繁的用于绘制自定义视图。Core Graphics是高度集成于UIView和其他UIKit部分的。Core Graphics数据结构和函数可以通过前缀CG来识别。在app中很多时候绘图等操作我们要利用CoreGraphic框架,它能绘制字符串、图形、渐变色等等,是一个很强大的工具。感兴趣的可以看我另外几篇。
1. CoreGraphic框架解析(一)—— 基本概览
2. CoreGraphic框架解析(二)—— 基本使用
3. CoreGraphic框架解析(三)—— 类波浪线的实现
4. CoreGraphic框架解析(四)—— 基本架构补充
5. CoreGraphic框架解析 (五)—— 基于CoreGraphic的一个简单绘制示例 (一)
6. CoreGraphic框架解析 (六)—— 基于CoreGraphic的一个简单绘制示例 (二)
7. CoreGraphic框架解析 (七)—— 基于CoreGraphic的一个简单绘制示例 (三)
8. CoreGraphic框架解析 (八)—— 基于CoreGraphic的一个简单绘制示例 (四)
9. CoreGraphic框架解析 (九)—— 一个简单小游戏 (一)
10. CoreGraphic框架解析 (十)—— 一个简单小游戏 (二)
11. CoreGraphic框架解析 (十一)—— 一个简单小游戏 (三)
12. CoreGraphic框架解析 (十二)—— Shadows 和 Gloss (一)
源码
1. Swift
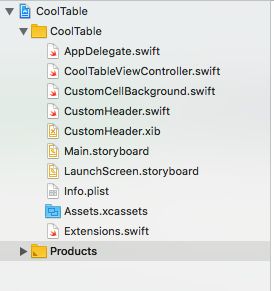
首先看下工程组织结构
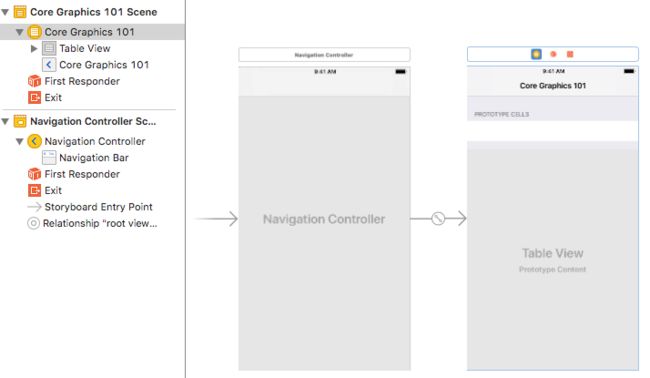
看一下sb中的内容
下面就是源码了
1. CoolTableViewController.swift
import UIKit
class CoolTableViewController: UITableViewController {
let thingsToLearn = ["Drawing Rects", "Drawing Gradients", "Drawing Arcs"]
let thingsLearned = ["Table Views", "UIKit", "Swift"]
override func numberOfSections(in tableView: UITableView) -> Int {
return 2
}
override func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, numberOfRowsInSection section: Int) -> Int {
return section == 0 ? thingsToLearn.count : thingsLearned.count
}
override func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, cellForRowAt indexPath: IndexPath) -> UITableViewCell {
let cell = tableView.dequeueReusableCell(withIdentifier: "Cell", for: indexPath)
if cell.backgroundView?.isKind(of: CustomCellBackground.self) != true {
cell.backgroundView = CustomCellBackground()
}
if cell.selectedBackgroundView?.isKind(of: CustomCellBackground.self) != true {
cell.selectedBackgroundView = CustomCellBackground()
}
cell.textLabel?.text = indexPath.section == 0 ? thingsToLearn[indexPath.row] : thingsLearned[indexPath.row]
return cell
}
override func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, heightForHeaderInSection section: Int) -> CGFloat {
return 50
}
override func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, viewForHeaderInSection section: Int) -> UIView? {
guard let customHeaderView = CustomHeader.loadViewFromNib() else {
return nil
}
customHeaderView.titleLabel.text = self.tableView(tableView, titleForHeaderInSection: section)
if section == 1 {
customHeaderView.lightColor = UIColor(red: 147/255.0, green: 105/255.0, blue: 216/255.0, alpha: 1)
customHeaderView.darkColor = UIColor(red: 72/255.0, green: 22/255.0, blue: 137/255.0, alpha: 1)
}
return customHeaderView
}
override func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, titleForHeaderInSection section: Int) -> String? {
return section == 0 ? "Things We'll Learn" : "Things Already Covered"
}
}
2. CustomCellBackground.swift
import UIKit
class CustomCellBackground: UIView {
let lightGrayColor = UIColor(red: 230/255.0, green: 230/255.0, blue: 230/255.0, alpha: 1)
let separatorColor = UIColor(red: 208/255.0, green: 208/255.0, blue: 208/255.0, alpha: 1)
override func draw(_ rect: CGRect) {
let context = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext()!
context.drawLinearGradient(rect: bounds, startColor: UIColor.white, endColor: lightGrayColor)
var strokeRect = bounds
context.setStrokeColor(UIColor.white.cgColor)
context.setLineWidth(1)
strokeRect.size.height -= 1
context.stroke(strokeRect.rectFor1PxStroke())
let startPoint = CGPoint(x: bounds.origin.x, y: bounds.origin.y + bounds.size.height - 1)
let endPoint = CGPoint(x: bounds.origin.x + bounds.width - 1, y: bounds.origin.y + bounds.size.height - 1)
context.draw1PxStroke(startPoint: startPoint, endPoint: endPoint, color: separatorColor)
}
}
3. CustomHeader.swift
import UIKit
class CustomHeader: UIView {
@IBOutlet public var titleLabel: UILabel!
var lightColor = UIColor(red: 105/255.0, green: 179/255.0, blue: 216/255.0, alpha: 1)
var darkColor = UIColor(red: 21/255.0, green: 92/255.0, blue: 136/255.0, alpha: 1)
@IBInspectable var coloredBoxHeight: CGFloat = 40
class func loadViewFromNib() -> CustomHeader? {
let bundle = Bundle.main
let nib = UINib(nibName: "CustomHeader", bundle: bundle)
guard
let view = nib.instantiate(withOwner: CustomHeader())
.first as? CustomHeader
else {
return nil
}
return view
}
override func draw(_ rect: CGRect) {
// Drawing code
var coloredBoxRect = bounds
coloredBoxRect.size.height = coloredBoxHeight
var paperRect = bounds
paperRect.origin.y += coloredBoxHeight
paperRect.size.height = bounds.height - coloredBoxHeight
let context = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext()!
// context.setFillColor(UIColor.red.cgColor)
// context.fill(coloredBoxRect)
//
// context.setFillColor(UIColor.green.cgColor)
// context.fill(paperRect)
let shadowColor = UIColor(red: 0.2, green: 0.2, blue: 0.2, alpha: 0.5)
context.saveGState()
context.setShadow(offset: CGSize(width: 0, height: 2), blur: 3.0, color: shadowColor.cgColor)
context.setFillColor(lightColor.cgColor)
context.fill(coloredBoxRect)
context.restoreGState()
context.drawGlossAndGradient(rect: coloredBoxRect, startColor: lightColor, endColor: darkColor)
context.setStrokeColor(darkColor.cgColor)
context.setLineWidth(1)
context.stroke(coloredBoxRect.rectFor1PxStroke())
}
}
4. Extensions.swift
import UIKit
extension CGContext {
func drawLinearGradient(rect: CGRect, startColor: UIColor, endColor: UIColor) {
let gradient = CGGradient(colorsSpace: nil, colors: [startColor.cgColor, endColor.cgColor] as CFArray, locations: [0, 1])!
let startPoint = CGPoint(x: rect.midX, y: rect.minY)
let endPoint = CGPoint(x: rect.midX, y: rect.maxY)
saveGState()
addRect(rect)
clip()
drawLinearGradient(gradient, start: startPoint, end: endPoint, options: [])
restoreGState()
}
func draw1PxStroke(startPoint: CGPoint, endPoint: CGPoint, color: UIColor) {
saveGState()
setLineCap(.square)
setStrokeColor(color.cgColor)
setLineWidth(1)
move(to: startPoint+0.5)
addLine(to: endPoint)
strokePath()
restoreGState()
}
func drawGlossAndGradient(rect: CGRect, startColor: UIColor, endColor: UIColor) {
drawLinearGradient(rect: rect, startColor: startColor, endColor: endColor)
let glossColor1 = UIColor.white.withAlphaComponent(0.35)
let glossColor2 = UIColor.white.withAlphaComponent(0.1)
var topHalf = rect
topHalf.size.height /= 2
drawLinearGradient(rect: topHalf, startColor: glossColor1, endColor: glossColor2)
}
}
extension CGRect {
func rectFor1PxStroke() -> CGRect {
return CGRect(x: origin.x + 0.5, y: origin.y + 0.5, width: size.width - 1, height: size.height - 1)
}
}
extension CGPoint {
static func +(left: CGPoint, right: CGFloat) -> CGPoint {
return CGPoint(x: left.x + right, y: left.y + right)
}
}
后记
本篇主要讲述了Shadows 和 Gloss,感兴趣的给个赞或者关注~~~