introduction
print(2+3*4) print((2+3)*4) print(2**10) print(6/3) print(7/3) print(7//3) print(7%3) print(3/6) print(3//6) print(3%6) print(2**100)
output
14 20 1024 2.0 2.33333333333 2 1 0.5 0 3 1267650600228229401496703205376
注意:3/6=0.5 3//6=0
逻辑运算符:and or not
2.list
| Operation | Name | Operator Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| indexing | [ ] | Access an element of a sequence |
| concatenation | + | Combine sequences together |
| repetition | * | Concatenate a repeated number of times |
| membership | in | Ask whether an item is in a sequence |
| length | len | Ask the number of items in the sequence |
| slicing | [ : ] | Extract a part of a sequence |
Note that the indices for lists (sequences) start counting with** 0**. The slice operation, myList[1:3], returns a list of items starting with the item indexed by 1 up to but not including the item indexed by 3.
下标从0开始,切片时为左闭右开
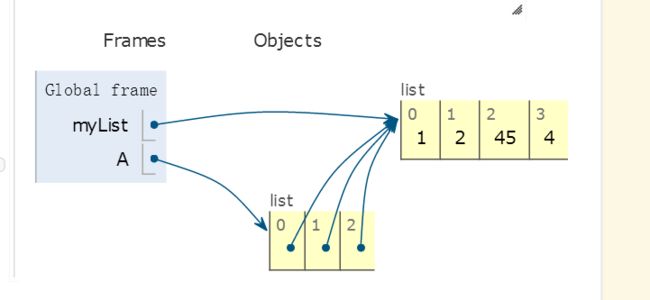
myList = [1,2,3,4] A = [myList]*3 print(A) myList[2]=45 print(A)
A:
[[1,2,45,4],[1,2,45,4],[1,2,45,4]]
** 注意 :** 列表的重复,是引用的对象的重复,如果引用的对象发生了改变,则重复后的list也发生了变化。
The variable A holds a collection of three references to the original list called myList. Note that a change to one element of myList shows up in all three occurrences in A.
| Method | Name | Use Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| append | alist.append(item) | Adds a new item to the end of a list |
| insert | alist.insert(i,item) | Inserts an item at the ith position in a list |
| pop | alist.pop() | Removes and returns the last item in a list |
| pop | alist.pop(i) | Removes and returns the ith item in a list |
| sort | alist.sort() | Modifies a list to be sorted |
| reverse | alist.reverse() | Modifies a list to be in reverse order |
| del | del alist[i] | Deletes the item in the ith position |
| index | alist.index(item) | Returns the index of the first occurrence of item |
| count | alist.count(item) | Returns the number of occurrences of item |
| remove | alist.remove(item) | Removes the first occurrence of item |
- range,左闭右开
>>> range(10)
range(0, 10)
>>> list(range(10))
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
>>> range(5,10)
range(5, 10)
>>> list(range(5,10))
[5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
>>> list(range(5,10,2))
[5, 7, 9]
>>> list(range(10,1,-1))
[10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2]
- string
>>> myName
'David'
>>> myName.upper()
'DAVID'
>>> myName.center(10)
' David '
>>> myName.find('v')
2
>>> myName.split('v')
['Da', 'id']
| Method | Name | Use Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| center | astring.center(w) | Returns a string centered in a field of size w |
| count | astring.count(item) | Returns the number of occurrences of item in the string |
| ljust | astring.ljust(w) | Returns a string left-justified in a field of size w |
| lower | astring.lower() | Returns a string in all lowercase |
| rjust | astring.rjust(w) | Returns a string right-justified in a field of size w |
| find | astring.find(item) | Returns the index of the first occurrence of item |
| split | astring.split(schar) | Splits a string into substrings at schar |
- list与string之间的区别:list可以被改变,string不可以.
- tuple与list很相似,但是tuple不可变,list可变
3.set
| Operation | Name | Operator Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| membership | in | Set membership |
| length | len | Returns the cardinality of the set |
| 丨 | aset丨 otherset | Returns a new set with all elements from both sets |
| & | aset & otherset | Returns a new set with only those elements common to both sets |
| - | aset - otherset | Returns a new set with all items from the first set not in second |
| <= | aset <= otherset | Asks whether all elements of the first set are in the second |
| Method | Name | Use Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| union | aset.union(otherset) | Returns a new set with all elements from both sets |
| intersection | aset.intersection(otherset) | Returns a new set with only those elements common to both sets |
| difference | aset.difference(otherset) | Returns a new set with all items from first set not in second |
| issubset | aset.issubset(otherset) | Asks whether all elements of one set are in the other |
| add | aset.add(item) | Adds item to the set |
| remove | aset.remove(item) | Removes item from the set |
| pop | aset.pop() | Removes an arbitrary element from the set |
| clear | aset.clear() | Removes all elements from the set |
>>> mySet
{False, 4.5, 3, 6, 'cat'}
>>> yourSet = {99,3,100}
>>> mySet.union(yourSet)
{False, 4.5, 3, 100, 6, 'cat', 99}
>>> mySet | yourSet
{False, 4.5, 3, 100, 6, 'cat', 99}
>>> mySet.intersection(yourSet)
{3}
>>> mySet & yourSet
{3}
>>> mySet.difference(yourSet)
{False, 4.5, 6, 'cat'}
>>> mySet - yourSet
{False, 4.5, 6, 'cat'}
>>> {3,100}.issubset(yourSet)
True
>>> {3,100}<=yourSet
True
>>> mySet.add("house")
>>> mySet
{False, 4.5, 3, 6, 'house', 'cat'}
>>> mySet.remove(4.5)
>>> mySet
{False, 3, 6, 'house', 'cat'}
>>> mySet.pop()
False
>>> mySet
{3, 6, 'house', 'cat'}
>>> mySet.clear()
>>> mySet
set()
>>>
4.dict
| Operator | Use | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| [] | myDict[k] | Returns the value associated with k, otherwise its an error |
| in | key in adict | Returns True if key is in the dictionary, False otherwise |
| del | del adict[key] | Removes the entry from the dictionary |
| Method | Name | Use Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| keys | adict.keys() | Returns the keys of the dictionary in a dict_keys object |
| values | adict.values() | Returns the values of the dictionary in a dict_values object |
| items | adict.items() | Returns the key-value pairs in a dict_items object |
| get | adict.get(k) | Returns the value associated with k, None otherwise |
| get | adict.get(k,alt) | Returns the value associated with k, alt otherwise |
5input and output
aName = input('Please enter your name: ')
output:
>>> print("Hello")
Hello
>>> print("Hello","World")
Hello World
>>> print("Hello","World", sep="***")
Hello***World
>>> print("Hello","World", end="***")
Hello World***>>>
print(aName, "is", age, "years old.")
print("%s is %d years old." % (aName, age))
| Character | Output Format |
|---|---|
| d, i | Integer |
| u | Unsigned integer |
| f | Floating point as m.ddddd |
| e | Floating point as m.ddddde+/-xx |
| E | Floating point as m.dddddE+/-xx |
| g | Use %e for exponents less than −4−4 or greater than +5+5, otherwise use %f |
| c | Single character |
| s | String, or any Python data object that can be converted to a string by using the str function. |
| % | Insert a literal % character |
| Modifier | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
| number | %20d | Put the value in a field width of 20 |
| - | %-20d | Put the value in a field 20 characters wide, left-justified |
| + | %+20d | Put the value in a field 20 characters wide, right-justified |
| 0 | %020d | Put the value in a field 20 characters wide, fill in with leading zeros. |
| . | %20.2f | Put the value in a field 20 characters wide with 2 characters to the right of the decimal point. |
| (name) | %(name)d | Get the value from the supplied dictionary using name as the key. |
>>> price = 24
>>> item = "banana"
>>> print("The %s costs %d cents"%(item,price))
The banana costs 24 cents
>>> print("The %+10s costs %5.2f cents"%(item,price))
The banana costs 24.00 cents
>>> print("The %+10s costs %10.2f cents"%(item,price))
The banana costs 24.00 cents
>>> itemdict = {"item":"banana","cost":24}
>>> print("The %(item)s costs %(cost)7.1f cents"%itemdict)
The banana costs 24.0 cents
>>>