搞大了!NASA发现了土卫二上有生命的新证据……

花小蜜
常识科普人
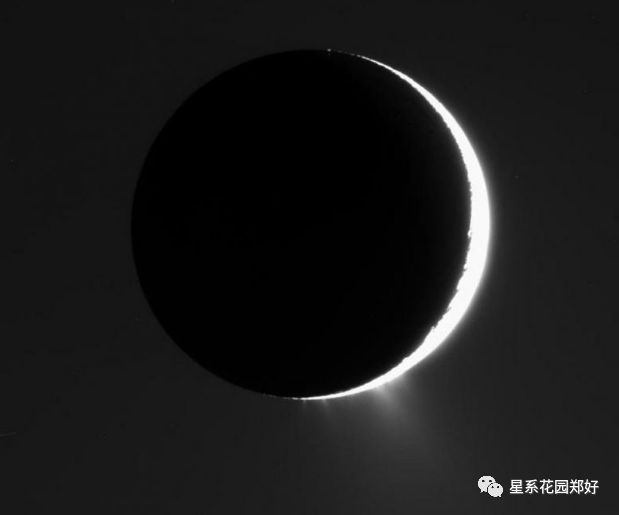
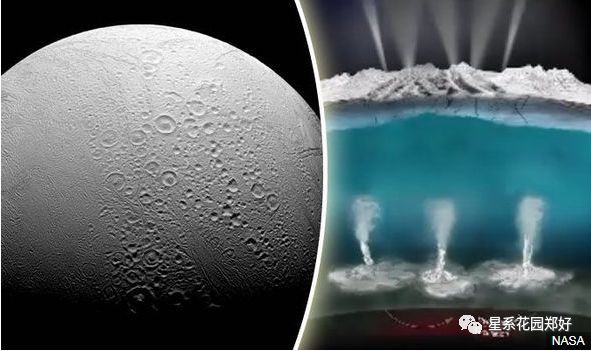
原本土星系中,被人类重点研究与向往的,是大气与海洋情况与地球相仿的土卫六·泰坦星,然而自从土卫二·恩克拉多斯星喷出那华丽的羽泉……人类惊呆了:
虽然太阳系内有海洋的岩石星众多
但土卫二的羽泉让人神往
它不仅证明了冰下液态海洋的存在
还被发现藏着有机物
NASA最新发现的氨基酸让人振奋
https://www.space.com/saturn-moon-enceladus-organic-compounds-in-plumes.html
https://www.sciencealert.com/nasa-just-revealed-enceladus-really-does-contain-the-building-blocks-of-life
https://www.theatlantic.com/science/archive/2019/06/titan-saturn-nasa-dragonfly/592882/
羽泉中被检测出有氨基酸
——————————————
Scientists just found the most basic ingredients for life bursting from an ocean on Saturn's moon Enceladus.
NASA科学家们刚刚发现了生命的最基本成分,从土星的卫星埃塞拉多斯星(2号卫星)的羽泉爆发中侦测到的。
A new analysis of NASA data reveals the presence of organic compounds in the plumes of liquid water that shoot into space from the ocean below Enceladus's icy crust.
对美国宇航局数据的一项新分析揭示了土卫二冰层下,从海洋射入太空的液态羽泉中,确系存在复杂有机化合物。
These compounds, which carry nitrogen and oxygen, play a key role in producing amino acids - complex molecules that serve as the building blocks of proteins. Without proteins, life as we know it on Earth couldn't exist.
这些携带氮和氧的化合物,在产生蛋白质等复杂分子过程中起着关键作用。没有蛋白质,我们在地球上所知道的生活就不可能存在。
Scientists have long suspected that the ocean below Enceladus's surface could harbour the ingredients for life. Researchers had detected other organic molecules coming from the icy moon before, but this is the first time anyone has detected them dissolved in the water.
长期以来,科学家们一直认为,土卫二表面以下的海洋可以储存生命的成分。研究人员已经检测到了来自这个冰冷星球的其他有机分子,但这是第一次有人检测到氨基酸溶解于液态水中。
That's critical, since it means the compounds could undergo deep-sea chemical reactions that produce amino acids.
这是至关重要的,因为这意味着这些化合物可以经历产生氨基酸的深海化学反应。
These findings were published Wednesday in the journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
这些发现发表在本周三的《皇家天文学会月刊》上。
"This work shows that Enceladus' ocean has reactive building blocks in abundance, and it's another green light in the investigation of the habitability of Enceladus," Frank Postberg, a co-author of the study, said in a press release.
该研究的合著者弗兰克·珀斯伯格在一份新闻稿中说:“这项研究表明,恩克拉多斯星的海洋有大量的反应性堆积,这是研究土星的二号卫星可以住人的另一个绿灯。”
氨基酸将在其深海创建生命
——————————————
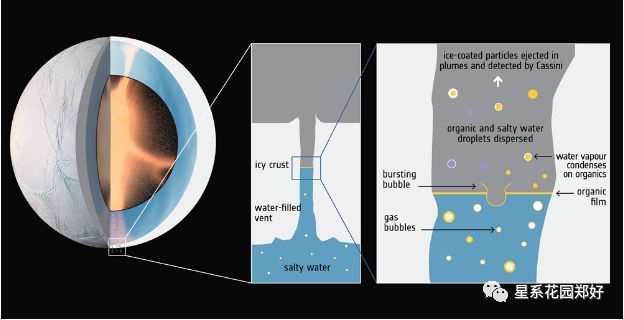
On Enceladus, jets of ocean water and ice regularly shoot out into space through warm cracks in the moon's crust.
在土卫二上,海水和冰的射流经常通过该星球的温暖裂缝射入太空。
The NASA scientists behind the new study analysed data on the chemical composition of those plumes, and found several new organic compounds, some containing nitrogen and some containing oxygen.
美国宇航局的科学家在这项新的研究之后分析了这些羽泉的化学成分,发现了一些新的有机化合物,一些含有氮和一些含氧。
These compounds were dissolved in the ocean water below Enceladus's surface. They then evaporated with the surface water, condensed, and froze into the moon's icy crust, according to the study. The plumes blew the compounds into space, where NASA's Cassini spacecraft sensed them as it flew nearby.
这些化合物溶解在土卫二表面的海水中。然后,随着地表水蒸发,凝结,冻结到该星球结冰的外壳上,根据该研究。这些羽泉将这些化合物吹向太空,美国宇航局的卡西尼号宇宙飞船在附近飞行时首次察觉到了它们。
The compounds are yet another sign that Enceladus might have its own version of a process that creates life on Earth.
这些化合物是土卫二可能有自己的,类似地球生命演化过程的另一个迹象。
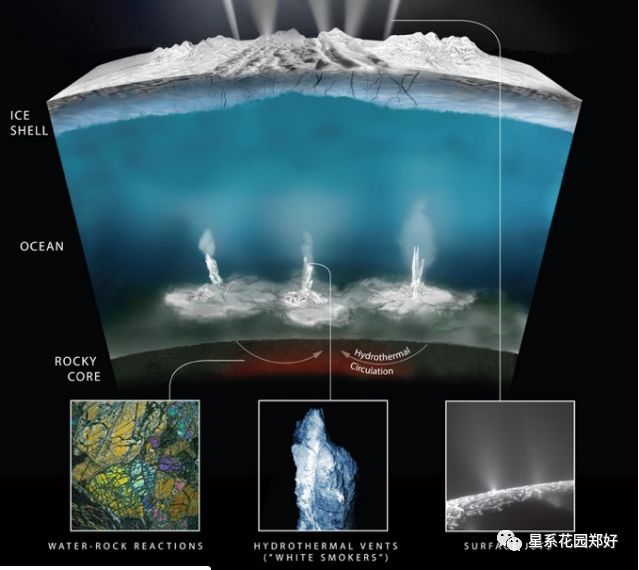
Deep in Earth's oceans, seawater mixes with magma that bubbles up through cracks in the ocean floor. That interaction produces smokyhydrothermal ventsthat can get as hot as 700 degrees Fahrenheit (370 degrees Celsius).
在地球海洋深处,海水与岩浆混合,岩浆从海底的裂缝中冒出来。这种相互作用产生的冒烟热液喷口温度可达700华氏度(370摄氏度)。
The vents spew hydrogen-rich hot water, fuelling chemical reactions that transform organic compounds into amino acids. Those amino acids can then stack onto each other like Legos to form proteins, which are crucial for replicating the genetic information that creates life.
从通风口喷出富含氢气的热水,加速了化学反应,将有机化合物转化为氨基酸。这些氨基酸可以像乐高积木一样堆积在一起,形成蛋白质高分子,这些蛋白质分子对于复制创造生命的遗传信息至关重要。
This process allows life to develop without the assistance of sunlight. That's important because Enceladus's ice surface is highly reflective and sends what little sunlight the moon receives back into space. Any life there would have to develop in the dark.
这个过程使得生命在没有阳光的帮助下得以发展。这很重要,因为土卫二的冰面高度反光,把该星球接收到的太阳光送回太空。那里的任何生命都必须在黑暗中演化。
Scientists believe that potential hydrothermal vents in the subsurface ocean on Enceladus might work similarly to those on Earth.
科学家们认为,在冰层下的海水里的潜在热液喷口,而土卫二可能类似于地球上初期的环境。
"If the conditions are right, these molecules coming from the deep ocean of Enceladus could be on the same reaction pathway as we see here on Earth," Nozair Khawaja, who led the research team behind the latest discovery, said in a release. "We don't yet know if amino acids are needed for life beyond Earth, but finding the molecules that form amino acids is an important piece of the puzzle."
“如果这些条件是吻合的,这些分子来自于恩克拉多斯的深海,我们可以在地球上看到同样的反应过程,”领导这项最新发现的研究小组的卡瓦贾教授在一次发布会中说。我们还不知道地球以外的生命是否需要氨基酸,但寻找到了形成氨基酸的分子是解开谜题的一个重要部分。
Last year, the team discovered similar organic molecules from the same data. But the molecules were not water-soluble; the researchers believe that they sat on the surface of the Enceladus ocean.
去年,研究小组从相同的数据中发现了类似的有机分子。但是这些分子不是水溶性的,研究人员认为它们是在土卫二海洋的表面。而今,水溶性氨基酸素材从海底喷出被发现……
Such compounds would need to dissolve into ocean water in order to interact with hydrothermal vents and produce life. Until now, scientists weren't sure if organic compounds on Enceladus did that.
这些化合物需要溶解到海水中,以便与热液通风口相互作用并产生生命。直到现在,科学家们还不确定土卫二上的有机化合物是否做到了这一点。
"Here we are finding smaller and soluble organic building blocks – potential precursors for amino acids and other ingredients required for life on Earth," Jon Hillier, another co-author of the study, said in the release.
该研究的另一位合著者乔·希利尔在其论文《释放》中说:“在这里我们发现了更小的和可溶的有机分子——氨基酸和其他地球生命的所需成分的潜在素材。”
卡西尼计划还展示了什么
——————————————
The data scientists used to arrive at both of these findings came from NASA's Cassini mission. The probe launched in 1997 and spent 13 years exploring Saturn and its moons.
科学家们用来得出这两个发现的数据,来自美国宇航局的卡西尼号任务。探测器于1997启动,花了13年时间探索土星及其卫星。
In September 2017, the mission ended when scientists intentionally sent the spacecraft plummeting into Saturn. They did this to avoid contaminating Enceladus or Titan, another nearby moon that could also harbour life, with Earthly microbes.
2017年9月,当科学家有意将飞船坠落土星时,任务结束了。他们这样做是为了避免污染土卫二或泰坦星,然而他们发现另一个附近的星球,它居然也能庇护生命,具有地球上的微生物。
Cassini discovered that Enceladus conceals a global ocean of liquid saltwater below its surface, and photographed jets of that water shooting into space. The probe flew through those plumes and collected data about their composition in 2008.
卡西尼发现,二号卫星恩克拉多斯在其结冰的表面下,隐藏了一个液态水的全球海洋,并且它拍摄了射入太空的羽泉。探测器穿过这些羽状物,收集了自2008年以来它们的成分数据。
Scientists plan to continue studying that and other data collected by Cassini for decades to come.
科学家们计划在未来几十年里继续研究卡西尼号收集的数据。
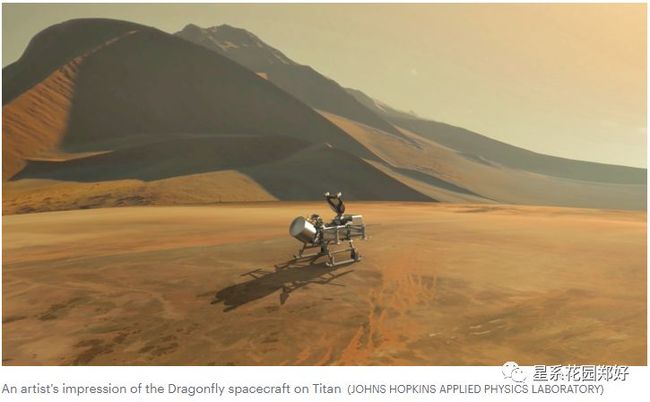
NASA also plans to send a probe to Saturn's moon Titan, which is another a prime target in the search for alien life because of its own abundant organic compounds. That mission is set to launch a nuclear-powered helicopter called Dragonfly toward Titan in 2026.
美国宇航局还计划向土星的最大卫星泰坦星发射一个探测器,泰坦是寻找外星生命的另一个主要目标,因为它本身含有丰富的有机化合物。该任务将于2026发射一艘名为“蜻蜓”的核动力飞船。
The spacecraft is expected to arrive at Titan in 2034, then start hunting for signs of life.
这艘新的太空船预计2034年抵达泰坦,然后开始寻找生命的迹象。

花小蜜
常识科普人
希望NASA这次公布的数据是真的,然后白宫给一大笔钱……他们赶紧发射一个崭新的土卫二飞船,以及立即兑现泰坦星计划!
请基于常识与良知
花5秒钟参与以下的投票