1.摘要
python是一种面向对象的解释型计算机程序设计语言,由荷兰人Guido van Rossum于1989年发明,Python是纯粹的自由软件, 源代码和解释器CPython遵循 GPL(GNU General Public License)协议。Python语法简洁清晰,特色之一是强制用空白符(white space)作为语句缩进。
本系统是基于Python的Flask框架web建设项目实现的。系统参照小米社区网站http://bbs.xiaomi.cn/,设计该系统目的在于给阅读爱好者书写并分享喜爱的文章,大家可以在网站上发表自己的言论和作品,点赞收藏或者评论自己喜爱的推文等等。
2.系统概要说明
2.1开发环境简介
MySQL简介
MySQL是一个关系型数据库管理系统,由瑞典MySQL AB 公司开发,目前属于 Oracle 旗下产品。MySQL 是最流行的关系型数据库管理系统之一,在 WEB 应用方面,MySQL是最好的 RDBMS (Relational Database Management System,关系数据库管理系统) 应用软件。
关系数据库将数据保存在不同的表中,而不是将所有数据放在一个大仓库内,这样就增加了速度并提高了灵活性。
MySQL所使用的 SQL 语言是用于访问数据库的最常用标准化语言。MySQL 软件采用了双授权政策,分为社区版和商业版,由于其体积小、速度快、总体拥有成本低,尤其是开放源码这一特点,一般中小型网站的开发都选择 MySQL 作为网站数据库。
Navicat for MySQL简介
Navicat for MySQL是强大的可视化数据库管理工具,是一套专为 MySQL 设计的高性能数据库管理及开发工具。它可以用于任何版本 3.21 或以上的 MySQL数据库服务器,并支持大部份 MySQL 最新版本的功能,包括触发器、存储过程、函数、事件、视图、管理用户等。
Python简介
Python, 是一种面向对象的解释型计算机程序设计语言,由荷兰人Guido van Rossum于1989年发明,第一个公开发行版发行于1991年。
Python是纯粹的自由软件, 源代码和解释器CPython遵循 GPL(GNU General Public License)协议。Python语法简洁清晰,特色之一是强制用空白符(white space)作为语句缩进。
Python具有丰富和强大的库。它常被昵称为胶水语言,能够把用其他语言制作的各种模块(尤其是C/C++)很轻松地联结在一起。
Pycharm简介
PyCharm是一种Python IDE,带有一整套可以帮助用户在使用Python语言开发时提高其效率的工具,比如调试、语法高亮、Project管理、代码跳转、智能提示、自动完成、单元测试、版本控制。此外,该IDE提供了一些高级功能,以用于支持Django框架下的专业Web开发。
首先,PyCharm用于一般IDE具备的功能,比如, 调试、语法高亮、Project管理、代码跳转、智能提示、自动完成、单元测试、版本控制
另外,PyCharm还提供了一些很好的功能用于Django开发,同时支持Google App Engine,更酷的是,PyCharm支持IronPython。
2.2系统功能实现
注册功能:用户注册开发给所有人,注册用户需要填写账号、密码、昵称等信息。
登陆功能:拥有该网站使用权的用户可以进行登陆,只有进行登陆的用户才可以发布、评论、收藏、点赞文章,当要退出登陆时可以点击注销。
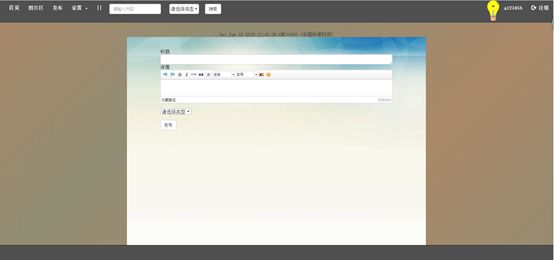
发布功能:拥有账号的用户登录后可以发布自己喜欢的文章,发布文章需要填写文章标题,文章内容和文章的类型,同时发布时可以选择字体的格式、大小或表情包。
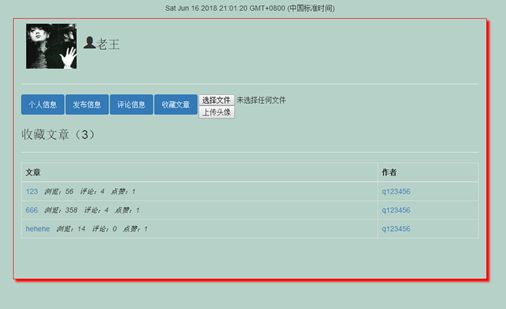
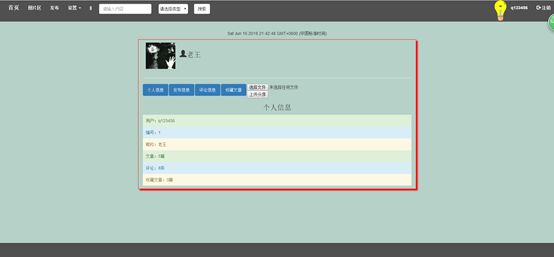
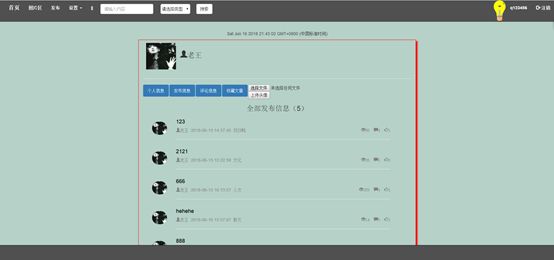
个人中心:个人中心是用户登陆或未登陆时可以访问到的界面,未登录时可以访问别人的个人中心,但不具有修改权限,只能查看别人的信息,登陆时可以访问自己的个人中心并具有修改权限。
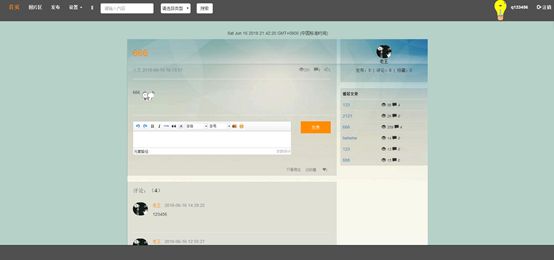
评论功能:拥有账号的用户登陆后可以随意评论文章,发表自己的意见。
收藏功能:拥有账号的用户登录后可以收藏自己喜爱的文章,并在个人中心可以查看已收藏的文章。
点赞功能:拥有账号的用户登陆后对喜爱的文章可以点赞支持。
高级分类功能:分类可以使读者在搜索自己喜爱的文章时更加方便,根据所分类别可以更快找到自己想要的文章。
排序功能:排序按最新发布或热度点击量进行排序,方便读者筛选想要的文章。
上传头像功能:拥有账号的用户登陆后可以上传自己喜欢的头像。
模糊搜索功能:模糊搜索、组合搜索可以帮助用户根据搜素字段搜素出喜爱的文章。
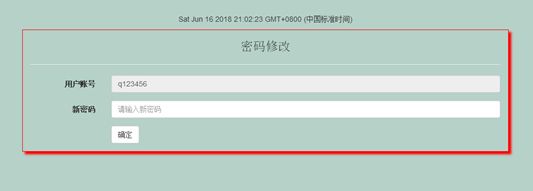
修改密码功能:修改密码功能帮助想修改密码的用户修改密码,保证账号安全性。
推荐功能:推荐功能根据阅读数推荐相应的文章,超过一定的阅读数就会被放在首页的推荐处,相同原理也可以推荐作者。
密码保护功能:密码保护用于密码存进数据库时进行加密,防止数据库被盗时用户账号密码外泄。
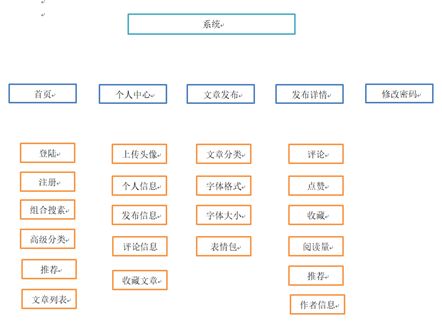
3.网站结构设计
3.1网站结构图
3.2代码实现
3.2.1登陆
class="login">
3.2.2注册
class="login">
3.2.3组合搜索
3.2.4高级分类
3.2.5推荐
| 推荐作者 | |
|---|---|
|
{% if foo.img is none %}
"{{ url_for('yonghu',username_id=foo.author_id,tag=1) }}">
|
文章数:{{ foo.fabu | length }} |
| 推荐文章 | |
|---|---|
| "{{ url_for('fabuview',fabu_id=foo.id) }}">{{ foo.title }} | class="glyphicon glyphicon-eye-open"> {{ foo.yuedu }} class="glyphicon glyphicon-comment"> {{ foo.comments|length }} |
3.2.6上传头像
{% if img is none %}
 "https://ss1.bdstatic.com/70cFvXSh_Q1YnxGkpoWK1HF6hhy/it/u=3298685419,1477967578&fm=27&gp=0.jpg"
style="width: 100px">
{% else %}
"https://ss1.bdstatic.com/70cFvXSh_Q1YnxGkpoWK1HF6hhy/it/u=3298685419,1477967578&fm=27&gp=0.jpg"
style="width: 100px">
{% else %}
 "/static/{{ img }}"
style="width: 100px">
{% endif %}
{% if sessionusername %}
"/static/{{ img }}"
style="width: 100px">
{% endif %}
{% if sessionusername %}
{% else %}
{% endif %}
3.2.7收藏
3.2.8点赞
3.2.9密码修改
3.2.10文章列表
{% for foo in fabus %}
class="fabukuai">
class="daohang-touxiang">
{% if foo.author.img is none %}
"{{ url_for('yonghu',username_id=foo.author_id,tag=1) }}">
 "https://ss1.bdstatic.com/70cFvXSh_Q1YnxGkpoWK1HF6hhy/it/u=3298685419,1477967578&fm=27&gp=0.jpg"
style="width: 50px">
{% else %}
"{{ url_for('yonghu',username_id=foo.author_id,tag=1) }}">
"https://ss1.bdstatic.com/70cFvXSh_Q1YnxGkpoWK1HF6hhy/it/u=3298685419,1477967578&fm=27&gp=0.jpg"
style="width: 50px">
{% else %}
"{{ url_for('yonghu',username_id=foo.author_id,tag=1) }}">
 "/static/{{ foo.author.img }}" style="width: 50px">
{% endif %}
class="daohang-neirong">
"/static/{{ foo.author.img }}" style="width: 50px">
{% endif %}
class="daohang-neirong">
<a
href="{{ url_for('fabuview',fabu_id=foo.id) }}">{{ foo.title }}
"{{ url_for('yonghu',username_id=foo.author_id,tag=1) }}"><span
class="glyphicon glyphicon-user">{{ foo.author.nickname }} 
{{ foo.creat_time }} 
{{ foo.leixing }}
class="glyphicon glyphicon-thumbs-up neirong-right">{{ foo.dianzangs|length }}
class="glyphicon glyphicon-comment neirong-right">{{ foo.comments|length }}
class="glyphicon glyphicon-eye-open neirong-right">{{ foo.yuedu }}
class="clear">
class="clear">
{# {{ foo.detail|safe }}
#}
{% endfor %}
3.3界面实现效果
3.3.1母版导航条
![]()
3.3.2首页
3.3.3登陆
3.3.4注册
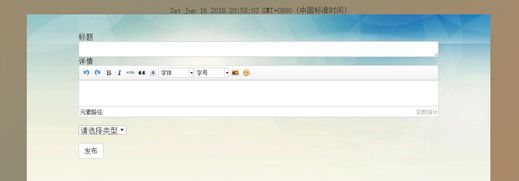
3.3.5发布页
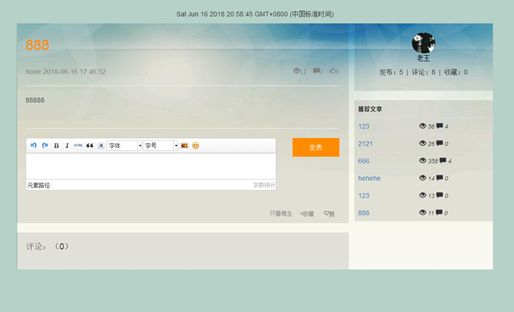
3.3.6发布详情页
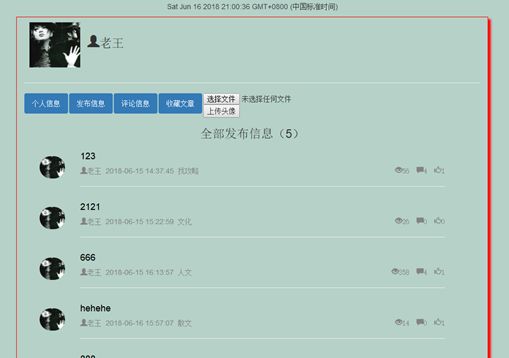
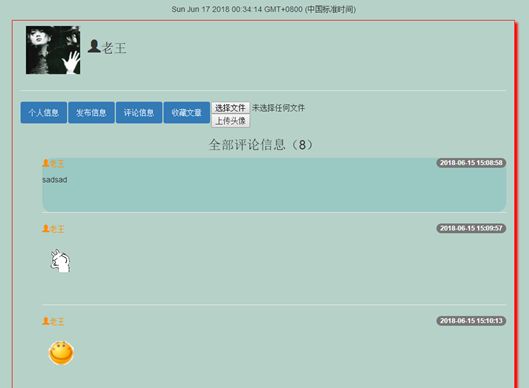
3.3.7个人中心页
3.3.8密码修改页
4.模块详细设计
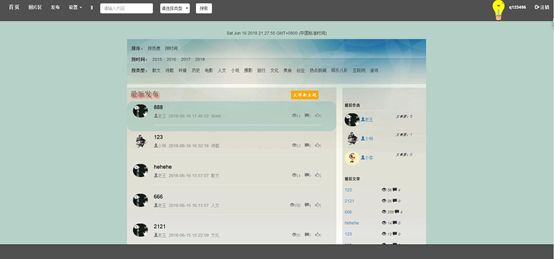
4.1首页
# 跳转首页。 @app.route('/') def daohang(): pl = request.args.get('pl') # 接收顺序排列的关键词,接收不到就按时间排列 if pl == '按热度': context = { 'fabus': Fabu.query.order_by('-yuedu').all(), 'author': User.query.all(), 'ydfabu': Fabu.query.filter(Fabu.yuedu > 5).all() # 当发布的文章阅读量大于多少时取出这些文章,显示在首页的推荐文章 # order_by('-creat_time')按时间降序排列,Fabu.query.all()查出了Fabu类的所有元组 } return render_template('daohang.html', **context) else: context = { 'fabus': Fabu.query.order_by('-creat_time').all(), 'author': User.query.all(), 'ydfabu': Fabu.query.filter(Fabu.yuedu > 5).all() # 当发布的文章阅读量大于多少时取出这些文章,显示在首页的推荐文章 # order_by('-creat_time')按时间降序排列,Fabu.query.all()查出了Fabu类的所有元组 } return render_template('daohang.html', **context)
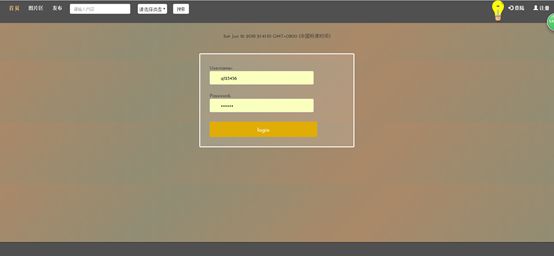
4.2登陆
# 跳转登陆。 @app.route('/denglu/', methods=['GET', 'POST']) # methods定义它有两种请求方式 def denglu(): if request.method == 'GET': return render_template('denglu.html') else: username = request.form.get('user') # post请求模式,安排对象接收数据 password = request.form.get('pass') user = User.query.filter(User.username == username).first() # 作查询,并判断 if user: # 判断用户名 if user.check_password(password): # 判断密码 session['user'] = username # 利用session添加传回来的值username session['user_id'] = user.id session.permanent = True # 设置session过期的时间 return redirect(url_for('daohang')) else: return u'用户密码错误' else: return u'用户不存在,请先注册'
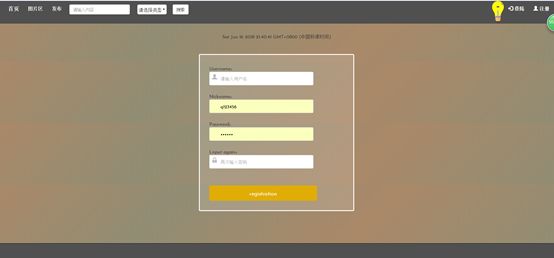
4.3注册
# 跳转注册。 @app.route('/zhuce/', methods=['GET', 'POST']) # methods定义它有两种请求方式,因为它在表单的请求是post,类似我们在idea中的sava请求模式 def zhuce(): if request.method == 'GET': return render_template('zhuce.html') else: username = request.form.get('user') # post请求模式,安排对象接收数据 password = request.form.get('pass') nickname = request.form.get('nickname') user = User.query.filter(User.username == username).first() # 作查询,并判断 if user: return u'该用户已存在' else: user = User(username=username, password=password, nickname=nickname) # 将对象接收的数据赋到User类中,即存到数据库 db.session.add(user) # 执行操作 db.session.commit() return redirect(url_for('denglu')) # redirect重定向
4.4注销
# 跳转注销。 @app.route('/logout') def logout(): session.clear() # 注销时删除所有session return redirect(url_for('daohang')) 4.5密码修改 # 跳转密码修改页。 @app.route('/password_update/') def password_update(user_id): users = User.query.filter(User.id == user_id).first() # 查询出要修改密码的该用户 return render_template('password_update.html', users=users) # 跳转修改密码后接受数据。 @app.route('/password_update1/', methods=['POST']) def password_update1(): username = request.form.get('username') # 接收username的值,知道要修改的是哪个用户 password = request.form.get('password') users = User.query.filter(User.username == username).first() # 查询出要修改用户的整条信息 users.password = password # 执行修改 db.session.commit() return redirect(url_for('yonghu', username_id=users.id, tag='1'))
4.6发布
# 跳转发布。 @app.route('/fabu/', methods=['GET', 'POST']) # methods定义它有两种请求方式 @loginFirst # 将decorator定义的增强函数放在待增强函数定义的上面 def fabu(): if request.method == 'GET': return render_template('fabu.html') else: title = request.form.get('title') # post请求模式,安排对象接收数据 detail = request.form.get('detail') leixing = request.form.get('leixing') yuedu = 0 author_id = User.query.filter( User.username == session.get('user')).first().id # 将session get到的user进行查询并取出id放到外键author_id中 fabu = Fabu(title=title, detail=detail, author_id=author_id, leixing=leixing, yuedu=yuedu) # 将对象接收的数据赋到Fabu类中,即存到数据库 db.session.add(fabu) # 执行操作 db.session.commit() # 提交到数据库 return redirect(url_for('daohang')) # redirect重定向
4.7发布详情
# 跳转发布详情 @app.route('/fabuview/') # 和idea的update一样,将id带到控制器 def fabuview(fabu_id): yes = Shoucang.query.filter( # yes用在用户详情页判断是否已收藏的按钮 and_( Shoucang.author_id == session.get('user_id'), Shoucang.fabu_id == fabu_id ) ).first() dzyes = Dianzang.query.filter( # dzyes用在用户详情页判断是否已点赞的按钮 and_( Dianzang.author_id == session.get('user_id'), Dianzang.fabu_id == fabu_id ) ).first() ydfabu = Fabu.query.filter(Fabu.yuedu > 5).all() fa = Fabu.query.filter(Fabu.id == fabu_id).first() # 根据主页带回来的id查询出整条元组记录,丢进fa comments = Comment.query.filter(Comment.fabu_id == fabu_id).all() # 根据带回来的Fabu的id在Comment查询出所有评论 fa.yuedu = fa.yuedu + 1 # 定义浏览功能,每次进去详情页,浏览次数加1 db.session.commit() return render_template('fabuview.html', fa=fa, comments=comments, yes=yes, dzyes=dzyes, ydfabu=ydfabu) # 把值fa丢进键fa,在fabuview.html页面调用
4.8评论
# 跳转评论。 @app.route('/comment/', methods=['POST']) @loginFirst # 装饰器,跳转某页面之前先进行登录 def comment(): detail = request.form.get('pinglun') # post请求模式,安排对象接收数据 author_id = User.query.filter(User.username == session.get('user')).first().id fabu_id = request.form.get('fa_id') comment = Comment(detail=detail, author_id=author_id, fabu_id=fabu_id) # 将对象接收的数据赋到Comment类中,即存到数据库 db.session.add(comment) # 执行操作 db.session.commit() # 提交到数据库 return redirect(url_for('fabuview', fabu_id=fabu_id)) # 重定向到fabuview请求时要带fabu_id
4.9用户详情
# 跳转用户详情 @app.route('/yonghu// ') # 为了把页面分开,我们在html页面传了一个tag参数 def yonghu(username_id, tag): user = User.query.filter(User.id == username_id).first() shoucang = Shoucang.query.filter(Shoucang.author_id == username_id).all() context = { 'userid': user.id, 'username': user.username, 'nickname': user.nickname, 'fabus': user.fabu, 'comments': user.comments, 'shoucang': shoucang, 'img': user.img } # 根据tag的不同去到不同页面,一个请求跳转3个不同页面 if tag == '1': return render_template('yonghu1.html', **context) elif tag == '2': return render_template('yonghu2.html', **context) elif tag == '3': return render_template('yonghu3.html', **context) else: return render_template('yonghu4.html', **context)
4.10组合搜索
@app.route('/search/') def search(): sousuo = request.args.get('sousuo') # args获取关键字,区别form sousuo3 = request.args.get('sousuo3') author = User.query.all() ydfabu = Fabu.query.filter(Fabu.yuedu > 5).all() fabus = Fabu.query.filter( and_( or_( # 两种查询条件 Fabu.title.contains(sousuo), # contains模糊查 Fabu.detail.contains(sousuo) ), Fabu.leixing.contains(sousuo3) ) ).order_by('-creat_time') return render_template('daohang.html', fabus=fabus, author=author, ydfabu=ydfabu) # fabus要和原首页数据模型一样
4.11高级分类
# 跳转高级分类查询 @app.route('/fenlei/') def fenlei(): fenlei = request.args.get('fenlei') # args获取关键字,区别form author = User.query.all() ydfabu = Fabu.query.filter(Fabu.yuedu > 5).all() fenlei_fabus = Fabu.query.filter( or_( # 两种查询条件 Fabu.title.contains(fenlei), # contains模糊查 Fabu.leixing.contains(fenlei), Fabu.creat_time.contains(fenlei) ) ).order_by('-creat_time') return render_template('daohang.html', fabus=fenlei_fabus, author=author, ydfabu=ydfabu) # fabus要和原首页数据模型一样
4.12收藏
# 跳转文章收藏 @app.route('/shoucang/', methods=['POST']) @loginFirst def shoucang(): scfabu_id = request.form.get('scfabu_id') scuser_id = request.form.get('scuser_id') shoucang = Shoucang(fabu_id=scfabu_id, author_id=scuser_id) db.session.add(shoucang) # 执行操作 db.session.commit() # 提交到数据库 return redirect(url_for('fabuview', fabu_id=scfabu_id))
4.13点赞
# 跳转文章点赞 @app.route('/dianzang/', methods=['POST']) @loginFirst def dianzang(): dzfabu_id = request.form.get('dzfabu_id') dzuser_id = request.form.get('dzuser_id') dianzang = Dianzang(fabu_id=dzfabu_id, author_id=dzuser_id) db.session.add(dianzang) # 执行操作 db.session.commit() # 提交到数据库 return redirect(url_for('fabuview', fabu_id=dzfabu_id))
4.14上传头像
# 上传头像 @app.route('/uploadLogo/', methods=['GET', 'POST']) def uploadLogo(user_id): user = User.query.filter(User.id == user_id).first() f = request.files['logo'] basepath = os.path.dirname(__file__) # 当前文件所在路径 upload_path = os.path.join(basepath, 'static/img', f.filename) # 注意:没有的文件夹一定要先创建,不然会提示没有该路径 f.save(upload_path) user.img = 'img/' + f.filename db.session.commit() return redirect(url_for('yonghu', username_id=user_id, tag=1))
5.数据库设计
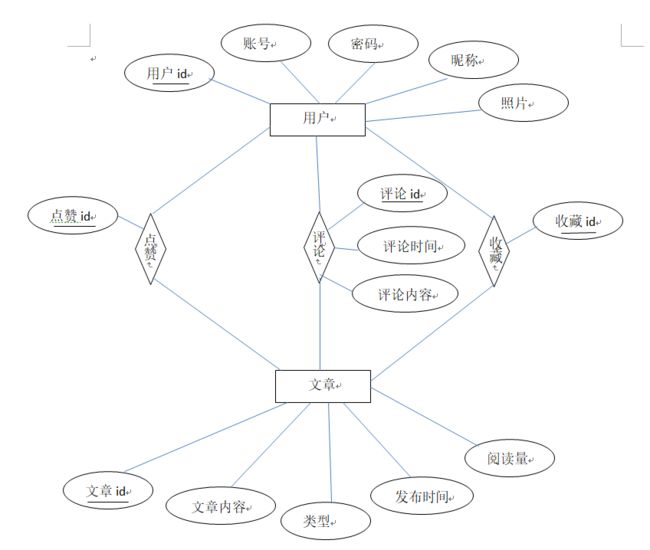
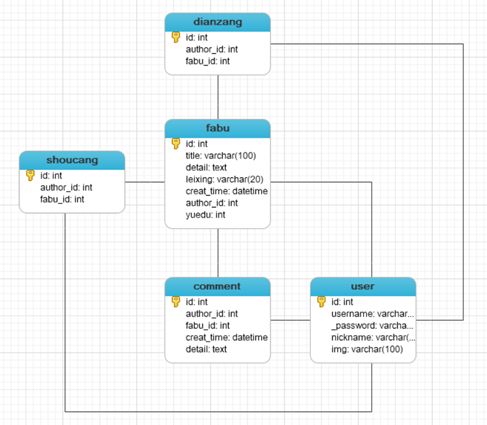
5.1E-R图
5.2逻辑模型设计
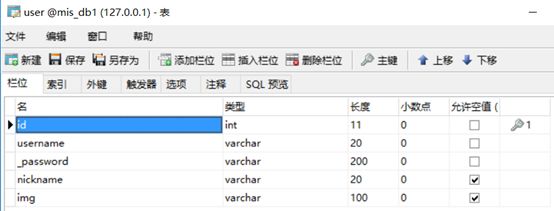
用户表:
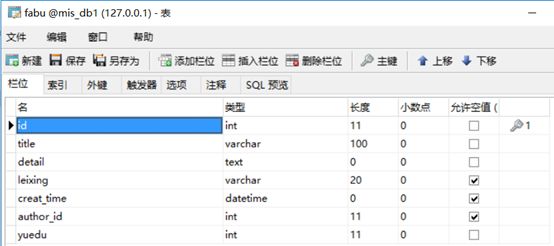
文章发布表:
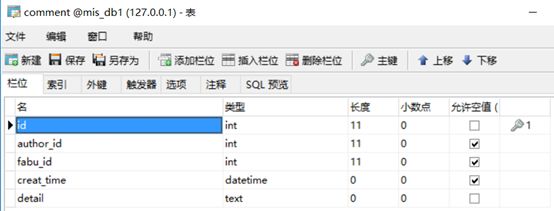
评论表:
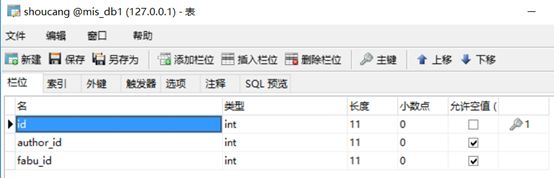
收藏表:
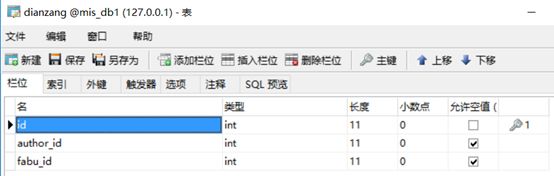
点赞表:
5.3数据库连接关系
5.4物理设计(代码实现)
class User(db.Model): # 创建类User __tablename__ = 'user' # 类对应的表名user id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True, autoincrement=True) # autoincrement自增长 username = db.Column(db.String(20), nullable=False) # nullable是否为空 _password = db.Column(db.String(200), nullable=False) # 密码加密内部使用 nickname = db.Column(db.String(20), nullable=True) img = db.Column(db.String(100)) @property # 定义函数,需要用属性时可以用函数代替 def password(self): # 密码加密外部使用 return self._password @password.setter def password(self, row_password): # 密码进来时进行加密,generate_password_hash是一个密码加盐哈希函数,生成的哈希值可通过check_password_hash()进行验证。 self._password = generate_password_hash(row_password) def check_password(self, row_password): # check_password_hash函数用于验证经过generate_password_hash哈希的密码。若密码匹配,则返回真,否则返回假。 result = check_password_hash(self._password, row_password) return result class Fabu(db.Model): # 问答 __tablename__ = 'fabu' id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True, autoincrement=True) title = db.Column(db.String(100), nullable=False) detail = db.Column(db.Text, nullable=False) leixing = db.Column(db.String(20), nullable=True) creat_time = db.Column(db.DateTime, default=datetime.now) # 提交时间会自己赋值 author_id = db.Column(db.Integer, db.ForeignKey('user.id')) # 数据类型是db.Integer,db.ForeignKey参数指定外键是哪个表中哪个id author = db.relationship('User', backref=db.backref('fabu')) # 建立关联,其author属性将返回与问答相关联的用户实例,相当于数据库中的表连接 # 第一个参数表明这个关系的另一端是哪个类,第二个参数backref,将向User类中添加一个fabu属性,从而定义反向关系,这一属性可访问Fabu类,获取的是模型对象 yuedu = db.Column(db.Integer, nullable=False) class Comment(db.Model): # 评论 __tablename__ = 'comment' id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True, autoincrement=True) author_id = db.Column(db.Integer, db.ForeignKey('user.id')) fabu_id = db.Column(db.Integer, db.ForeignKey('fabu.id')) creat_time = db.Column(db.DateTime, default=datetime.now) detail = db.Column(db.Text, nullable=False) fabu = db.relationship('Fabu', backref=db.backref('comments', order_by=creat_time.desc)) # order_by=creat_time.desc按时间降序 author = db.relationship('User', backref=db.backref('comments')) class Shoucang(db.Model): # 收藏 __tablename__ = 'shoucang' id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True, autoincrement=True) author_id = db.Column(db.Integer, db.ForeignKey('user.id')) fabu_id = db.Column(db.Integer, db.ForeignKey('fabu.id')) fabu = db.relationship('Fabu', backref=db.backref('shoucangs')) author = db.relationship('User', backref=db.backref('shoucangs')) class Dianzang(db.Model): # 点赞 __tablename__ = 'dianzang' id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True, autoincrement=True) author_id = db.Column(db.Integer, db.ForeignKey('user.id')) fabu_id = db.Column(db.Integer, db.ForeignKey('fabu.id')) fabu = db.relationship('Fabu', backref=db.backref('dianzangs')) author = db.relationship('User', backref=db.backref('dianzangs'))
6.系统实现的关键算法与数据结构
主要运用前端from表单传参数到后台,后台执行代码后跳转页面并携带数据,然后数据在页面上展示或循环展示,以及前后端运用多个if判断函数,session在上下文处理器的运用等。
6.1后台代码if函数判断
@app.route('/') def daohang(): pl = request.args.get('pl') # 接收顺序排列的关键词,接收不到就按时间排列 if pl == '按热度': context = { 'fabus': Fabu.query.order_by('-yuedu').all(), 'author': User.query.all(), 'ydfabu': Fabu.query.filter(Fabu.yuedu > 5).all() # 当发布的文章阅读量大于多少时取出这些文章,显示在首页的推荐文章 # order_by('-creat_time')按时间降序排列,Fabu.query.all()查出了Fabu类的所有元组 } return render_template('daohang.html', **context) else: context = { 'fabus': Fabu.query.order_by('-creat_time').all(), 'author': User.query.all(), 'ydfabu': Fabu.query.filter(Fabu.yuedu > 5).all() # 当发布的文章阅读量大于多少时取出这些文章,显示在首页的推荐文章 # order_by('-creat_time')按时间降序排列,Fabu.query.all()查出了Fabu类的所有元组 } return render_template('daohang.html', **context)
6.2前台代码if函数判断
{% if foo.author.img is none %}
"{{ url_for('yonghu',username_id=foo.author_id,tag=1) }}">
 "https://ss1.bdstatic.com/70cFvXSh_Q1YnxGkpoWK1HF6hhy/it/u=3298685419,1477967578&fm=27&gp=0.jpg"
style="width: 50px">
{% else %}
"{{ url_for('yonghu',username_id=foo.author_id,tag=1) }}">
"https://ss1.bdstatic.com/70cFvXSh_Q1YnxGkpoWK1HF6hhy/it/u=3298685419,1477967578&fm=27&gp=0.jpg"
style="width: 50px">
{% else %}
"{{ url_for('yonghu',username_id=foo.author_id,tag=1) }}">
 "/static/{{ foo.author.img }}" style="width: 50px">
{% endif %}
"/static/{{ foo.author.img }}" style="width: 50px">
{% endif %}
6.3前台代码数据循环
{% for foo in fabus %}
class="fabukuai">
class="daohang-touxiang">
{% if foo.author.img is none %}
"{{ url_for('yonghu',username_id=foo.author_id,tag=1) }}">
 "https://ss1.bdstatic.com/70cFvXSh_Q1YnxGkpoWK1HF6hhy/it/u=3298685419,1477967578&fm=27&gp=0.jpg"
style="width: 50px">
{% else %}
"{{ url_for('yonghu',username_id=foo.author_id,tag=1) }}">
"https://ss1.bdstatic.com/70cFvXSh_Q1YnxGkpoWK1HF6hhy/it/u=3298685419,1477967578&fm=27&gp=0.jpg"
style="width: 50px">
{% else %}
"{{ url_for('yonghu',username_id=foo.author_id,tag=1) }}">
 "/static/{{ foo.author.img }}" style="width: 50px">
{% endif %}
class="daohang-neirong">
"/static/{{ foo.author.img }}" style="width: 50px">
{% endif %}
class="daohang-neirong">
<a
href="{{ url_for('fabuview',fabu_id=foo.id) }}">{{ foo.title }}
"{{ url_for('yonghu',username_id=foo.author_id,tag=1) }}"><span
class="glyphicon glyphicon-user">{{ foo.author.nickname }} 
{{ foo.creat_time }} 
{{ foo.leixing }}
class="glyphicon glyphicon-thumbs-up neirong-right">{{ foo.dianzangs|length }}
class="glyphicon glyphicon-comment neirong-right">{{ foo.comments|length }}
class="glyphicon glyphicon-eye-open neirong-right">{{ foo.yuedu }}
class="clear">
class="clear">
{# {{ foo.detail|safe }}
#}
{% endfor %}
6.4前台form表单携带参数到后台
6.5session及上下文处理器
session['user'] = username # 利用session添加传回来的值username session['user_id'] = user.id session.permanent = True # 设置session过期的时间 @app.context_processor # 上下文处理器,定义变量然后在所有模板中都可以调用,类似idea中的model def mycontext(): user = session.get('user') user_id = session.get('user_id') if user: return {'sessionusername': user, 'sessionuserid': user_id} # 包装到username,在所有html模板中可调用 else: return {} # 返回空字典,因为返回结果必须是dict
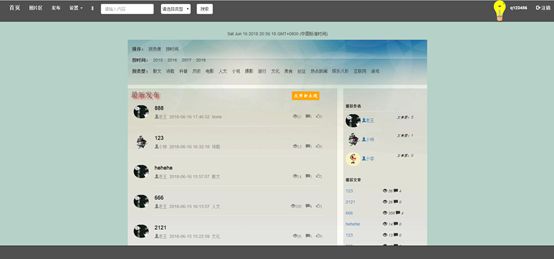
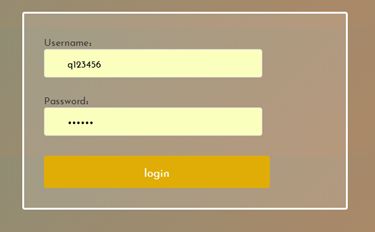
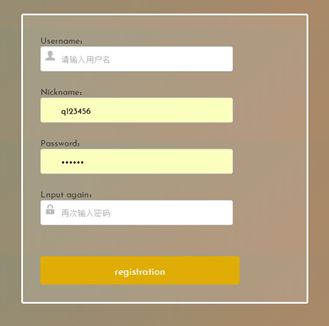
7.成品展示
7.1首页
7.2注册页
7.3登陆页
7.4文章发布页
7.5发布详情页
7.6个人中心页
7.7密码修改页