前言
Android的view绘制流程是一个比较重要的问题,理解好view的绘制流程,对平时开发工作非常有帮助,同时也是面试中常问的问题。
本文尝试从源码角度,结合其他人的博客,描述一下我对view绘制的一些理解
概述
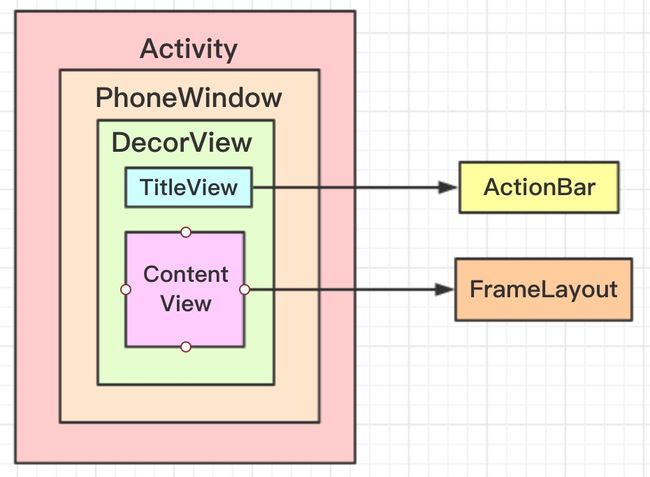
每个Activity都有一个window接口实现PhoneWindow,用于承载用户界面。contentView就是R.id.content,setContentView()就是设置它的子View。
Window
窗口是图像显示的一个容器,独占一个surface实例的显示区域,surface由WindowManagerService分配,看一看成一张画布,由canvas或者openGL在上面进行绘制后,通过SurfaceFlinger将多块surface按一定顺序排列混合好,输出到FrameBuffer中,得以显示。
android.view.Window包含三个核心组件:
- WindowManager.LayoutParams:布局参数
- callback:回调,一般在Activity中实现
- ViewTree:窗口所承载的控件树
PhoneWindow
它是Window接口唯一的具体实现。setContentView()方法设置Activity时,实际上完成了PhoneWindow的ViewTree的设置;而requestWindowFeature()用来定制Activity关联的PhoneWindow的外观,实际上也是将外观特性参数存储到了PhoneWindow的mFeatures中,在窗口绘制阶段生成外观模板时,根据mFeatures生成特定外观。
setContentView()
此方法完成了Activity的contentView创建,但是并没有进行绘制。自定义activity继承自Activity和AppCompatActivity时,此方法的执行逻辑不一样。
- 先说Activity:
public void setContentView(@LayoutRes int layoutResID) {
getWindow().setContentView(layoutResID);
initWindowDecorActionBar();
}
getWindow()返回Activity关联的PhoneWindow:
@Override
public void setContentView(int layoutResID) {
// Note: FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS may be set in the process of installing the window
// decor, when theme attributes and the like are crystalized. Do not check the feature
// before this happens.
if (mContentParent == null) {
// mContentParent即为上面提到的ContentView的父容器,若为空则调用installDecor()生成
installDecor();
} else if (!hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) {
mContentParent.removeAllViews();
}
if (hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) {
final Scene newScene = Scene.getSceneForLayout(mContentParent, layoutResID,
getContext());
transitionTo(newScene);
} else {
// 调用mLayoutInflater.inflate()方法来填充布局
// 填充布局也就是把我们设置的ContentView加入到mContentParent中
mLayoutInflater.inflate(layoutResID, mContentParent);
}
mContentParent.requestApplyInsets();
// cb即为该Window所关联的Activity
final Callback cb = getCallback();
if (cb != null && !isDestroyed()) {
// 调用onContentChanged()回调方法通知Activity窗口内容发生了改变
cb.onContentChanged();
}
mContentParentExplicitlySet = true;
}
- AppCompatActivity:
@Override
public void setContentView(@LayoutRes int layoutResID) {
getDelegate().setContentView(layoutResID);
}
getDelegate()返回继承自AppCompatDelegate的代理类,根据不同api的level调用不同类。但是无论api是多少,这里的逻辑都是一样的。
@Override
public void setContentView(int resId) {
ensureSubDecor();
ViewGroup contentParent = (ViewGroup) mSubDecor.findViewById(android.R.id.content);
contentParent.removeAllViews();
LayoutInflater.from(mContext).inflate(resId, contentParent);
mOriginalWindowCallback.onContentChanged();
}
逻辑比较简单,不多说了。
LayoutInflater.inflate()
setContentView()调用了LayoutInflater.inflate()来进行资源文件解析。
public View inflate(@LayoutRes int resource, @Nullable ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot) {
final Resources res = getContext().getResources();
final XmlResourceParser parser = res.getLayout(resource);
try {
return inflate(parser, root, attachToRoot);
} finally {
parser.close();
}
}
无论是Activity还是AppCompatActivity都把ContentView作为root参数传进去,最终调用inflate(XmlPullParser, viewGroup, boolean)填充布局。
public View inflate(XmlPullParser parser, @Nullable ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot) {
synchronized (mConstructorArgs) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "inflate");
final Context inflaterContext = mContext;
final AttributeSet attrs = Xml.asAttributeSet(parser);
Context lastContext = (Context) mConstructorArgs[0];
mConstructorArgs[0] = inflaterContext;
View result = root;
try {
// Look for the root node.
int type;
// 一直读取xml文件,直到遇到开始标记
while ((type = parser.next()) != XmlPullParser.START_TAG &&
type != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) {
// Empty
}
// 最先遇到的不是开始标记,报错
if (type != XmlPullParser.START_TAG) {
throw new InflateException(parser.getPositionDescription()
+ ": No start tag found!");
}
final String name = parser.getName();
...
// 单独处理标签
if (TAG_MERGE.equals(name)) {
// 若包含标签,父容器(即root参数)不可为空且attachRoot须为true,否则报错
if (root == null || !attachToRoot) {
throw new InflateException(" 单独处理
void rInflate(XmlPullParser parser, View parent, Context context,
AttributeSet attrs, boolean finishInflate) throws XmlPullParserException, IOException {
// 获取当前标记的深度,根标记的深度为0
final int depth = parser.getDepth();
int type;
boolean pendingRequestFocus = false;
while (((type = parser.next()) != XmlPullParser.END_TAG ||
parser.getDepth() > depth) && type != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) {
// 不是开始标记则继续下一次迭代
if (type != XmlPullParser.START_TAG) {
continue;
}
final String name = parser.getName();
// 对一些特殊标记做单独处理
if (TAG_REQUEST_FOCUS.equals(name)) {
pendingRequestFocus = true;
consumeChildElements(parser);
} else if (TAG_TAG.equals(name)) {
parseViewTag(parser, parent, attrs);
} else if (TAG_INCLUDE.equals(name)) {
if (parser.getDepth() == 0) {
throw new InflateException("做处理
parseInclude(parser, context, parent, attrs);
} else if (TAG_MERGE.equals(name)) {
throw new InflateException(" 上面的inflate()和rInflate()方法中都调用了rInflateChildren()方法:
final void rInflateChildren(XmlPullParser parser, View parent, AttributeSet attrs, boolean finishInflate) throws XmlPullParserException, IOException {
rInflate(parser, parent, parent.getContext(), attrs, finishInflate);
}
View的绘制
ViewRoot
View的绘制是由ViewRootImpl负责的。
每个应用窗口window的decorView都有一个ViewRootImpl与之关联,他们之间由WindowManager(确切来说WindowManger接口的实现类WindowManagerImpl,继而调用WindowManagerGlobal类)来维护关系。当ActivityThread调用handleResumeActivity()时,相当于调用了activity的onResume(),decorView与ViewRootImpl建立联系:WindowManager.addView--WindowManagerImpl.addView--WindowManagerGlobal.addView:
public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params,
Display display, Window parentWindow) {
...
root = new ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display);
view.setLayoutParams(wparams);
mViews.add(view);
mRoots.add(root);
mParams.add(wparams);
// do this last because it fires off messages to start doing things
try {
root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
...
}
}
View的绘制是由ViewRootImpl完成,setView内部会调用requestLayout()完成异步刷新请求。
public void setView(View view, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs,
View panelParentView) {
...
// Schedule the first layout -before- adding to the window
// manager, to make sure we do the relayout before receiving
// any other events from the system.
requestLayout();
...
}
@Override
public void requestLayout() {
if (!mHandlingLayoutInLayoutRequest) {
checkThread();
mLayoutRequested = true;
//View绘制入口
scheduleTraversals();
}
}
具体细节需要了解Activity启动流程。
View绘制起点
scheduleTraversals()方法来调度一次完成的绘制流程,向主线程发送一个遍历消息,最终调用ViewRootImpl的performTraversals()调用:
private void performTraversals() {
...
performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
...
performLayout(lp, mWidth, mHeight);
...
performDraw();
...
}
- measure: 判断是否需要重新计算View的大小,需要的话则计算;
- layout: 判断是否需要重新计算View的位置,需要的话则计算;
- draw: 判断是否需要重新绘制View,需要的话则重绘制。
measure阶段
计算每个view需要多大尺寸。
performTraversals()中通过measureHierarchy(),计算出根view的measureSpec,随后调用performMeasure()、onMeasure()计算各层次veiw的大小。
// 传入的desiredWindowXxx为窗口尺寸
private boolean measureHierarchy(final View host, final WindowManager.LayoutParams lp,
final Resources res,
final int desiredWindowWidth, final int desiredWindowHeight) {
int childWidthMeasureSpec;
int childHeightMeasureSpec;
boolean windowSizeMayChange = false;
...
boolean goodMeasure = false;
...
if (!goodMeasure) {
//获取根的measureSpec信息,约束了decorView的宽高
childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(desiredWindowWidth, lp.width);
childHeightMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(desiredWindowHeight, lp.height);
performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
if (mWidth != host.getMeasuredWidth() || mHeight != host.getMeasuredHeight()) {
windowSizeMayChange = true;
}
}
...
return windowSizeMayChange;
}
最终,获取到viewRoot的width黑height的MeasureSpec后,传给performMeasure()。spectMode为EXACTLY,spectSize为window尺寸。
private void performMeasure(int childWidthMeasureSpec, int childHeightMeasureSpec) {
if (mView == null) {
return;
}
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "measure");
try {
mView.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
}
mView即为decorView,执行View.measure()这个不可继承的final方法。
/**
* 调用这个方法来算出一个View应该为多大。参数为父View对其宽高的约束信息。
* 实际的测量工作在onMeasure()方法中进行
*/
public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
// 判断是否需要重新计算measureSpec
boolean optical = isLayoutModeOptical(this);
if (optical != isLayoutModeOptical(mParent)) {
Insets insets = getOpticalInsets();
int oWidth = insets.left + insets.right;
int oHeight = insets.top + insets.bottom;
widthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.adjust(widthMeasureSpec, optical ? -oWidth : oWidth);
heightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.adjust(heightMeasureSpec, optical ? -oHeight : oHeight);
}
// Suppress sign extension for the low bytes
long key = (long) widthMeasureSpec << 32 | (long) heightMeasureSpec & 0xffffffffL;
if (mMeasureCache == null) mMeasureCache = new LongSparseLongArray(2);
// 若mPrivateFlags中包含PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT标记,则强制重新布局
// 比如调用View.requestLayout()会在mPrivateFlags中加入此标记
final boolean forceLayout = (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT) == PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT;
// Optimize layout by avoiding an extra EXACTLY pass when the view is
// already measured as the correct size. In API 23 and below, this
// extra pass is required to make LinearLayout re-distribute weight.
final boolean specChanged = widthMeasureSpec != mOldWidthMeasureSpec
|| heightMeasureSpec != mOldHeightMeasureSpec;
final boolean isSpecExactly = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY
&& MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec) == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
final boolean matchesSpecSize = getMeasuredWidth() == MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec)
&& getMeasuredHeight() == MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
final boolean needsLayout = specChanged
&& (sAlwaysRemeasureExactly || !isSpecExactly || !matchesSpecSize);
// 需要重新布局
if (forceLayout || needsLayout) {
// first clears the measured dimension flag
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET;
resolveRtlPropertiesIfNeeded();
// 先尝试从缓从中获取,若forceLayout为true或是缓存中不存在或是
// 忽略缓存,则调用onMeasure()重新进行测量工作
int cacheIndex = forceLayout ? -1 : mMeasureCache.indexOfKey(key);
if (cacheIndex < 0 || sIgnoreMeasureCache) {
// measure ourselves, this should set the measured dimension flag back
onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;
} else {
// 缓存命中,直接从缓存中取值即可,不必再测量
long value = mMeasureCache.valueAt(cacheIndex);
// Casting a long to int drops the high 32 bits, no mask needed
setMeasuredDimensionRaw((int) (value >> 32), (int) value);
mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;
}
// flag not set, setMeasuredDimension() was not invoked, we raise
// an exception to warn the developer
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET) != PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET) {
throw new IllegalStateException("View with id " + getId() + ": "
+ getClass().getName() + "#onMeasure() did not set the"
+ " measured dimension by calling"
+ " setMeasuredDimension()");
}
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED;
}
mOldWidthMeasureSpec = widthMeasureSpec;
mOldHeightMeasureSpec = heightMeasureSpec;
mMeasureCache.put(key, ((long) mMeasuredWidth) << 32 |
(long) mMeasuredHeight & 0xffffffffL); // suppress sign extension
}
forceLayout为true,表示强制重新布局,可以通过View.requestLayout()来实现;
-
needsLayout为true,这需要specChanged为true(表示本次传入的MeasureSpec与上次传入的不同),并且以下三个条件之一成立:
- sAlwaysRemeasureExactly为true: 该变量默认为false;
- isSpecExactly为false: 若父View对子View提出了精确的宽高约束,则该变量为true,否则为false;
- matchesSpecSize为false: 表示父View的宽高尺寸要求与上次测量的结果不同。
对于decorView来说,实际执行测量工作的是FrameLayout的onMeasure()方法。View.onMeasure():
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}
而FrameLayout.onMeasure():
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int count = getChildCount();
final boolean measureMatchParentChildren =
MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ||
MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
mMatchParentChildren.clear();
int maxHeight = 0;
int maxWidth = 0;
int childState = 0;
//每一个子view最大宽度和最大高度
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = getChildAt(i);
if (mMeasureAllChildren || child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
measureChildWithMargins(child, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec, 0);
final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth,
child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin);
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight,
child.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin);
childState = combineMeasuredStates(childState, child.getMeasuredState());
if (measureMatchParentChildren) {
if (lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT ||
lp.height == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
mMatchParentChildren.add(child);
}
}
}
}
// Account for padding too
// 最大宽度、高度加上父view和前景区域的padding
maxWidth += getPaddingLeftWithForeground() + getPaddingRightWithForeground();
maxHeight += getPaddingTopWithForeground() + getPaddingBottomWithForeground();
// Check against our minimum height and width
// 是否设置了最小高宽,最大的那个设置为最大高宽
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight, getSuggestedMinimumHeight());
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, getSuggestedMinimumWidth());
// Check against our foreground's minimum height and width
// 检查前景图像的最小宽高
final Drawable drawable = getForeground();
if (drawable != null) {
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight, drawable.getMinimumHeight());
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, drawable.getMinimumWidth());
}
setMeasuredDimension(resolveSizeAndState(maxWidth, widthMeasureSpec, childState),
resolveSizeAndState(maxHeight, heightMeasureSpec,
childState << MEASURED_HEIGHT_STATE_SHIFT));
count = mMatchParentChildren.size();
if (count > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = mMatchParentChildren.get(i);
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec;
if (lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
final int width = Math.max(0, getMeasuredWidth()
- getPaddingLeftWithForeground() - getPaddingRightWithForeground()
- lp.leftMargin - lp.rightMargin);
childWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(
width, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
} else {
childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(widthMeasureSpec,
getPaddingLeftWithForeground() + getPaddingRightWithForeground() +
lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin,
lp.width);
}
final int childHeightMeasureSpec;
if (lp.height == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
final int height = Math.max(0, getMeasuredHeight()
- getPaddingTopWithForeground() - getPaddingBottomWithForeground()
- lp.topMargin - lp.bottomMargin);
childHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(
height, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
} else {
childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(heightMeasureSpec,
getPaddingTopWithForeground() + getPaddingBottomWithForeground() +
lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin,
lp.height);
}
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
}
}
FrameLayout是ViewGroup子类,而ViewGroup中有一个View[]类型成员变量mChildren,代表当前viewGroup的所有子view的集合,该变量为private,但是可以通过publish的getChildAt(int position)获取到View[position]的子view,以及getChildCount()获取所有子view数量。
- 通过getChildAt()获取到每一个子view,随后measureChildWithMargins()对每一个子view进行测量,计算出所有子view中,最大宽度和最大高度,加上父View的padding和前景区域的padding,然后会检查是否设置了最小宽高,并与其比较,将两者中较大的设为最终的最大宽高。最后,若设置了前景图像,我们还要检查前景图像的最小宽高。
- 得到了maxHeight和maxWidth的最终值,表示当前容器View用这个尺寸就能够正常显示其所有子View(同时考虑了padding和margin)。而后我们需要调用resolveSizeAndState()方法来结合传来的MeasureSpec来获取最终的测量宽高,并保存到mMeasuredWidth与mMeasuredHeight成员变量中。
- 我们可以看到,容器View通过measureChildWithMargins()方法对所有子View进行测量后,才能得到自身的测量结果。也就是说,对于ViewGroup及其子类来说,要先完成子View的测量,再进行自身的测量(考虑进padding等)。
protected void measureChildWithMargins(View child,
int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int widthUsed,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec, int heightUsed) {
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin
+ widthUsed, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin
+ heightUsed, lp.height);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
最终,子view的测量时通过子view自身child.measure()完成的。子view测量需要自身的measureSpec,这个就需要父view的measureSpec和子view自身的layoutParams参数决定,子view的layoutParams代表着子view自身期待的大小。getChildMeasureSpec():
public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding, int childDimension) {
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(spec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(spec);
int size = Math.max(0, specSize - padding);
int resultSize = 0;
int resultMode = 0;
switch (specMode) {
// Parent has imposed an exact size on us
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size. So be it.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent has imposed a maximum size on us
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... so be it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size, but our size is not fixed.
// Constrain child to not be bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent asked to see how big we want to be
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... let him have it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size... find out how big it should
// be
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size.... find out how
// big it should be
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
}
break;
}
//noinspection ResourceType
return MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode);
}
首先,根据父view的measureSpec算出specMode和specSize,在计算出父view留给子view的最大可用空间size。
- SpecMode为EXACTLY,表示父View对子View指定了确切的宽高限制,此时子View的LayoutParams:
- childDimension为具体大小:子view的resultSize为childDimension,即子View在LayoutParams指定的具体大小值;SpecMode为EXACTLY,即这种情况下若该子View为容器View,它也有能力给其子View指定确切的宽高限制(子View只能在这个宽高范围内),若为普通View,它的最终测量大小就为childDimension
- childDimension为match_parent:表示子View想和父View一样大。SpecSize为size,即父View的剩余可用大小;SpecMode为EXACTLY
- childDimension为wrap_content:表示子View想自己决定自己的尺寸(根据其内容的大小动态决定)。这种情况下子View的确切测量大小只能在其本身的onMeasure()方法中计算得出,父View此时无从知晓。所以暂时将子View的SpecSize设为size(父View的剩余大小);令子View的SpecMode为AT_MOST,表示了若子View为ViewGroup,它没有能力给其子View指定确切的宽高限制,毕竟它本身的测量宽高还悬而未定。
- SpecMode为AT_MOST:
- childDimension为具体大小:子View的SpecSize为childDimension,SpecMode为EXACTLY
- childDimension为match_parent:表示子View想和父View一样大,故令子View的SpecSize为size,但是由于父View本身的测量宽高还无从确定,所以只是暂时令子View的测量结果为父View目前的可用大小。这时令子View的SpecMode为AT_MOST。
- childDimension为wrap_content:表示子View想自己决定大小(根据其内容动态确定)。然而这时父View还无法确定其自身的测量宽高,所以暂时令子View的SpecSize为size,SpecMode为AT_MOST。
结论:当子View的测量结果能够确定时,子View的SpecMode就为EXACTLY;当子View的测量结果还不能确定(只是暂时设为某个值)时,子View的SpecMode为AT_MOST。
(可参考一张表格,自行谷歌)
子view层层遍历,调用measure(),完成测量。当递归地执行完所有子View的测量工作后,会调用resolveSizeAndState()方法来根据之前的测量结果确定最终对FrameLayout的测量结果并存储起来。
public static int resolveSizeAndState(int size, int measureSpec, int childMeasuredState) {
final int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
final int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
final int result;
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (specSize < size) {
// 父View给定的最大尺寸小于完全显示内容所需尺寸
// 则在测量结果上加上MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL
result = specSize | MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL;
} else {
result = size;
}
break;
// 若specMode为EXACTLY,则不考虑size,result直接赋值为specSize
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
default:
result = size;
}
return result | (childMeasuredState & MEASURED_STATE_MASK);
}
上面介绍的onMeasure()是FrameLayout的,而普通view的onMeasure():
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}
普通View(非ViewgGroup)来说,只需完成自身的测量工作即可。
public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) {
int result = size;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
result = size;
break;
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
}
return result;
}
View的getDefaultSize()方法对于AT_MOST和EXACTLY这两种情况都返回了SpecSize作为result。所以若我们的自定义View直接继承了View类,我们就要自己对wrap_content (对应了AT_MOST)这种情况进行处理,否则对自定义View指定wrap_content就和match_parent效果一样了。—— 自定义View的注意事项
但是如果是View的派生类,如TextView、Button、ImageView等,它们的onMeasure方法系统了都做了重写,不会这么简单直接拿 MeasureSpec 的size来当大小,而去会先去测量字符或者图片的高度等,然后拿到View本身content这个高度(字符高度等),如果MeasureSpec是AT_MOST,而且View本身content的高度不超出MeasureSpec的size,那么可以直接用View本身content的高度(字符高度等),而不是像View.java 直接用MeasureSpec的size做为View的大小。
layout阶段
DecorView继承自FrameLayout,onLayout()会执行super().onLayout()。FrameLayout的onLayout类似于onMeasure,getChildAt()获得child,调用每个child的layout()。
View.layout()
public void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) {
...
boolean changed = isLayoutModeOptical(mParent) ?
setOpticalFrame(l, t, r, b) : setFrame(l, t, r, b);
if (changed || (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) == PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) {
onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);
...
}
...
}
setFrame()方法四个参数描述了View相对其父View的位置,setFrame()方法中会判断View的位置是否发生了改变,若发生了改变,则需要对子View进行重新布局,changed。
protected boolean setFrame(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
boolean changed = false;
if (mLeft != left || mRight != right || mTop != top || mBottom != bottom) {
changed = true;
// Remember our drawn bit
int drawn = mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_DRAWN;
int oldWidth = mRight - mLeft;
int oldHeight = mBottom - mTop;
int newWidth = right - left;
int newHeight = bottom - top;
boolean sizeChanged = (newWidth != oldWidth) || (newHeight != oldHeight);
// Invalidate our old position
invalidate(sizeChanged);
...
}
return changed;
}
子view布局通过onLayout()实现,普通View( 非ViewGroup)不含子View,所以View类的onLayout()方法为空。
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
}
ViewGroup.layout()
@Override
public final void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) {
if (!mSuppressLayout && (mTransition == null || !mTransition.isChangingLayout())) {
if (mTransition != null) {
mTransition.layoutChange(this);
}
super.layout(l, t, r, b);
} else {
// record the fact that we noop'd it; request layout when transition finishes
mLayoutCalledWhileSuppressed = true;
}
}
LayoutTransition是用于处理ViewGroup增加和删除子视图的动画效果,也就是说如果当前ViewGroup未添加LayoutTransition动画,或者LayoutTransition动画此刻并未运行,那么调用super.layout(l, t, r, b),继而调用到ViewGroup中的onLayout,否则将mLayoutSuppressed设置为true,等待动画完成时再调用requestLayout()
ViewGroup.onLayout()
ViewGroup类的onLayout()方法是abstract,不同的布局管理器有着不同的布局方式。
decorView,即FrameLayout的onLayout():
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
layoutChildren(left, top, right, bottom, false /* no force left gravity */);
}
void layoutChildren(int left, int top, int right, int bottom, boolean forceLeftGravity) {
final int count = getChildCount();
final int parentLeft = getPaddingLeftWithForeground();
final int parentRight = right - left - getPaddingRightWithForeground();
final int parentTop = getPaddingTopWithForeground();
final int parentBottom = bottom - top - getPaddingBottomWithForeground();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = getChildAt(i);
if (child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int width = child.getMeasuredWidth();
final int height = child.getMeasuredHeight();
int childLeft;
int childTop;
int gravity = lp.gravity;
if (gravity == -1) {
gravity = DEFAULT_CHILD_GRAVITY;
}
final int layoutDirection = getLayoutDirection();
final int absoluteGravity = Gravity.getAbsoluteGravity(gravity, layoutDirection);
final int verticalGravity = gravity & Gravity.VERTICAL_GRAVITY_MASK;
switch (absoluteGravity & Gravity.HORIZONTAL_GRAVITY_MASK) {
case Gravity.CENTER_HORIZONTAL:
childLeft = parentLeft + (parentRight - parentLeft - width) / 2 +
lp.leftMargin - lp.rightMargin;
break;
case Gravity.RIGHT:
if (!forceLeftGravity) {
childLeft = parentRight - width - lp.rightMargin;
break;
}
case Gravity.LEFT:
default:
childLeft = parentLeft + lp.leftMargin;
}
switch (verticalGravity) {
case Gravity.TOP:
childTop = parentTop + lp.topMargin;
break;
case Gravity.CENTER_VERTICAL:
childTop = parentTop + (parentBottom - parentTop - height) / 2 +
lp.topMargin - lp.bottomMargin;
break;
case Gravity.BOTTOM:
childTop = parentBottom - height - lp.bottomMargin;
break;
default:
childTop = parentTop + lp.topMargin;
}
child.layout(childLeft, childTop, childLeft + width, childTop + height);
}
}
}
- parentLeft为子View显示区域的左边缘到父View的左边缘的距离,根据父view的padding值确定。
- 子View的可见性不为GONE才会进行布局
- childLeft代表了最终子View的左边缘距父View左边缘的距离,由parentLeft,即父view的padding,和子view的margin,以及view自身宽度等因素计算而成。不过不同的verticalGravity、absoluteGravity等形式,计算法师不同
- childTop同理。
- 最后会调用child.layout()方法对子View的位置参数进行设置,若子View是容器View,则会递归地对其子View进行布局。
draw()
decorView.draw()继承View.draw()
public void draw(Canvas canvas) {
. . .
// 绘制背景,只有dirtyOpaque为false时才进行绘制,下同
int saveCount;
if (!dirtyOpaque) {
drawBackground(canvas);
}
. . .
// 绘制自身内容
if (!dirtyOpaque) onDraw(canvas);
// 绘制子View
dispatchDraw(canvas);
. . .
// 绘制滚动条等
onDrawForeground(canvas);
}
省略了实现滑动时渐变边框效果相关的逻辑
View类的onDraw()方法为空,因为每个View绘制自身的方式都不尽相同,对于decorView来说,由于它是容器View,所以它本身并没有什么要绘制的。
-
dispatchDraw()方法用于绘制子View,显然普通View(非ViewGroup)并不能包含子View,所以View类中这个方法的实现为空。ViewGroup类的dispatchDraw()方法中会依次调用drawChild()方法来绘制子View
protected boolean drawChild(Canvas canvas, View child, long drawingTime) { return child.draw(canvas, this, drawingTime); }
这个方法调用了View.draw(Canvas, ViewGroup,long)方法来对子View进行绘制。在draw(Canvas, ViewGroup, long)方法中,首先对canvas进行了一系列变换,以变换到将要被绘制的View的坐标系下。完成对canvas的变换后,便会调用View.draw(Canvas)方法进行实际的绘制工作,此时传入的canvas为经过变换的,在将被绘制View的坐标系下的canvas。
进入到View.draw(Canvas)方法后,会向之前介绍的一样,执行以下几步:
- 绘制背景;
- 通过onDraw()绘制自身内容;
- 通过dispatchDraw()绘制子View;
- 绘制滚动条
参考:深入理解Android之View的绘制流程
Android View的绘制流程