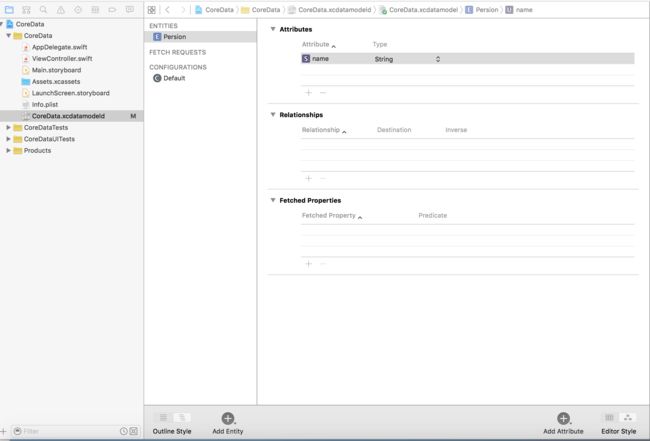
创建项目的时候勾选使用Coredata、工程里面会含有.xcdatamodeld结尾的文件。点击该文件后在右侧视图中点击Add Entity添加任意名称的实体。Coredata可以包含多个实体(Entity) 每个实体类似于数据库的一张表,每个实体包含了attribute、relationship、Fetched Properties。attribute里面保存该实体的属性,类似于关系型数据库里面的一张表里面包含各个字段。relationship用来表示每个实体之间的关系,可以是一对一和一对多。
attribute包含了各种属性类型(type)自定义的数据类型使用Transformable类型 前提是该自定义类型遵守NSCoding协议
注:只有当type的类型为binarydata attribute type时 如果文件内容较大可以选中该属性然后勾选Allows External Storage,这样只是保存文件的路径
1.保存数据
func saveAttribute(name: String) {
//获取工程自动创建的managedObjectContext
let appDelegate =
UIApplication.sharedApplication().delegate as! AppDelegate
let managedContext = appDelegate.managedObjectContext
//根据"Person" key来获取创建的实体 例子中的实体名称为"Person"
let entity = NSEntityDescription.entityForName("Person",
inManagedObjectContext:managedContext)
//将数据模型与实体进行关联 An entity description is the piece that links the entity definition from your data model with an instance of NSManagedObject at runtime
let person = NSManagedObject(entity: entity!,
insertIntoManagedObjectContext: managedContext)
//保存属性值
person.setValue(name, forKey: "name")
//save失败后抛出异常
do {
//将所保存的属性值全部提交保存
try managedContext.save()
people.append(person)
} catch let error as NSError {
print("Could not save \(error), \(error.userInfo)")
}
}
2.读取数据
func fetchRequset() {
let appDelegate =
UIApplication.sharedApplication().delegate as! AppDelegate
let managedContext = appDelegate.managedObjectContext
//NSFetchRequest负责从CoreData获取数据 获取Persion的所有实体
let fetchRequest = NSFetchRequest(entityName: "Person")
//执行获取 并返回一个数组,数组包含所有的实体
do {
let results =
try managedContext.executeFetchRequest(fetchRequest)
people = results as! [NSManagedObject]
} catch let error as NSError {
print("Could not fetch \(error), \(error.userInfo)")
}
}
3.自己创建model来保存实体 xcode可以根据实体中的属性自动创建
选中要为其创建类的实体 ->Editor -> Create NSManagedObject Subclass... ,之后会自动创建两个文件 Persion.swift和Persion+CoreDataProperties.swift 如下:
Persion.swift
import Foundation
import CoreData
class Persion: NSManagedObject {
// Insert code here to add functionality to your managed object subclass
}
Persion+CoreDataProperties.swift
import Foundation
import CoreData
extension Persion {
@NSManaged var name: String?
}
当我们添加或删除了实体里面所包含的属性,可以用上面的步骤 选中要为其创建类的实体 ->Editor -> Create NSManagedObject Subclass... 重新创建。此时会覆盖Persion+CoreDataProperties.swift里面的内容,而Persion.swift中的内容不会被覆盖。
//从plist中读取数据再将数据保存到CoreData
let path = NSBundle.mainBundle().pathForResource("SampleData",
ofType: "plist")
let dataArray = NSArray(contentsOfFile: path!)!
for dict : AnyObject in dataArray {
let entity = NSEntityDescription.entityForName("Persion",
inManagedObjectContext: managedContext)
let persion = Persion(entity: entity!,
insertIntoManagedObjectContext: managedContext)
let btDict = dict as! NSDictionary
persion.name = btDict["name"] as? String
//保存颜色
let tintColorDict = btDict["tintColor"] as? NSDictionary
let red = dict["red"] as! NSNumber
let green = dict["green"] as! NSNumber
let blue = dict["blue"] as! NSNumber
let color = UIColor(red: CGFloat(red)/255.0,
green: CGFloat(green)/255.0,
blue: CGFloat(blue)/255.0,
alpha: 1)
persion.tintColor = color
//保存图片
let imageName = btDict["imageName"] as? String
let image = UIImage(named:imageName!)
let photoData = UIImagePNGRepresentation(image!)
persion.photoData = photoData
}
//读取并保存为[Persion]数组
let request = NSFetchRequest(entityName:"Persion")
do {
let results =
try managedContext.executeFetchRequest(request) as! [Persion]
} catch let error as NSError {
print("Could not fetch \(error), \(error.userInfo)")
}
注:
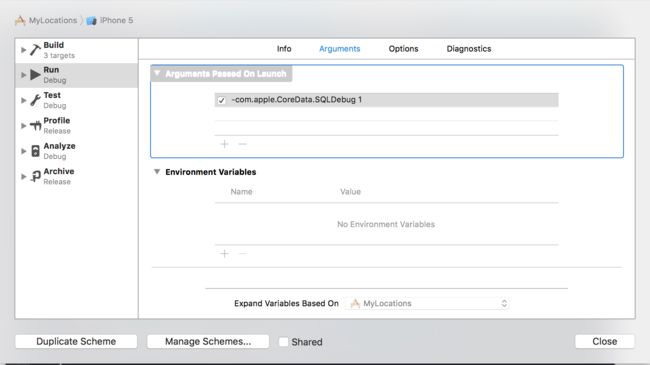
使用Coredata时也需要创建sqlite数据库,我们不对其进行操作而是通过Coredata间接对其进行操作。可以开启debug模式观看其具体操作:添加-com.apple.CoreData.SQLDebug 1