目录
- 1 netlify
- 2 Github Pages
- 3 无状态组件(函数式组件)
- 4 优化 PureComponent
- 5 Fragment
- 6 context
- 7 高阶组价
7.1 使用高阶组件重构
7.2 实际项目使用高阶优化1
7.3 参考高阶代码 - 8 react-powerplug
- 9 高阶组件,处理多个平级组件
- 10 propTypes 、defaultProps
- 11 Render Props
- 12 Error Boundary
- 13 bind this
- 14 16.3 Context
- 15 使用16.3 Context 改写 redux
- 16 可变数据
- 17 this.props.children
- 18 随记
1 netlify
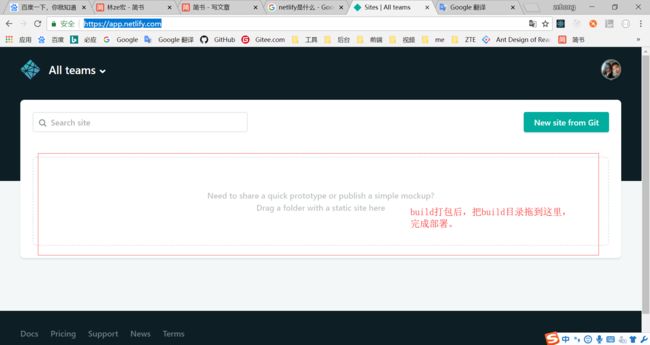
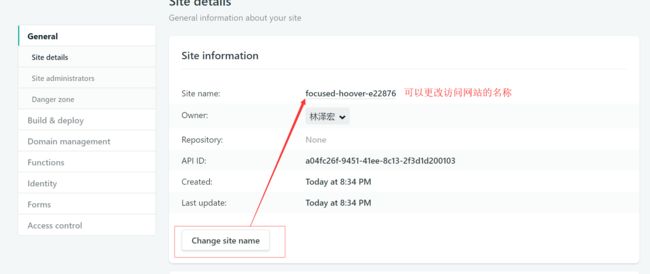
netlify 是一个提供托管静态网站的服务。
官网:https://app.netlify.com/
2 Github Pages
部署到 Github Pages(Github Pages是面向用户、组织和项目开放的公共静态页面搭建托管服务)
步骤:
- 安装 gh-pages
https://github.com/tschaub/gh-pages
npm install gh-pages --save-dev
- 在 package.json 增加 homepage
"homepage": "https://hongzelin.github.io/GitHubPageTest",
说明:https://用户名.github.io/仓库名
- 在 package.json 在 scripts 增加 deploy
"scripts": {
"predeploy": "yarn run build", // 这个是在 执行 deploy命令之前执行,打出静态包,放在 gh-pages 新分支上
"deploy": "gh-pages -d build" // 参考 gh-pages 官网
}
- 运行
yarn run deploy
说明:这时候在GitHub项目仓库会打出来新的分支 gh-pages,
接下来,直接访问 homepage 配置的网址即可。
3 无状态组件(函数式组件)
参考:https://www.jianshu.com/p/63569386befc
理解基础概念:
import React from 'react';
const Header = (props) => {
return (
Header
);
};
export default Header;
说明:无状态组件,也叫函数式组件;定义一个箭头函数,传入 props 参数。
只有 return,没有 render 方法;
注意:如果需要操作状态,这时候需要配合高阶组价一起使用。
参考:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/24776678?group_id=802649040843051008
4 优化 PureComponent
组件继承 PureComponent ,避免组件重复渲染
import React, { Component, PureComponent } from 'react';
import logo from './logo.svg';
import './App.css';
// 无状态组件一般写法,在 props 没有改变的时候,也会重复渲染
// const Temp = (props) => {
// console.log('render Temp');
// return (
// { props.val }
// );
// }
// 使用 es6 的写法,继承 PureComponent ,解决在 props 没有改变的时候,重复渲染问题
class Temp extends PureComponent {
render() {
console.log('render Temp');
return (
{ this.props.val }
);
}
}
class App extends Component {
state = {
val: 1
}
componentDidMount() {
setInterval(() => { // 演示,值没有改变的时候,无状态组件是否还是会重新渲染。
this.setState({
val: 1
})
}, 2000)
}
// shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
// console.log('nextState', nextState);
// console.log('current state', this.state);
// return (
// this.state.val === nextState.val ? false : true
// )
// }
render() {
console.log('render App');
return (

Welcome to React
To get started, edit src/App.js and save to reload.
5 Fragment
Fragment 是为了解决需要根节点报错问题;
使用 Fragment,在 DOM 生成并不会引入多余的标签;
另一个方法也可以使用:<> ... ,包裹解决;
import React, { Component, Fragment } from 'react';
import logo from './logo.svg';
import './App.css';
const Temp = (props) => {
return (
list 1
list 1
)
}
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
{/* ul的子节点一定是li */}
);
}
}
export default App;
6 context
参考:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000002878442
通过 context 传递属性的方式可以大量减少,显式通过 props 逐层传递属性的方式。这样可以减少组件之间的直接依赖关系。
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import './App.css';
import PropTypes from 'prop-types';
const Topic = (props) => {
return (
7 高阶组价
参考:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/0aae7d4d9bc1
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/24776678?group_id=802649040843051008
简单理解,高阶组价就是传入一个组件参数,返回一个组件。
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import './App.css';
const PropsLogger = (WrapperComponent) => {
return class extends Component {
render() {
return Hello { props.name }
)
})
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
7.1 使用高阶组件重构
重构前
- src/components/User.js
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class User extends Component {
constructor() {
super();
this.state = {
loading: true,
user: null
};
}
componentDidMount() {
fetch('https://randomuser.me/api/')
.then(res => res.json())
.then(user => {
this.setState({
loading: false,
user: user
});
})
}
render() {
if(this.state.loading) {
return (
loading
)
} else {
return (
{this.state.user.results[0].email}
)
}
}
}
export default User;
- src/components/Joke.js
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class Joke extends Component {
constructor() {
super();
this.state = {
loading: true,
jokes: null
};
}
componentDidMount() {
fetch('http://api.icndb.com/jokes/random/3')
.then(res => res.json())
.then(jokes => {
this.setState({
loading: false,
jokes: jokes
});
})
}
render() {
if(this.state.loading) {
return (
loading
)
} else {
return (
{
this.state.jokes.value.map(joke => (
{ joke.joke }
))
}
)
}
}
}
export default Joke;
重构后:使用高阶组件
- src/hoc/withFetch.js
import React, { Component } from 'react';
const withFetch = (url) => (View) => {
return class extends Component {
constructor() {
super();
this.state = {
loading: true,
data: null
};
}
componentDidMount() {
fetch(url)
.then(res => res.json())
.then(data => {
this.setState({
loading: false,
data: data
});
})
}
render() {
if(this.state.loading) {
return (
loading
)
} else {
return - src/components/Joke.js(调用高阶组件)
import React from 'react';
import withFetch from '../hoc/withFetch';
const Joke = withFetch('http://api.icndb.com/jokes/random/3')(props => {
return (
{
props.data.value.map(joke => (
{ joke.joke }
))
}
)
})
export default Joke;
- src/components/User.js
import React from 'react';
import withFetch from '../hoc/withFetch';
const User = withFetch('https://randomuser.me/api/')(props => {
return (
{props.data.results[0].email}
)
})
export default User;
7.2 实际项目使用高阶优化1
页面引用不同的组件,关键点,传入给各个组件 props 属性!!!
import React from 'react'
import OperatorUI from './OperatorUI'
import StartUI from './StartUI'
import EndUI from './EndUI'
import StrategyUI from './StrategyUI'
getRenderSortFlow(info, styleObj) {
let { type } = info;
type = type.indexOf('strategy') > -1 ? 'strategy' : type;
switch (type) {
case 'start': // 开始节点
return (
StartUI 组件:
import React from 'react'
import HocNodeUI from '../HocUI/HocNodeUI'
const StartUI = HocNodeUI(({ info }) => (
{info.name}
))
export default StartUI;
EndUI 组件:
import React from 'react'
import HocNodeUI from '../HocUI/HocNodeUI'
const EndUI = HocNodeUI(({ info }) => (
{info.name}
))
export default EndUI;
OperatorUI 组件:
import React from 'react'
import { Icon } from '@ali/wind'
import HocNodeUI from '../HocUI/HocNodeUI'
const del = (e, id, eventObj) => {
e.stopPropagation();
if (id) {
eventObj.onRemove(id);
}
}
const OperatorUI = HocNodeUI(({ info, eventObj }) => (
del(e, info.uuid, eventObj)}
/>
))
export default OperatorUI;
StrategyUI 组件:
import React from 'react'
import { Icon } from '@ali/wind'
import HocNodeUI from '../HocUI/HocNodeUI'
import './StrategyUI.less'
const del = (e, id, eventObj) => {
e.stopPropagation();
if (id) {
eventObj.onRemove(id);
}
}
const StrategyUI = HocNodeUI(({ info, eventObj }) => (
<⁄>
{info.name}
del(e, info.uuid, eventObj)}
/>
))
export default StrategyUI;
/*
* @Author: lin.zehong
* @Date: 2019-06-13 10:22:11
* @Last Modified by: lin.zehong
* @Last Modified time: 2019-06-13 13:58:50
* @Desc: 高阶:开始、结束、算子、策略等UI高阶
*/
import React, { Component } from 'react'
import { connect } from 'dva'
import PropTypes from 'prop-types'
import { selectors } from '../../../models/tasksFlow'
import './HocNodeUI.less'
const HocNodeUI = (WrappedComponent) => {
const mapStateToProps = state => ({
isActiveAlgo: selectors.getIsActiveAlgo(state),
})
@connect(mapStateToProps, null)
class HocUI extends Component {
static propTypes = {
eventObj: PropTypes.objectOf(PropTypes.any),
info: PropTypes.objectOf(PropTypes.any),
styleObj: PropTypes.objectOf(PropTypes.any),
isActiveAlgo: PropTypes.string,
}
render() {
const { info, styleObj, eventObj, isActiveAlgo } = this.props;
return (
{
eventObj.onClick(e, info)
}}
onMouseUp={(e) => {
eventObj.onMouseUp(e, info)
}}
>
注意:
1:除了使用高阶包裹的方式,组件使用高阶也可以使用注解的方式:
import React from 'react'
import PropTypes from 'prop-types'
import HocNodeUI from '../HocUI/HocNodeUI'
@HocNodeUI
class EndUI extends React.Component {
render() {
const { info } = this.props;
return (
{info.name}
)
}
}
EndUI.propTypes = {
info: PropTypes.objectOf(PropTypes.any),
}
// const EndUI = HocNodeUI(({ info }) => (
//
//
//
//
//
// {info.name}
//
//
// ))
export default EndUI;
2:传递参数给高阶组件
/*
* @Author: lin.zehong
* @Date: 2019-06-13 10:22:11
* @Last Modified by: lin.zehong
* @Last Modified time: 2019-06-13 15:15:09
* @Desc: 高阶:开始、结束、算子、策略等UI高阶
*/
import React, { Component } from 'react'
import { connect } from 'dva'
import PropTypes from 'prop-types'
import { selectors } from '../../../models/tasksFlow'
import './HocNodeUI.less'
const HocNodeUI = (class_name) => (WrappedComponent) => {
const mapStateToProps = state => ({
isActiveAlgo: selectors.getIsActiveAlgo(state),
})
@connect(mapStateToProps, null)
class HocUI extends Component {
static propTypes = {
eventObj: PropTypes.objectOf(PropTypes.any),
info: PropTypes.objectOf(PropTypes.any),
styleObj: PropTypes.objectOf(PropTypes.any),
isActiveAlgo: PropTypes.string,
}
render() {
const { info, styleObj, eventObj, isActiveAlgo } = this.props;
return (
{
eventObj.onClick(e, info)
}}
onMouseUp={(e) => {
eventObj.onMouseUp(e, info)
}}
>
方式一:使用注释,也就是高阶的参数:
import React from 'react'
import PropTypes from 'prop-types'
import HocNodeUI from '../HocUI/HocNodeUI'
@HocNodeUI('l-o-wrap')
class EndUI extends React.Component {
render() {
const { info } = this.props;
return (
{info.name}
)
}
}
EndUI.propTypes = {
info: PropTypes.objectOf(PropTypes.any),
}
··········································································
方式二:使用高阶包裹方式:
import React from 'react'
import { Icon } from '@ali/wind'
import HocNodeUI from '../HocUI/HocNodeUI'
const del = (e, id, eventObj) => {
e.stopPropagation();
if (id) {
eventObj.onRemove(id);
}
}
const OperatorUI = HocNodeUI('l-o-wrap')(({ info, eventObj }) => (
del(e, info.uuid, eventObj)}
/>
))
export default OperatorUI;
··········································································
方式三:如果不需要传递参数,也是需要括号调用:
import React from 'react'
import { Icon } from '@ali/wind'
import HocNodeUI from '../HocUI/HocNodeUI'
import './StrategyUI.less'
const del = (e, id, eventObj) => {
e.stopPropagation();
if (id) {
eventObj.onRemove(id);
}
}
const StrategyUI = HocNodeUI()(({ info, eventObj }) => (
<⁄>
{info.name}
del(e, info.uuid, eventObj)}
/>
))
export default StrategyUI;
7.3 参考高阶代码
import React, { Component } from 'react'
import PropTypes from 'prop-types'
import './HocUI.less'
/**
* 用于包装在绘图区域拖拽生成的节点,方便后期扩展功能或者UI
* 页面上面渲染的每个节点都需要从此高阶组件过,
* 那么就在这里对正、反渲染的逻辑进行判断,给节点做拦截,
* 新增一些方法、属性、样式上去
*
* @param WrappedComponent
* @returns {{new(): {render(): *}}}
* @constructor
*/
function HocNodeFlowMenu(className) {
return function (WrappedComponent) {
return class HocNodeFlowMenuUI extends Component {
static propTypes = {
info: PropTypes.objectOf(PropTypes.any),
styleObj: PropTypes.objectOf(PropTypes.any),
eventObj: PropTypes.objectOf(PropTypes.any),
}
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
visiable: false,
}
this.handleMouseMove = this.handleMouseMove.bind(this);
this.handleMouseLeave = this.handleMouseLeave.bind(this);
}
handleMouseMove() {
this.setState(() => ({
visiable: true,
}))
}
handleMouseLeave() {
this.setState(() => ({
visiable: false,
}))
}
render() {
const { info, styleObj, eventObj } = this.props;
return (
{
eventObj.onClick(info)
}}
onMouseUp={(e) => {
eventObj.onMouseUp(e, info)
}}
onContextMenu={(e) => {
eventObj.onContextmenu(e)
}}
>
8 react-powerplug
react-powerplug 插件
- 重构前
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import './App.css';
class Counter extends Component {
state = {
counter: 0
}
increment = () => {
this.setState(prevState => ({ counter: prevState.counter + 1 }));
}
decrement = () => {
this.setState(prevState => ({ counter: prevState.counter - 1 }));
}
render() {
return (
Counter: { this.state.counter }
);
}
}
export default Counter;
- 重构后
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import './App.css';
import { State } from 'react-powerplug'
class Counter extends Component {
render() {
return (
{({ state, setState }) => (
Counter: { state.counter }
)}
);
}
}
export default Counter;
9 高阶组件,处理多个平级组件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import './App.css';
const Wrapper = ({ children }) => children;
const Hello = ({ name }) => {
return (
React 16 rocks
Hello, { name }!
)
}
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
10 propTypes 、defaultProps
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import './App.css';
import PropTypes from 'prop-types';
class Hello extends Component {
// static defaultProps = {
// name: "rails365"
// }
render() {
return (
Hello, { this.props.money }, { this.props.name }
{
this.props.movies.map(movie => - { movie.title }
)
}
)
}
}
Hello.propTypes = {
money: PropTypes.number,
onChange: PropTypes.func.isRequired,
name: PropTypes.oneOfType([
PropTypes.string,
PropTypes.number
]),
// movies是个数组,PropTypes.shape表示数组里面的每个元素是个对象,再对里面的对象进行细致限制。
movies: PropTypes.arrayOf(PropTypes.shape({
id: PropTypes.number,
title: PropTypes.string,
visit_count: PropTypes.number
}))
}
// Hello.defaultProps = {
// name: "rails365"
// }
class App extends Component {
onChange() {
}
state = {
movies: [
{ id: 1, title: 'title 1', visit_count: 1 },
{ id: 2, title: 'title 2', visit_count: 2 }
]
}
render() {
return (
11 Render Props
参考:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/31267131
https://reactjs.org/docs/render-props.html
- 重写前
import React from 'react';
const withMouse = (Component) => {
return class extends React.Component {
state = { x: 0, y: 0 }
handleMouseMove = (event) => {
this.setState({
x: event.clientX,
y: event.clientY
})
}
render() {
return (
The mouse position is ({ x }, { y })
)
}
const AppWithMouse = withMouse(App)
export default AppWithMouse;
- 重写后
import React from 'react';
import PropTypes from 'prop-types';
class Mouse extends React.Component {
static propTypes = {
render: PropTypes.func.isRequired
}
state = { x: 0, y: 0 }
handleMouseMove = (event) => {
this.setState({
x: event.clientX,
y: event.clientY
})
}
render() {
return (
{ this.props.render(this.state) }
)
}
}
const Position = ({ x, y }) => {
return (
The mouse position is ({ x }, { y })
)
}
const Position1 = ({ x, y }) => {
return (
The mouse position is ({ x }, { y })
)
}
const App = () => {
return (
(
The mouse position is ({ x }, { y })
)} />
)
}
export default App;
12 Error Boundary
针对的是其子节点,在生产环境,如果该子节点发生错误,则只有
- src/App.js
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import './App.css';
import Broken from './Broken';
import ErrorBoundary from './ErrorBoundary';
class App extends Component {
state = {
counter: 0
}
increment = () => {
this.setState(prevState => ({ counter: prevState.counter + 1 }));
}
decrement = () => {
this.setState(prevState => ({ counter: prevState.counter - 1 }));
}
render() {
return (
Hello rails365
Error: { error.toString() }
}>
Counter: { this.state.counter }
);
}
}
export default App;
- src/ErrorBoundary.js
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import PropTypes from 'prop-types';
class ErrorBoundary extends Component {
static propTypes = {
children: PropTypes.oneOfType([
PropTypes.node,
PropTypes.arrayOf(PropTypes.node)
]).isRequired
}
state = {
hasError: false,
error: null,
errorInfo: null
}
componentDidCatch(error, errorInfo) {
this.setState({
hasError: true,
error: error,
errorInfo: errorInfo
})
}
render() {
if (this.state.hasError) {
return { this.props.render(this.state.error, this.state.errorInfo) }
}
return this.props.children;
}
}
export default ErrorBoundary;
13 bind this
参考:https://www.jianshu.com/p/018665bc4ce2
基本有4/5种写法
- 最好的写法是使用es6,箭头函数的写法
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import logo from './logo.svg';
import './App.css';
class App extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
name: ''
}
}
handleChange = e => {
this.setState({
name: e.target.value
})
}
render() {
return (

Welcome to React
{ this.state.name }
);
}
}
export default App;
14 16.3 Context
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import './App.css';
// 第一步,创建 context
const myContext = React.createContext()
// 第二步,创建 Provider Component
class MyProvider extends Component {
state = {
name: "rails365",
age: 27
}
render() {
return (
{ this.props.children }
)
}
}
const Family = (props) => {
return (
Family
Person
{ ({ state }) => My age is { state.age }
}
);
}
}
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
Hello App
);
}
}
export default App;
16.3 Context 进一步理解
- src/App.js
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import './App.css';
import { CDNFlagIcon } from "react-flag-kit";
const ThemeContext = React.createContext();
const localeMap = {
"en-US": { locale: "en-US", flag: "US", content: "Hello, World!" },
"fr-FR": { locale: "fr-FR", flag: "FR", content: "Bonjour le monde!" },
"es-ES": { locale: "es-ES", flag: "ES", content: "¡Hola Mundo!" }
};
class LocaleSwitcher extends Component {
state = localeMap["en-US"]
render() {
return (
this.setState(localeMap[e.target.value])
}}
>
{ this.props.children }
);
}
}
const LocaleSelect = () => {
return (
{context => (
)}
)
}
const LocaleFlag = (props) => {
return (
{ context =>
)
}
const LocaleContent = (props) => {
return (
{ context => { context.state.content }
}
)
}
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
);
}
}
export default App;
15 使用16.3 Context 改写 redux
主要思想,哪里提供数据,哪里消费数据
- src/contexts/ReminderContext.js
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { bake_cookie, read_cookie } from 'sfcookies';
export const ReminderContext = React.createContext();
export class ReminderProvider extends Component {
state = {
reminders: read_cookie("reminders") || []
}
addReminder = (text, dueDate) => {
let reminders = [];
reminders = [
...this.state.reminders,
{ id: Math.random(), text, dueDate }
];
this.setState({
reminders: reminders
});
bake_cookie("reminders", reminders);
}
deleteReminder = (id) => {
let reminders = [];
reminders = this.state.reminders.filter(reminder => reminder.id !== id);
this.setState({
reminders: reminders
});
bake_cookie("reminders", reminders);
}
clearReminders = () => {
this.setState({
reminders: []
});
bake_cookie("reminders", []);
}
render() {
return (
{ this.props.children }
);
}
}
- src/index.js
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import './index.css';
import App from './components/App';
import registerServiceWorker from './registerServiceWorker';
import { ReminderContext, ReminderProvider } from './contexts/ReminderContext';
ReactDOM.render(
{ ({ reminders, clearReminders, addReminder, deleteReminder }) =>
(
,
document.getElementById('root')
);
registerServiceWorker();
- src/components/App.js
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import PropTypes from 'prop-types';
import moment from 'moment';
class App extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
text: '',
dueDate: ''
};
}
addReminder() {
this.props.addReminder(this.state.text, this.state.dueDate);
}
deleteReminder(id) {
this.props.deleteReminder(id);
}
clearReminders() {
this.props.clearReminders();
}
renderReminders() {
const { reminders } = this.props;
return (
{
reminders.map(reminder => {
return (
-
{ reminder.text }
{ moment(new Date(reminder.dueDate)).fromNow() }
this.deleteReminder(reminder.id) }
>
✕
);
})
}
);
}
render() {
return (
Reminder Pro
this.setState({text: event.target.value}) }
/>
this.setState({dueDate: event.target.value}) }
/>
{ this.renderReminders() }
this.clearReminders() }
>
Clear Reminders
);
}
}
App.propTypes = {
reminders: PropTypes.array.isRequired,
addReminder: PropTypes.func.isRequired,
deleteReminder: PropTypes.func.isRequired,
clearReminders: PropTypes.func.isRequired
}
export default App;
16 可变数据
- 学习资源
https://medium.com/@fknussel/arrays-objects-and-mutations-6b23348b54aa
https://github.com/hfpp2012/redux-reminder-pro/blob/master/src/reducers/index.js
https://redux.js.org/recipes/structuring-reducers/immutable-update-patterns
https://lodash.com/docs/
17 this.props.children
- 学习资源
https://reactjs.org/docs/composition-vs-inheritance.html
https://mxstbr.blog/2017/02/react-children-deepdive/#enforcing-a-single-child
https://reactjs.org/docs/jsx-in-depth.html
https://reactjs.org/docs/react-api.html#createelement
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/29464577/why-doesnt-this-props-children-map-work
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/35616029/react-createelement-vs-cloneelement
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000008587988
https://learn.co/lessons/react-this-props-children
18 随记
AuthorizedRoute:
在应用程序中限制未登录的用户访问某些路由是非常常见的,还有对于授权和未授权的用户 UI 也可能大不一样,为了解决这样的需求,我们可以考虑为应用程序设置一个主入口
https://www.ctolib.com/topics-122237.html
PureComponent :
解决无状态组件重复渲染问题。
你可以实现shouldComponentUpdate函数来指明在什么样的确切条件下,你希望这个组件得到重绘。如果你编写的是纯粹的组件(界面完全由 props 和 state 所决定),你可以利用PureComponent来为你做这个工作。
扩展:Medium 网站访问不到
打开 hosts 文件(C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts),向其中添加:
# Medium Start
104.16.120.127 medium.com
104.16.120.145 api.medium.com
104.16.120.145 cdn-static-1.medium.com
104.16.120.145 cdn-images-1.medium.com
104.16.120.145 cdn-images-2.medium.com
# Medium End