考试情况
共八个大题,每个大题有若干小题。
Lecture 1
- Symbolic approach
Encode all the information into computer
Rationalism 理性主义 relevant grammer,linguistic knowledge - Statistical approach
Infer language properties from language samples
Empiricism 经验主义 collect a large collection of texts relevance.
Lecture 2 Mathmatic Foundations
1. Entropy
- Defined by the second law of thermodynamics
- In Information theory, average uncerainty of a single random variable
-
Larger entropy value, higher uncertainty, higher difficulty to accurate estimation.
2. Perplexity in NLP
- a common way of evaluating language models.
- A language model is a probability distribution over
entire sentences or texts - Uniform distribution of words in lexicon
— Largest Entropy
— Highset Perplexity
— Hardest to predicate
3. Expectation
Mean or average of a random variable.
4.Variance
A measure of whether the values of the RV tend to vary over trials.
Lecture 3 Linguistics
考察词素,找出双音节的,给你一段话,举例说明。。三音节没考
1. Character Encoding 字符编码
- GB. "National Standard" in Chinese
— MSB(Most Significant Bit) is set to 1, and every chinese character is represented by a two-byte code.
— The MSB of both the first and second bytes are set to 1. - GBK. "National Standard Extension"
— Including tranditional characters. - GB18030.
— Officially mandatory for all software products sold in the PRC.
— Supports both simplified and traditional Chinese characters. - Big5.
— The first byte ranges from 0xA0 to 0xF9
— The second byte ranges from 0x40 to 0x7E, 0xA0 to 0xFE
— ASCII characters are still represented with a single
byte.
— The MSB of the first byte of a Big5 character is
always 1
— Big5 is an 8-bit encoding with a 15-bit code space. - Unicode
— Industry standard, Universal Character Set
— Implemented by different character encodings
— UTF-8: uses 1 byte for all ASCII characters, up to 4
— UCS-2: uses 2 bytes for all characters, but does not include every character in the Unicode
— UTF-16: using 4 bytes to encode characters missing from UCS-2 bytes for other characters
2. Morphemes 词素
- The basic morphologic units, the smallest meaningful elements
- Cannot be further analyzed into smaller parts and still retain meaning
- generalization that one syllable is one morpheme represented by one character
- One character morphemes
— 吧: 酒吧 清吧 咖啡吧 - Multi-character morphemes
— 葡萄 菩萨 马达: 葡萄酒 葡萄干 - chinese words was regarded as monosyllabic language
3. Chinese Word
- Distinct from both morphemes at lower level and phrases as a higer level.
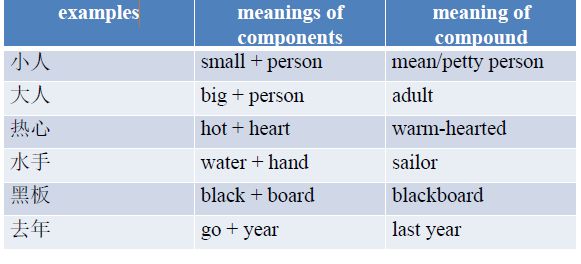
4. Chinese Word Formation - Disyllabic compounds 中文构词-双音节复合词
-
Modified noun compounds Over 53%
— have descriptive modifiers in front of nouns
— the meaning of the whole may different from the simple addition of the meanings of the parts
-
Modified verb compounds
— have modifiers in front of verbs
— specifying the manner in which the verbal action is carried out
-
Coordinative compounds 协同复合词
— Synonymous compounds: the two component morphemes have similar or identical meanings
— do not seem to be English equivalent
-
Antonymous compounds
— obvious differences in meanings
— the parts of speech of whole can be different
-
Verb-object compounds
— an be either verbal or nominal 要么是名词要么是动词
-
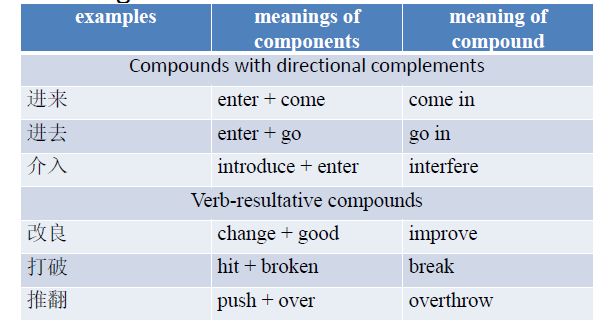
Verb complement compounds
— Verbal morpheme is followed by a complement
— Indicating the direction or the result of the verb
-
Subject-predicate compounds
— a subject and a predicate
-
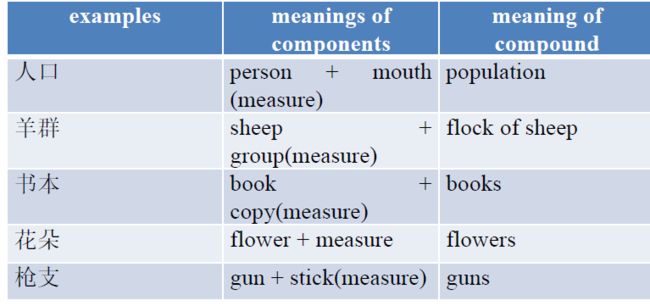
Noun-measure complement compounds
— Morphemes do not exhibit any of the usual grammatical relationships
— denote a generic kind that noun is member of
5. Chinese Word Formation - Tri-syllabic compounds 中文构词-三音节复合词
(p30)
6. Chinese Word Formation - Quad-syllabic compounds 中文构词-四音节复合词
(p35)
7. Chinese Word Formation - Affixation Reduplication Ionization 附加 重复
-
Words can be formed by adding affixes to the root.
• AABB vs. ABAB vs. A里AB
8. Challenges in Chinese Processing - Ambiguities
能够学会判断三种歧义
- Lexical Ambiguities
— 他很好吃
— 炸鸡很好吃 - Structural Ambiguities
— Overlapping ambiguity 交集型歧义
网球场 美国会
— Combinatorial ambiguity 组合型歧义
才能 学生会
— Mixed Type 混合型歧义
太平淡(too dull) 太平(peace) 平淡
Lecture 5 Unknown Word Identification and Noralization
Abbreviation in Chinese
- Reduced Abbreviation(缩略型缩写): 空军政治部 —— 空政
- Eliminated Abbreviation(消去型缩写): 清华大学——清华
- Generalized Abbreviation(概括型缩写): 八荣八耻 三从四德
Lecture 6 Collocation
1. Qualitative Properties
- Recurrent co-occurrences
— collocations occur frequently in similar context and they always
appear in certain fixed patterns - Habitual use
— cannot be described by general syntactic or semantic rules
2. Quantitative Properties
Recurrent
— Features based on co-occurrence frequencyConventional nature:
— The words are used in combination: strong co-occurrence
— Context of collocations shows high homogeneity: features based
on entropy and mutual information of contextLimited substitutability and limited modifiability##### 3. Automatic Collocation Extraction Approaches
— Synonymy substitution ratio
— Feature characterizes the distribution significance of how two
words co-occur at different positions
— the number of peak co-occurrenceLimited extent compositional
— Translate verification
— Translate testingMajor automatic collocation extraction approaches:
— Window-based statistical approach (真题重点)
— Syntax-based approach
— Semantic-based approach
— Categorization-based approach
3. Window-based statistical approach
- 一句话,给定一个词,统计这个词前后出现其它词的频度,记在一张表里面
- Idea
— Based on the property of collocation: Recurrent and habitual use
— For a given headword, collect all of the co-words surrounding this headword within fixed context windows
— Identifies the word combinations with statistical lexical significance as collocations - Discriminative features 区别的特性
— Features based on lexical co-occurrence frequency significance
— Features based on lexical co-occurrence distribution significance
— Features based on context - Advantages
— Easy to Establish
— Can extract both bi-gram and n-gram, uninterrupted and interrupted collocations - Disadvantages
— Require a large training corpus
— Not focus on syntactic and semantic relationship. Cannot distinguish true collocations and pseudo collocations. The precision is not ideal
— Methods only using co-occurrence statistics cannot achieve a good recall since some low frequency collocations are lost
— Identify various collocations by using same criteria and threshold
Lecture 7 Word Meanings
考点:对Terminology能够拼写,能够解释意思
Terminology
- Homonyms 同音
— one of group of words that share the same spelling and the same pronounciation but have different meanings
— Bank a financial institution / river bank - Synonyms 同义
— different words having similar or identical meanings
— students/ pupil; buy/purchase - Synset 同义词集
— s set of one or more synonyms - Antonyms 反义
— different words having contradictory or contrary meanings
— Perfect/imperfect big/small - Hypernymy 上位
— the semantic relation of being super-ordinate or belonging to a higher rank of class
— "living things" is a hypernyme of "human" - Hyponymy 下位
— the semantic relation of being sub-ordinate of belonging to a lower rank of class
— 'adult' is a hyponymy of "human" - Holonym 整体
— a word that defines the relationship between a term denoting the whole and a term denoting a part of, or a member of the whole.
— "tree" is a holonymy of "bark树皮", "trunk 树干" - Meronym 部分
— a word that names a part of a larger whole
— “finger" is a meronym of "hand"
— "wheel" is a meronym of "automobike" - Metonymy 转指
— a figure of speech in which a concept is referred to by the name of something closely associated with that cencept.
— White House vs. President Beijing vs. China - Proposition
— it refers to the meaning of a statement
— All men are created equal is a proposition
WordNet
- WordNet is lexical database for the English language
- Groups English words into synsets, provides short, general definitions, and records the various semantic relations between these synonym sets.
How? - organize the lexical knowledge ccording to word senses rather word form.
- WordNet is organized based on Synset
- Every synset contains a group of synonymous words or collocations
- Different senses of a word are in different synsets
- The meaning of the synsets is further clarified with short defining glosses
- Synsets are connected to other synsets via a number of semantic relations
HowNet
- HowNet is a extra-linguistic common-sense knowledge system for the computation of meaning in human language technology
- The concept definition in HowNet is based on sememes.
- HowNet constructs a graph structure of its knowledge base on the inter-concept relations and inter-attribute relations.
- Hypothesizes that all concepts can be reduced to the relevant sememes
Lecture 8 Word Sense Disambigulation
Two Assumption
- One sense per Collocation 每个搭配一个语义
— 相邻词提供了可用于判断目标词语义的线索。
— nearby words provide strong and consistent clues to the sense of a target word, conditional on relative distance, order and syntactic relationship. - One Sense per Discourse 每个文本一个语义
— 给定的文本,目标词语义有很强的一致性。
— The sense of a target word is highly consistent within any given document.
— True for topic dependent words
— Not true for verbs
ATTENTION
如果觉得好,请打赏 :)