前言
HashMap可以说是我们日常开发中特别经常使用到的对象映射关系集合类了,本文将结合JDK1.8源码从线程安全、数据结构、初始化、扩容、增删改查、特性总结等几个部分去分析HashMap
线程安全
HashMap是非线程安全的,不支持并发。我们可以从它的数据迭代器中可以得知,当产生线程安全问题时会抛出抛出ConcurrentModificationException异常。内部是通过一个modCount变量记录集合的变化,在扩容与删除及清空等操作都会将modCount自增,以此来标记集合的改变。
如何实现线程安全
1.通过Colletions.synchronizedMap获取线程安全的Map对象
2.使用并发库下的ConcurrentMap
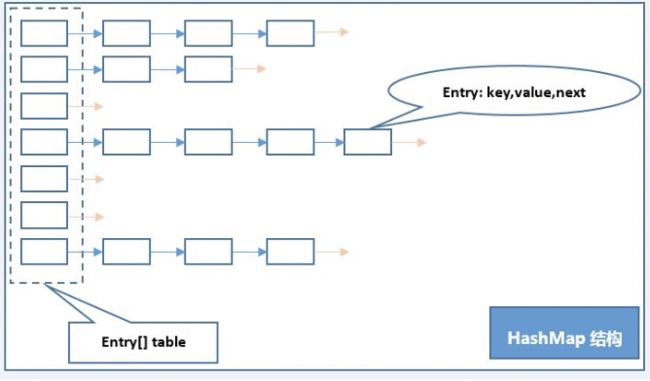
数据结构
哈希表(数据+单链表),结合了两者的优势,采用拉链法解决哈希冲突。哈希冲突的常用解决方法包括拉链法和开发地址法,由于使用了链表链接冲突元素,那么证明它自然采用的是拉链法
初始化
提供了四个重载构造方法,除了默认的无参构造器外还可以指定初始容量以及初始集合内容以及同时指定容量与加载因子。无参构造器仅仅指定扩容因子为默认值0.75;指定集合时泽通过entrySet遍历将每个item指定putVal进行添加;容量指的是数组长度length的大小
public HashMap() {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; // all other fields defaulted
}
public HashMap(int initialCapacity) { ... }
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { ... }
final void putMapEntries(Map m, boolean evict) {
int s = m.size();
if (s > 0) {
// 表为null 进行初始化
if (table == null) { // pre-size
// 计算新的扩容阀值
float ft = ((float)s / loadFactor) + 1.0F;
int t = ((ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
(int)ft : MAXIMUM_CAPACITY); // 扩容阀值越界判断
if (t > threshold) // 阀值初始化,首次的时候阀值=容量
threshold = tableSizeFor(t);
}
else if (s > threshold)
resize();
for (Map.Entry e : m.entrySet()) {
K key = e.getKey();
V value = e.getValue();
putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, evict);
}
}
}
// 初始化容量,移位操作比符号运算效率更高
// 此处tableSizeFor最后返回的有效位都是1,最后n+1恒为2的n次幂。先注意下,后面会提到。也就是说最后容量result总是>=cap
static final int tableSizeFor(int cap) {
int n = cap - 1;
n |= n >>> 1;
n |= n >>> 2;
n |= n >>> 4;
n |= n >>> 8;
n |= n >>> 16;
return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1;
}
扩容
HashMap的扩容主要步骤如下:更新阀值 -> 构建新的哈希桶 -> 将元素移动到新哈希桶中,正常情况下每次扩容后为原容量2,使得容量总是为2的n次幂。实际的扩容操作,首先是根据三种情况进行。第一种情况是此次扩容属于首次扩容,如果旧阀值大于0(使用了两个有参构造器),则新容量即为旧阀值。第二种情况是此次扩容属于首次扩容,该HashMap使用无参构造器进行初始化,那么新容量为默认值16,阀值为160.75。第三种情况,此处扩容非首次扩容,那么新容量为旧容量2,新阀值为旧阀值2
// 扩容函数
final Node[] resize() {
Node[] oldTab = table; // 旧哈希表
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length; // 旧容量
int oldThr = threshold; // 旧阀值
int newCap, newThr = 0; // 新容量与新阀值
if (oldCap > 0) { // 旧容量大于0,属于非首次扩容情况
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { // 越界保护
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab; // 无法继续扩容
}
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold 新阀值为旧阀值*2
}
// 首次扩容,且初始化时指定了阀值
else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold
// 由于初始化的阀值通过tableSizeFor获得,因此最后的结果也是2的n次幂
newCap = oldThr; // 新容量直接等于初始化的阀值
// 首次扩容,切初始化时使用的默认无参构造器
else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY; // 新容量为默认容量16
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY); // 新阀值为默认容量*默认加载因子,即16*0.75
}
// 指定新阀值为新容量*加载因子
if (newThr == 0) {
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
threshold = newThr;
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node[] newTab = (Node[])new Node[newCap];
table = newTab;
// 以下开始进行数据迁移
if (oldTab != null) {
// 遍历节点,注意哈希表结构。如果存在哈希碰撞的情况,某个节点可能还有链表节点。
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node e;
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) { // 临时存储目标节点
oldTab[j] = null; // 旧表对应位置元素置空,方便gc
// next为null表示该节点没有hash碰撞找到下标赋值,采用hash & (newCap - 1),使用&与操作来代替%取模操作,提高效率。为了使&能够达到更加均匀的分布,减少hash碰撞,因此newCap的取值总是2的n次方
if (e.next == null)
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e; // 放到新表
// 如果发生过哈希碰撞 ,而且是节点数超过8个,转化成了红黑树
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
// 如果发生过哈希碰撞,节点数未超过8个
// 存在碰撞的话,那么对于的链表上的节点有两种可能
// 第一种,hash与新容量取模后小于旧容量,即值与hash与旧容量取模一样(低位)
// 第二种,hash与新容量取模后大于旧容量,即值为hash与旧容量取模 + 旧容量(高位)
else { // preserve order
// 低位链表头尾节点
Node loHead = null, loTail = null;
// 高位链表头尾节点
Node hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node next; // 操作节点
do {
next = e.next; // 操作节点赋值
// 通过hash与旧容量的与操作是否为0(高效)(注意是oldCap而不是olcCap-1)
// 判断与新容量取模后的值是否大于旧容量
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
// 结果==0表示处于低位
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}
else { // 结果!=0表示处于高位
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null); // while循环,处理链表上所有节点
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead; // 放到新表中
}
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead; // 放到新表中
}
}
}
}
}
return newTab;
}
Hash处理
获取key的Hash值时不是直接返回其hashCode方法的值,而是通过“扰动函数”进行处理后返回。hashCode()是int类型,取值范围是40多亿,只要哈希函数映射的比较均匀松散,碰撞几率是很小的。但是由于HashMap的哈希桶长度要远远小于hashCode(),因为一般采用取余的方式获取key对应的桶下标,在HashMap中采用与操作来实现取余,如果直接使用hashCode()会忽略高位,导致碰撞几率增大。扰动函数就是为了解决hash碰撞的。它会综合hash值高位和低位的特征,并存放在低位,因此在与运算时,相当于高低位一起参与了运算,以减少hash碰撞的概率
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
增改操作
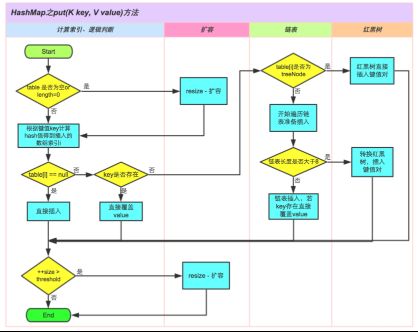
若数组为空则进行扩容,获取index下标,若对应位置上没有元素则直接赋值,若有元素先判断是否key一致(hash与equals均一致),一致则进行覆盖。不一致则表示发生碰撞,而HashMap采用拉链法解决碰撞,在对应链表上需要是否有key一致的元素,有则覆盖,没有则在末尾插入节点。(会修改modCount变量)最后,按需扩容。
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
// JDK 1.8 新增方法,若对应key的value之前存在,则不覆盖
public V putIfAbsent(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, true, true);
}
public void putAll(Map m) {
putMapEntries(m, true);
}
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node[] tab; Node p; int n, I;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
// index位置没有元素,直接赋值
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node e; K k;
// index上元素key与目标key一致
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
// 红黑树(当链表节点数大于8,转为红黑树)
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else { // 链表节点数小于8
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
// 到末尾节点,仍没有找到key一致的节点
// 将此元素插入到该链表末尾
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
// 当链表节点数大于8,转为红黑树
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
// 链表中存在key一致的节点
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
// 上述过程找到了key一致的元素,修改value
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
// 是否覆盖value
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);// 回调
return null;
}
// 为LinkedHashMap提供的回调函数
void afterNodeAccess(Node p) { } // 访问(查)
void afterNodeInsertion(boolean evict) { } // 插入(增)
void afterNodeRemoval(Node p) { } // 移除(删)
删操作
根据key为条件或者以key-value为条件。首先找到key一致元素(链表头,或者链表中),然后从数组或链表中剔除。修改modCount与size
public V remove(Object key) {
Node e;
return (e = removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true)) == null ?
null : e.value;
}
public boolean remove(Object key, Object value) {
return removeNode(hash(key), key, value, true, true) != null;
}
final Node removeNode(int hash, Object key, Object value,
boolean matchValue, boolean movable) {
Node[] tab; Node p; int n, index;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(p = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
Node node = null, e; K k; V v;
// 通过index找到key相同的元素
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
node = p;
// 发生碰撞,在对应链表中寻找
else if ((e = p.next) != null) {
if (p instanceof TreeNode)
node = ((TreeNode)p).getTreeNode(hash, key);
else {
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key ||
(key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
node = e;
break;
}
p = e; // P为被删除前一个(当目标即为第一个时p==node)
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
// 移除元素,修改指针
if (node != null && (!matchValue || (v = node.value) == value ||
(value != null && value.equals(v)))) {
if (node instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode)node).removeTreeNode(this, tab, movable);
else if (node == p) // 链表首个元素,数组位置指向其next
tab[index] = node.next;
else
p.next = node.next; // p.next跨过目标元素
++modCount;
--size;
afterNodeRemoval(node); // 删除回调
return node;
}
}
return null;
}
查:通过hash去查找元素value
public V get(Object key) {
Node e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
}
public boolean containsKey(Object key) {
return getNode(hash(key), key) != null;
}
final Node getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node[] tab; Node first, e; int n; K k;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
// 表头
if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
// 表中
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
return ((TreeNode)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
do {
// key一致(hash相等,equals成立)
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null; // 没找到
}
// 双层for:数字 + 链表
public boolean containsValue(Object value) {
Node[] tab; V v;
if ((tab = table) != null && size > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < tab.length; ++i) {
for (Node e = tab[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if ((v = e.value) == value ||
(value != null && value.equals(v)))
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
无序性
从HashIterator类中我们可以看出元素的遍历是从哈希桶从低到高,链表从前到后
abstract class HashIterator {
Node next; // next entry to return
Node current; // current entry
int expectedModCount; // for fast-fail
int index; // current slot
......
final Node nextNode() {
Node[] t;
Node e = next;
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
if (e == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
if ((next = (current = e).next) == null && (t = table) != null) {
do {} while (index < t.length && (next = t[index++]) == null);
}
return e;
}
特性总结
HashMap采用数组+单链表结构,key与value均可为null
(在JDK1.7中专门有个HashMapEntry对象用于存储key为null的元素,而JDK1.8中则是针对key==null的情况返回hash为0来进行实现)
HashMap中的高效运算:(1)通过&来进行取模,hash&(cap - 1)(2)在旧元素拷贝到新的哈希桶中,通过&进行高低位判断,hash&oldCap
HashMap中的碰撞优化:(1)哈希桶的容量总是为2的n次方,为了让hash结果分布均匀,减少hash碰撞(2)扰动函数:避免取模时只关注hashCode低位,减少hash碰撞,让高低位同时参数hash计算。hash = (h = key.hashCode()) ^ h >>> 16
HashMap与HashTable的区别
HashTable是线程安全的,且不允许key、value是null
HashTable默认容量是11
HashTable是直接使用key的hashCode()作为hash值
HashTable取哈希桶下标是直接用模运算%.(因为其默认容量也不是2的n次方,所以也无法用位运算替代模运算)
扩容时,新容量是原来的2倍+1。int newCapacity = (oldCapacity << 1) + 1