占小狼 转载请注明原创出处,谢谢!
本文主要分析Netty服务端的启动过程。
Netty是基于Nio实现的,所以也离不开selector、serverSocketChannel、socketChannel和selectKey等,只不过Netty把这些实现都封装在了底层。
从示例可以看出,一切从ServerBootstrap开始。
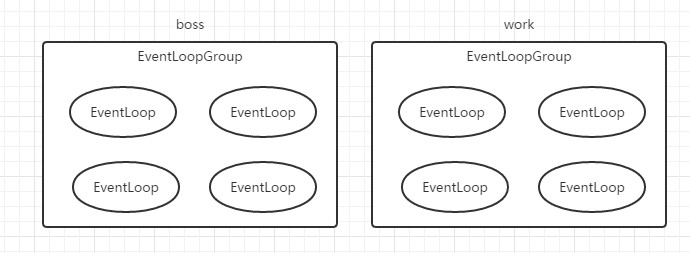
ServerBootstrap实例中需要两个NioEventLoopGroup实例,按照职责划分成boss和work,有着不同的分工:
1、boss负责请求的accept
2、work负责请求的read、write
NioEventLoopGroup
NioEventLoopGroup主要管理eventLoop的生命周期。
eventLoop是什么?姑且把它看成是内部的一个处理线程,数量默认是处理器个数的两倍。
NioEventLoopGroup构造方法:
public NioEventLoopGroup() {
this(0);
}
public NioEventLoopGroup(int nThreads) {
this(nThreads, null);
}
public NioEventLoopGroup(int nThreads, ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
this(nThreads, threadFactory, SelectorProvider.provider());
}
public NioEventLoopGroup(
int nThreads, ThreadFactory threadFactory, final SelectorProvider selectorProvider) {
super(nThreads, threadFactory, selectorProvider);
}
MultithreadEventLoopGroup是NioEventLoopGroup的父类,构造方法:
protected MultithreadEventLoopGroup(int nThreads, ThreadFactory threadFactory, Object... args) {
super(nThreads == 0? DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS : nThreads, threadFactory, args);
}
其中 DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS 为处理器数量的两倍。
MultithreadEventExecutorGroup是核心,管理eventLoop的生命周期,先看看其中几个变量。
1、children:EventExecutor数组,保存eventLoop。
2、chooser:从children中选取一个eventLoop的策略。
构造方法:
protected MultithreadEventExecutorGroup(int nThreads, ThreadFactory threadFactory, Object... args) {
if (nThreads <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("nThreads: %d (expected: > 0)", nThreads));
}
if (threadFactory == null) {
threadFactory = newDefaultThreadFactory();
}
children = new SingleThreadEventExecutor[nThreads];
if (isPowerOfTwo(children.length)) {
chooser = new PowerOfTwoEventExecutorChooser();
} else {
chooser = new GenericEventExecutorChooser();
}
for (int i = 0; i < nThreads; i ++) {
boolean success = false;
try {
children[i] = newChild(threadFactory, args);
success = true;
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: Think about if this is a good exception type
throw new IllegalStateException("failed to create a child event loop", e);
} finally {
if (!success) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j ++) {
children[j].shutdownGracefully();
}
for (int j = 0; j < i; j ++) {
EventExecutor e = children[j];
try {
while (!e.isTerminated()) {
e.awaitTermination(Integer.MAX_VALUE, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
} catch (InterruptedException interrupted) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
break;
}
}
}
}
}
final FutureListener1、根据数组的大小,采用不同策略初始化chooser,如果大小为2的幂次方,则采用PowerOfTwoEventExecutorChooser,否则使用GenericEventExecutorChooser。
其中判断一个数是否是2的幂次方的方法,觉得很赞。
private static boolean isPowerOfTwo(int val) {
return (val & -val) == val;
}
2、newChild方法重载,初始化EventExecutor时,实际执行的是NioEventLoopGroup中的newChild方法,所以children元素的实际类型为NioEventLoop。
接下去看看NioEventLoop类。
NioEventLoop
每个eventLoop会维护一个selector和taskQueue,负责处理客户端请求和内部任务,如ServerSocketChannel注册和ServerSocket绑定等。
NioEventLoop构造方法:
NioEventLoop(NioEventLoopGroup parent, ThreadFactory threadFactory, SelectorProvider selectorProvider) {
super(parent, threadFactory, false);
if (selectorProvider == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("selectorProvider");
}
provider = selectorProvider;
selector = openSelector();
}
当看到 selector = openSelector() 时,有没有觉得亲切了许多,这里先不管 selector,看看SingleThreadEventLoop类。
SingleThreadEventLoop是NioEventLoop的父类,构造方法:
protected SingleThreadEventLoop(EventLoopGroup parent, ThreadFactory threadFactory, boolean addTaskWakesUp) {
super(parent, threadFactory, addTaskWakesUp);
}
啥事都没做...
继续看SingleThreadEventLoop的父类SingleThreadEventExecutor
从类名上可以看出,这是一个只有一个线程的线程池, 先看看其中的几个变量:
1、state:线程池当前的状态
2、taskQueue:存放任务的队列
3、thread:线程池维护的唯一线程
4、scheduledTaskQueue:定义在其父类AbstractScheduledEventExecutor中,用以保存延迟执行的任务。
...
构造方法:
protected SingleThreadEventExecutor(EventExecutorGroup parent, ThreadFactory threadFactory, boolean addTaskWakesUp) {
if (threadFactory == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("threadFactory");
}
this.parent = parent;
this.addTaskWakesUp = addTaskWakesUp;
thread = threadFactory.newThread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
boolean success = false;
updateLastExecutionTime();
try {
SingleThreadEventExecutor.this.run();
success = true;
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("Unexpected exception from an event executor: ", t);
} finally {
for (;;) {
int oldState = STATE_UPDATER.get(SingleThreadEventExecutor.this);
if (oldState >= ST_SHUTTING_DOWN || STATE_UPDATER.compareAndSet(
SingleThreadEventExecutor.this, oldState, ST_SHUTTING_DOWN)) {
break;
}
}
// Check if confirmShutdown() was called at the end of the loop.
if (success && gracefulShutdownStartTime == 0) {
logger.error(
"Buggy " + EventExecutor.class.getSimpleName() + " implementation; " +
SingleThreadEventExecutor.class.getSimpleName() + ".confirmShutdown() must be called " +
"before run() implementation terminates.");
}
try {
// Run all remaining tasks and shutdown hooks.
for (;;) {
if (confirmShutdown()) {
break;
}
}
} finally {
try {
cleanup();
} finally {
STATE_UPDATER.set(SingleThreadEventExecutor.this, ST_TERMINATED);
threadLock.release();
if (!taskQueue.isEmpty()) {
logger.warn(
"An event executor terminated with " +
"non-empty task queue (" + taskQueue.size() + ')');
}
terminationFuture.setSuccess(null);
}
}
}
}
});
threadProperties = new DefaultThreadProperties(thread);
taskQueue = newTaskQueue();
}
代码很长,内容很简单:
1、初始化一个线程,并在线程内部执行NioEventLoop类的run方法,当然这个线程不会立刻执行。
2、使用LinkedBlockingQueue类初始化taskQueue。
到目前为止,相关的处理线程已经初始化完成。
ServerBootstrap
通过serverBootstrap.bind(port)启动服务,过程如下:
/**
* Create a new {@link Channel} and bind it.
*/
public ChannelFuture bind() {
validate();
SocketAddress localAddress = this.localAddress;
if (localAddress == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("localAddress not set");
}
return doBind(localAddress);
}
doBind实现如下
private ChannelFuture doBind(final SocketAddress localAddress) {
final ChannelFuture regFuture = initAndRegister();
final Channel channel = regFuture.channel();
if (regFuture.cause() != null) {
return regFuture;
}
if (regFuture.isDone()) {
// At this point we know that the registration was complete and successful.
ChannelPromise promise = channel.newPromise();
doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);
return promise;
} else {
// Registration future is almost always fulfilled already, but just in case it's not.
final PendingRegistrationPromise promise = new PendingRegistrationPromise(channel);
regFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
Throwable cause = future.cause();
if (cause != null) {
// Registration on the EventLoop failed so fail the ChannelPromise directly to not cause an
// IllegalStateException once we try to access the EventLoop of the Channel.
promise.setFailure(cause);
} else {
// Registration was successful, so set the correct executor to use.
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2586
promise.executor = channel.eventLoop();
}
doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);
}
});
return promise;
}
}
1、方法initAndRegister返回一个ChannelFuture实例regFuture,通过regFuture可以判断initAndRegister执行结果。
2、如果regFuture.isDone()为true,说明initAndRegister已经执行完,则直接执行doBind0进行socket绑定。
3、否则regFuture添加一个ChannelFutureListener监听,当initAndRegister执行完成时,调用operationComplete方法并执行doBind0进行socket绑定。
所以只有当initAndRegister操作结束之后才能进行bind操作。
initAndRegister实现
final ChannelFuture initAndRegister() {
final Channel channel = channelFactory().newChannel();
try {
init(channel);
} catch (Throwable t) {
channel.unsafe().closeForcibly();
// as the Channel is not registered yet we need to force the usage of the GlobalEventExecutor
return new DefaultChannelPromise(channel, GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE).setFailure(t);
}
ChannelFuture regFuture = group().register(channel);
if (regFuture.cause() != null) {
if (channel.isRegistered()) {
channel.close();
} else {
channel.unsafe().closeForcibly();
}
}
return regFuture;
}
1、负责创建服务端的NioServerSocketChannel实例
2、为NioServerSocketChannel的pipeline添加handler
3、注册NioServerSocketChannel到selector
大部分的过程和NIO中类似。
NioServerSocketChannel
对Nio的ServerSocketChannel和SelectionKey进行了封装。
构造方法:
public NioServerSocketChannel() {
this(newSocket(DEFAULT_SELECTOR_PROVIDER));
}
private static ServerSocketChannel newSocket(SelectorProvider provider) {
try {
return provider.openServerSocketChannel();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ChannelException(
"Failed to open a server socket.", e);
}
}
public NioServerSocketChannel(ServerSocketChannel channel) {
super(null, channel, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
config = new NioServerSocketChannelConfig(this, javaChannel().socket());
}
1、方法newSocket利用 provider.openServerSocketChannel() 生成Nio中的ServerSocketChannel对象。
2、设置SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT事件。
AbstractNioMessageChannel构造方法
protected AbstractNioMessageChannel(Channel parent, SelectableChannel ch, int readInterestOp) {
super(parent, ch, readInterestOp);
}
啥也没做...
AbstractNioChannel构造方法
protected AbstractNioChannel(Channel parent, SelectableChannel ch, int readInterestOp) {
super(parent);
this.ch = ch;
this.readInterestOp = readInterestOp;
try {
ch.configureBlocking(false);
} catch (IOException e) {
try {
ch.close();
} catch (IOException e2) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn(
"Failed to close a partially initialized socket.", e2);
}
}
throw new ChannelException("Failed to enter non-blocking mode.", e);
}
}
设置当前ServerSocketChannel为非阻塞通道。
AbstractChannel构造方法
protected AbstractChannel(Channel parent) {
this.parent = parent;
unsafe = newUnsafe();
pipeline = new DefaultChannelPipeline(this);
}
1、初始化unsafe,这里的Unsafe并非是jdk中底层Unsafe类,用来负责底层的connect、register、read和write等操作。
2、初始化pipeline,每个Channel都有自己的pipeline,当有请求事件发生时,pipeline负责调用相应的hander进行处理。
unsafe和pipeline的具体实现原理会在后续进行分析。
回到ServerBootstrap的init(Channel channel)方法,添加handler到channel的pipeline中。
void init(Channel channel) throws Exception {
final Map, Object> options = options();
synchronized (options) {
channel.config().setOptions(options);
}
final Map, Object> attrs = attrs();
synchronized (attrs) {
for (Entry, Object> e: attrs.entrySet()) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
AttributeKey key = (AttributeKey) e.getKey();
channel.attr(key).set(e.getValue());
}
}
ChannelPipeline p = channel.pipeline();
final EventLoopGroup currentChildGroup = childGroup;
final ChannelHandler currentChildHandler = childHandler;
final Entry, Object>[] currentChildOptions;
final Entry, Object>[] currentChildAttrs;
synchronized (childOptions) {
currentChildOptions = childOptions.entrySet().toArray(newOptionArray(childOptions.size()));
}
synchronized (childAttrs) {
currentChildAttrs = childAttrs.entrySet().toArray(newAttrArray(childAttrs.size()));
}
p.addLast(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
public void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
ChannelHandler handler = handler();
if (handler != null) {
pipeline.addLast(handler);
}
pipeline.addLast(new ServerBootstrapAcceptor(
currentChildGroup, currentChildHandler, currentChildOptions, currentChildAttrs));
}
});
}
1、设置channel的options和attrs。
2、在pipeline中添加一个ChannelInitializer对象。
init执行完,需要把当前channel注册到EventLoopGroup。
其实最终目的是为了实现Nio中把ServerSocket注册到selector上,这样就可以实现client请求的监听了。看看Netty中是如何实现的:
public ChannelFuture register(Channel channel, ChannelPromise promise) {
return next().register(channel, promise);
}
public EventLoop next() {
return (EventLoop) super.next();
}
public EventExecutor next() {
return children[Math.abs(childIndex.getAndIncrement() % children.length)];
}
因为EventLoopGroup中维护了多个eventLoop,next方法会调用chooser策略找到下一个eventLoop,并执行eventLoop的register方法进行注册。
public ChannelFuture register(final Channel channel, final ChannelPromise promise) {
...
channel.unsafe().register(this, promise);
return promise;
}
channel.unsafe()是什么?
NioServerSocketChannel初始化时,会创建一个NioMessageUnsafe实例,用于实现底层的register、read、write等操作。
eventLoop.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
register0(promise);
}
});
private void register0(ChannelPromise promise) {
try {
if (!ensureOpen(promise)) {
return;
}
Runnable postRegisterTask = doRegister();
registered = true;
promise.setSuccess();
pipeline.fireChannelRegistered();
if (postRegisterTask != null) {
postRegisterTask.run();
}
if (isActive()) {
pipeline.fireChannelActive();
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
// Close the channel directly to avoid FD leak.
closeForcibly();
if (!promise.tryFailure(t)) {
}
closeFuture.setClosed();
}
}
public void execute(Runnable task) {
if (task == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("task");
}
boolean inEventLoop = inEventLoop();
if (inEventLoop) {
addTask(task);
} else {
startThread();
addTask(task);
if (isShutdown() && removeTask(task)) {
reject();
}
}
if (!addTaskWakesUp) {
wakeup(inEventLoop);
}
}
1、register0方法提交到eventLoop线程池中执行,这个时候会启动eventLoop中的线程。
2、方法doRegister()才是最终Nio中的注册方法,方法javaChannel()获取ServerSocketChannel。
protected Runnable doRegister() throws Exception {
boolean selected = false;
for (;;) {
try {
selectionKey = javaChannel().register(eventLoop().selector, 0, this);
return null;
} catch (CancelledKeyException e) {
if (!selected) {
// Force the Selector to select now as the "canceled" SelectionKey may still be
// cached and not removed because no Select.select(..) operation was called yet.
eventLoop().selectNow();
selected = true;
} else {
// We forced a select operation on the selector before but the SelectionKey is still cached
// for whatever reason. JDK bug ?
throw e;
}
}
}
}
ServerSocketChannel注册完之后,通知pipeline执行fireChannelRegistered方法,pipeline中维护了handler链表,通过遍历链表,执行InBound类型handler的channelRegistered方法,最终执行init中添加的ChannelInitializer handler。
public final void channelRegistered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx)
throws Exception {
boolean removed = false;
boolean success = false;
try {
initChannel((C) ctx.channel());
ctx.pipeline().remove(this);
removed = true;
ctx.fireChannelRegistered();
success = true;
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("Failed to initialize a channel. Closing: " + ctx.channel(), t);
} finally {
if (!removed) {
ctx.pipeline().remove(this);
}
if (!success) {
ctx.close();
}
}
}
1、initChannel方法最终把ServerBootstrapAcceptor添加到ServerSocketChannel的pipeline,负责accept客户端请求。
2、在pipeline中删除对应的handler。
3、触发fireChannelRegistered方法,可以自定义handler的channelRegistered方法。
到目前为止,ServerSocketChannel完成了初始化并注册到seletor上,启动线程执行selector.select()方法准备接受客户端请求。
细心的同学已经发现,ServerSocketChannel的socket还未绑定到指定端口,那么这一块Netty是如何实现的?
Netty把注册操作放到eventLoop中执行。
private static void doBind0(
final ChannelFuture regFuture,
final Channel channel,
final SocketAddress localAddress,
final ChannelPromise promise) {
channel.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (regFuture.isSuccess()) {
channel.bind(localAddress, promise)
.addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE_ON_FAILURE);
} else {
promise.setFailure(regFuture.cause());
}
}
});
}
public ChannelFuture bind(SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise) {
return pipeline.bind(localAddress, promise);
}
@Override
public ChannelFuture bind(SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise) {
return tail.bind(localAddress, promise);
}
@Override
public ChannelFuture bind(SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise) {
if (localAddress == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("localAddress");
}
validatePromise(promise, false);
return findContextOutbound().invokeBind(localAddress, promise);
}
private ChannelFuture invokeBind(final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {
EventExecutor executor = executor();
if (executor.inEventLoop()) {
invokeBind0(localAddress, promise);
} else {
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
invokeBind0(localAddress, promise);
}
});
}
return promise;
}
private void invokeBind0(SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise) {
try {
((ChannelOutboundHandler) handler()).bind(this, localAddress, promise);
} catch (Throwable t) {
notifyOutboundHandlerException(t, promise);
}
}
@Override
public void bind(
ChannelHandlerContext ctx, SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise)
throws Exception {
unsafe.bind(localAddress, promise);
}
最终由unsafe实现端口的bind操作。
public final void bind(final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {
if (!ensureOpen(promise)) {
return;
}
try {
boolean wasActive = isActive();
...
doBind(localAddress);
promise.setSuccess();
if (!wasActive && isActive()) {
pipeline.fireChannelActive();
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
promise.setFailure(t);
closeIfClosed();
}
}
protected void doBind(SocketAddress localAddress) throws Exception {
javaChannel().socket().bind(localAddress, config.getBacklog());
}
bind完成后,且ServerSocketChannel也已经注册完成,则触发pipeline的fireChannelActive方法,所以在这里可以自定义fireChannelActive方法,默认执行tail的fireChannelActive。
@Override
public ChannelPipeline fireChannelActive() {
head.fireChannelActive();
if (channel.config().isAutoRead()) {
channel.read();
}
return this;
}
channel.read()方法会触发pipeline的行为:
@Override
public Channel read() {
pipeline.read();
return this;
}
@Override
public ChannelPipeline read() {
tail.read();
return this;
}
@Override
public ChannelHandlerContext read() {
findContextOutbound().invokeRead();
return this;
}
private void invokeRead() {
EventExecutor executor = executor();
if (executor.inEventLoop()) {
invokeRead0();
} else {
Runnable task = invokeRead0Task;
if (task == null) {
invokeRead0Task = task = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
invokeRead0();
}
};
}
executor.execute(task);
}
}
private void invokeRead0() {
try {
((ChannelOutboundHandler) handler()).read(this);
} catch (Throwable t) {
notifyHandlerException(t);
}
}
最终会在pipeline中找到handler执行read方法,默认是head。
至此为止,server已经启动完成。
END,我是占小狼。