Objective-C 中的消息与消息转发
1.Objective-C方法调用
我们知道objc的消息机制是由运行时实现,如果我们像这样调用
[receiver message];
经过clang转化成C后变成了这样
((void (*)(id, SEL))(void *)objc_msgSend)((id)receiver, sel_registerName("message"));
如果我们去掉强制转换,并用@selector语法糖代替sel_registerName(),可以得到
objc_msgSend(receiver, @selector(message));
所以OC中的方法调用,在运行时都会转换成向对象发送消息,即objc_msgSend的调用。
如果我们现在想要实验一下objc_msgSend,
- 需要在项目里的Build Settings 搜索ENABLE_STRICT_OBJC_MSGSEND,并将其设置成No。
- 然后导入
#import:objc-runtime.h里面包括有#include和#include,前面一个和运行时添加方法,变量等有关。后一个和消息调用有关。
函数定义:
在id objc_msgSend(id self, SEL _cmd, ...)
解释:
将一个消息发送给一个对象,并且返回一个值。
其中,self是消息的接受者,_cmd是selector, …是可变参数列表。
当向一般对象发送消息时,调用objc_msgSend;当向super发送消息时,调用的是objc_msgSendSuper; 如果返回值是一个结构体,则会调用objc_msgSend_stret或objc_msgSendSuper_stret。
2.Objective-C发送消息时的数据结构
数据结构说明:
typedef struct objc_class *Class;
typedef struct objc_object *id;
struct objc_object {
Class isa;
};
struct objc_class {
Class isa;
}
/// 不透明结构体, selector
typedef struct objc_selector *SEL;
/// 函数指针, 用于表示对象方法的实现
typedef id (*IMP)(id, SEL, ...);
关于Class和isa的说明,请参照
iOS的类与对象
SEL:表示选择器,这是一个不透明结构体。但是实际上,通常可以把它理解为一个字符串。例如printf("%s",@selector(isEqual:))会打印出”isEqual:”。运行时维护着一张全局的SEL的表,将相同字符串的方法名映射到唯一一个SEL。 通过sel_registerName(char *name)方法,可以查找到这张表中方法名对应的SEL。苹果提供了一个语法糖@selector用来方便地调用该函数。
IMP:是一个函数指针。objc中的方法最终会被转换成纯C的函数,IMP就是为了表示这些函数的地址。
3.objc_msgSend如何进行发消息
为了加快响应速度,苹果对这个方法做了很多优化,用伪代码可以加深我们对苹果内部的优化:
id objc_msgSend(id self, SEL op, ...) {
if (!self) return nil;
IMP imp = class_getMethodImplementation(self->isa, SEL op);
imp(self, op, ...); //调用这个函数,伪代码...
}
//查找IMP
IMP class_getMethodImplementation(Class cls, SEL sel) {
if (!cls || !sel) return nil;
IMP imp = lookUpImpOrNil(cls, sel);
if (!imp) return _objc_msgForward; //这个是用于消息转发的
return imp;
}
IMP lookUpImpOrNil(Class cls, SEL sel) {
if (!cls->initialize()) {
_class_initialize(cls);
}
Class curClass = cls;
IMP imp = nil;
do { //先查缓存,缓存没有时重建,仍旧没有则向父类查询
if (!curClass) break;
if (!curClass->cache) fill_cache(cls, curClass);
if(getImp(curClass->cache, sel)) { //如果缓存里有IMP,直接从缓存里取
imp = getImp(curClass->cache, sel);
} else {//如果缓存里没有IMP,从类里面查询
imp = getImp(curClass ->_method_list_t,sel);
if(imp) { //如果从类里面查询到IMP,把IMP放到cache中
putImp(curClass->cache,imp);
}
}
if (imp) break;
} while (curClass = curClass->superclass);
return imp;
}
解释:首先在Class的cache中查找imp(没缓存则初始化缓存),如果没找到,则导class的方法列表查找,如果查到则把IMP放人cache中,如果没有找到则向父类的Class查找。如果一直查找到根类仍旧没有实现,则用_objc_msgForward函数指针代替imp。最后,执行这个imp。
_objc_msgForward是用于消息转发的。这个函数的实现并没有在objc-runtime的开源代码里面,而是在Foundation框架里面实现的。加上断点启动程序后,会发现__CFInitialize这个方法会调用objc_setForwardHandler函数来注册一个实现。
4.objc_msgSend消息转发
上面可以知道,当向一个对象发送一条消息,但它并没有实现的时候,_objc_msgForward会尝试做消息转发。为了展示消息转发的具体动作,这里尝试向一个对象发送一条错误的消息,并查看一下_objc_msgForward是如何进行转发的。
首先开启调试模式、打印出所有运行时发送的消息:
我们在代码里执行下面的方法:instrumentObjcMessageSends(YES);
然后我们执行一个不存在的方法
instrumentObjcMessageSends(YES);
NyanCat *cat = [[NyanCat alloc] init];
[cat performSelector:(@selector(hello))];
运行时发送的所有消息都会打印到/tmp/msgSend-xxxx文件里了
以上就是消息转发的流程
1.调用resolveInstanceMethod:方法,允许用户在此时为该Class动态添加实现。如果有实现了,则调用并返回。如果仍没实现,继续下面的动作。
2.调用forwardingTargetForSelector:方法,尝试找到一个能响应该消息的对象。如果获取到,则直接转发给它。如果返回了nil,继续下面的动作。
3.调用methodSignatureForSelector:方法,尝试获得一个方法签名。如果获取不到,则直接调用doesNotRecognizeSelector抛出异常。
4.调用forwardInvocation:方法,将地3步获取到的方法签名包装成Invocation传入,如何处理就在这里面了。
5.如果以上四个流程我们都没做消息转发,那么就会抛出doesNotRecognizeSelector
上面这4个方法均是模板方法,开发者可以override,由runtime来调用。理论上消息的转发可以在以上的任何一个地方进行,最常见的实现消息转发,就是重写方法3和4,吞掉一个消息或者代理给其他对象都是没问题的。我们来分析下各个阶段应该如何做消息转发
5.objc_msgSend消息转发方法
5.1 重写resolveInstanceMethod
如果我们在NyanCat.m添加下面两个方法做消息转发,为这个NyanCat动态生成一个@selector(hello)的IMP
这里需要注意class_addMethod(Class cls, SEL name, IMP imp, const char *types)的最后一个参数types,用来标识IMP函数实现的返回值与参数,
具体的type encodings 可以参考apple官方提供的type encodings对应表:
这里没有的hello方法没有参数也没有返回值,所以填v@:就好
+ (BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel {
class_addMethod([self class], sel, (IMP)dynamicMethodIMP,"v@:");
return YES;
}
void dynamicMethodIMP(id self, SEL _cmd) {
NSLog(@"sel is %@", NSStringFromSelector(_cmd));
}
我们添加后再次运行
instrumentObjcMessageSends(YES);
NyanCat *cat = [[NyanCat alloc] init];
[cat performSelector:(@selector(hello))];
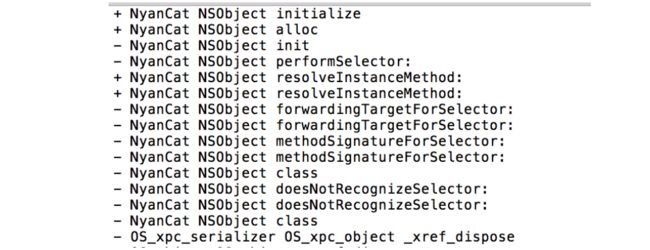
我们发现运行时的调用顺序如图所示,resolveInstanceMethod后成功定位到了hello,并打印出sel is hello,说明消息转发成功。
5.2 重写forwardingTargetForSelector
如果我们重写了forwardingTargetForSelector
- (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector {
if ([[People class] respondsToSelector: aSelector]) {
return [People class];
}
return [super forwardingTargetForSelector: aSelector];
}
我们发现运行时的调用顺序如图所示,forwardingTargetForSelector后成功被转发到了Person类,并打印出sel is hello,说明消息转发成功。我们这里return的是Class,当然也可以在这里return instance,那么就会映射到实例方法了。
5.3 重写methodSignatureForSelector 和forwardInvocation
1.无参数,无返回值
- (NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)aSelector {
return [[People class] instanceMethodSignatureForSelector:@selector(hello)];
}
- (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)anInvocation {
People *people = [[People alloc] init];
[anInvocation invokeWithTarget:people];
[anInvocation setSelector:@selector(hello)];
}
2.无参数,有返回值
- (NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)aSelector {
return [[People class] instanceMethodSignatureForSelector:@selector(hello)];
}
- (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)anInvocation {
People *people = [[People alloc] init];
[anInvocation setSelector:@selector(hello)];
[anInvocation invokeWithTarget:people];
NSInteger returnValue = 0;
[anInvocation getReturnValue:&returnValue];
NSLog(@"returnValue = %ld",(long)returnValue);
}
3.有参数,有返回值(且返回值为对象)
- (NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)aSelector {
return [[People class] instanceMethodSignatureForSelector:@selector(hello:)];
}
- (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)anInvocation {
People *people = [[People alloc] init];
NSString *arg1 = @"testArg1";
[anInvocation setArgument:&arg1 atIndex:2];
[anInvocation setTarget:people];
[anInvocation setSelector:@selector(hello:)];
[anInvocation invoke];
void *vc = nil;
id returnValue3;
[anInvocation getReturnValue:&vc];
returnValue3 = (__bridge id)vc;
NSLog(@"返回值:%@",[returnValue3 class]);
}
注意:
当返回值为对象是,arc情况下容易出现崩溃问题,如下两种解决方案。arc下vc如果用strong的,默认NSInvocation实现认为,已经对返回对象retain一次,实际上并没有,当返回对象出了作用域时候,已经被收回。导致崩溃。
解决方案1
void *vc = nil;
[method3Invocation getReturnValue:&vc];
NSLog(@"vc:%@",(__bridge ViewController*)vc);
解决方案2
id * __unsafe_unretained vc = nil;
[method3Invocation getReturnValue:&vc];
NSLog(@"vc:%@",vc);
5.4 如果不想要重写methodSignatureForSelector 和forwardInvocation,而是要通过一个中转站对消息转发,要如何做呢?
//People类实现下面三个方法
-(void)method1Test {
NSLog(@"method1Test");
}
-(NSInteger)method2Test {
NSLog(@"method2Test");
return 1;
}
-(id)method3Test:(NSString*)str {
NSLog(@"参数:%@",str);
return self;
}
在一个作为中转站的类进行方法动态派发。
//1.无参数,无返回值
//通过选择器获取方法签名
People *people = [People new];
SEL selector = @selector(method1Test);
NSMethodSignature *methodSig = [[People class] instanceMethodSignatureForSelector:selector];
//通过方法签名获得调用对象
NSInvocation *methodInvocation = [NSInvocation invocationWithMethodSignature:methodSig];
[methodInvocation setTarget:people];
[methodInvocation setSelector:selector];
[methodInvocation invoke];
//2.无参数,有返回值,返回值不为对象
selector = @selector(method2Test);
methodSig = [[People class] instanceMethodSignatureForSelector:selector];
NSInvocation *method2Invocation = [NSInvocation invocationWithMethodSignature:methodSig];
[method2Invocation setSelector:selector];
[method2Invocation setTarget:people];
[method2Invocation invoke];
NSInteger returnValue = 0;
[method2Invocation getReturnValue:&returnValue];
NSLog(@"返回值:%ld",returnValue);
//3.有参数,有返回值,返回值为对象
selector = @selector(method3Test:);
NSMethodSignature *method3Sign = [[People class] instanceMethodSignatureForSelector:selector];
NSInvocation *method3Invocation = [NSInvocation invocationWithMethodSignature:method3Sign];
[method3Invocation setTarget:people];
[method3Invocation setSelector:selector];
NSString *arg1 = @"testArg1";
[method3Invocation setArgument:&arg1 atIndex:2];
[method3Invocation invoke];
void *vc = nil;
id returnValue3;
[method3Invocation getReturnValue:&vc];
returnValue3 = (__bridge id)vc;
NSLog(@"返回值:%@",[returnValue3 class]);
}