springboot的部署测试监控
部署
基于maven
打包
JAR
打包方式一般采用的jar包,使用springboot的默认方式即可;
使用maven命令:
mvn clean package -Dmaven.test.skip=true执行成功之后,可以在对应的target目录下找到对应的包,比如: eg-zuul-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
WAR
运行
内置容器运行
springboot内置了web container容器 tomcat, 可以直接使用 java -jar命令运行;
例如:
java -jar xxx/target/eg-zuul-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar 外置容器运行
也可使用war的方式,使用外置的tomcat运行,不过代码需要改造一下:
1 改造打包方式
打包方式改为 war包;
在pom.xml中,在version标签的下面添加配置:
war 2 添加改造启动代码
package com.springbootpractice.egzuul;
import org.springframework.boot.builder.SpringApplicationBuilder;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.support.SpringBootServletInitializer;
/**
* @author carterbrother
* @description 通过外置的容器运行springboot
* @date 2019年06月21日 15:32
* @Copyright (c) carterbrother
*/
public class ServletInitializer extends SpringBootServletInitializer {
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder builder) {
return builder.sources(EgZuulApplication.class);
}
}原理是: 从servlet3.1开始,运行无web.xml的web程序,只需要实现ServletContainerInitializer接口,而SpringBootServletInitializer扩展了该类,所以可以实现无xml启动;
3 配置外置tomcat
4 忽略打包检查
org.apache.maven.plugins
maven-war-plugin
2.3
false
热部署
开发的时候用到, spring-boot-devtools ;
引入依赖:
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-devtools
true
暴露的配置信息可以配置更多细节方面的处理:
测试
基于junit 和 mockito (消除各种环境对于http带来的困难)
测试业务层
测试REST
package com.springbootpractice.eguser;
import com.springbootpractice.api.user.dto.UserPro;
import com.springbootpractice.eguser.service.UserService;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.boot.test.web.client.TestRestTemplate;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import java.util.Map;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
public class EgUserApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Autowired
private TestRestTemplate testRestTemplate;
@Test
public void testUserService() {
UserPro userPro = new UserPro();
userPro.setId(1L);
userPro.setUserName("xxxaaa");
final Map map = userService.insertUser(userPro);
Assert.assertEquals("插入失败",true,map.get("success"));
final UserPro userProReturn = userService.getUserPro(1L);
Assert.assertEquals(userPro,userProReturn);
}
@Test
public void testUserRest() {
UserPro userPro = new UserPro();
userPro.setId(2L);
userPro.setUserName("BBBB");
Map map = testRestTemplate.postForObject("/insert", userPro, Map.class);
Assert.assertEquals("插入失败",true,map.get("success"));
UserPro userProReturn = testRestTemplate.getForObject("/user/{id}", UserPro.class, 2L);
Assert.assertEquals(userPro,userProReturn);
}
} Mock测试
当依赖的服务还没有开发完毕,而需要测试的功能却强烈依赖,可以使用Mock来测试;
package com.springbootpractice.egproduct;
import com.springbootpractice.api.user.UserApi;
import com.springbootpractice.api.user.dto.UserPro;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.mockito.BDDMockito;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.boot.test.mock.mockito.MockBean;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
public class EgProductApplicationTests {
@MockBean
private UserApi userApi;
@Test
public void mockUserApiTest() {
UserPro mockUserPro = new UserPro();
mockUserPro.setId(1L);
mockUserPro.setUserName("xxxx");
BDDMockito.given(userApi.getUserPro(1L)).willReturn(mockUserPro);
UserPro userProReturn = userApi.getUserPro(1L);
Assert.assertEquals(userProReturn,mockUserPro);
}
}
监控
基于 actuator ,监控运行状态,进行一些简单的管理
WEB监控
引入依赖:
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-actuator
org.springframework.hateoas
spring-hateoas
0.24.0.RELEASE
默认只开放了 health , info ;
如果要开放所有的监控点:
management.endpoint.web.exposure.include=*
常见的监控点有:
| url | 监控说明 |
|---|---|
| health | 监控信息 |
| info | |
| beans | 容器中的Bean |
| mappings | url mapping |
| env | 配置参数 |
| shutdown | 关闭服务 |
| conditions | 自动装配相关的信息 |
对敏感的配置信息,可以使用spring-security来控制保护起来;
shutdown端点默认是关闭的,开启的配置属性是:
management.endpoint.shutdown.enabled=true
开启之后 访问 /actuator/shutdown 需要是post请求才能调用;
一般的配置端点开关的方式是:
//默认所有的端点都是关闭的,然后选择一些需要暴露的端点进行打开
management.endpoints.enabled-by-default=false
标注@Endpoint注解类,
@ReadOperation标注方法 标识GET方法
@WriteOperation 标识POST方法
@DeleteOperation 标识Delete方法
package com.springbootpractice.egproduct.endpoint;
import org.springframework.boot.actuate.endpoint.annotation.Endpoint;
import org.springframework.boot.actuate.endpoint.annotation.ReadOperation;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author carterbrother
* @description 新增actuator的一个端点
* @date 2019年06月21日 18:42
* @Copyright (c) carterbrother
*/
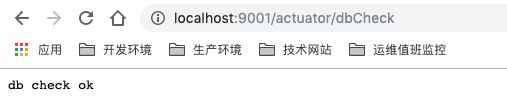
@Endpoint(id = "dbCheck",enableByDefault = true)
@Component
public class DBCheckEndpoint {
@ReadOperation
public String test(){
return "db check ok";
}
}
actuator内置了很多的健康指标 需要配置才能显示,配置方法:
management.endpoint.health.show-details=always
package com.springbootpractice.egproduct.health;
import org.springframework.boot.actuate.health.AbstractHealthIndicator;
import org.springframework.boot.actuate.health.Health;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetAddress;
/**
* @author carterbrother
* @description 进行网络检查
* @date 2019年06月21日 18:30
* @Copyright (c) carterbrother
*/
@Component
public class WWWHealthIndicator extends AbstractHealthIndicator {
@Override
protected void doHealthCheck(Health.Builder builder) throws Exception {
if (ping()){
builder.withDetail("message","可以正常连接互联网").up();
return;
}
builder.withDetail("message","无法连接互联网").unknown();
}
private boolean ping() {
try {
return InetAddress.getByName("www.baidu.com").isReachable(3000);
} catch (IOException e) {
return false;
}
}
}
JMX监控
相对于http监控,也提供了jmx的监控方式;
典型使用方式使用的是jdk的 jconsole,使用jmx协议连接本地的jvm,进行监控,MBean下的Health下可以查看到返回信息;以此来进行监控。
原创不易,转载请注明出处。