深入理解算法, 会让你很好的理解其他算法思想 ,其实对于算法大多数都是很好理解的
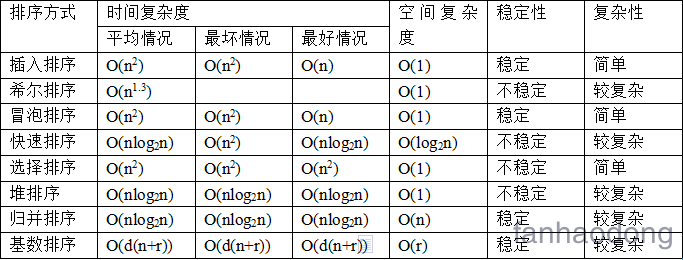
时间复杂度 , 空间复杂度
1. 选择排序
/**
* 选择排序 , 从开始位置每次找出最小那个数字, 放到起始位置 ,然后起始位置迭代重复操作
*
* @author: Anthony
*/
public class SelectSort {
private static void sort(int[] arr, int start, int len) {
for (int i = start; i < len; ++i) {
int min = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < len; ++j) {
if (arr[min] > arr[j]) {
min = j;
}
}
Common.swap(arr, i, min);
}
}
}2. 冒泡排序
/**
* 冒泡排序 ; 就是将大的数组往上冒(我这里上指的是数组尾端) , 所以冒一次就可以将一个最大的数冒的最上面, 所以不需要每次都全部冒
*
*
* @author: Anthony
*/
public class BubbleSort {
private static void sort(int[] arr, int start, int len) {
for (int i = start; i < len; i++) {
for (int j = start; j < len - start - 1; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
Common.swap(arr, j, j + 1);
}
}
}
}
}3. 插入排序
/**
* 插入排序 比如 2,3,1 数组 , 假如此时到1了进行插入排序, 1先拿出来, 3和1比较大,就向后移动一下,然后2和1比较还是大就继续向后移动, 此时就可以找到合适位置插入了
*
* @author: Anthony
*/
public class InsertSort {
private static void sort(int[] arr) {
/**
* 空 或者 0 / 1 都直接返回
*/
if (null == arr || arr.length <= 1) {
return;
}
// 2 3 1
for (int index = 1; index < arr.length; index++) {
// 当前位置 , 开始必须从第二个开始
int temp = arr[index];
// 左边位置
int left = index - 1;
// 移动坐标其实就是 ...
while (left >= 0 && arr[left] > temp) {
// 互换位置
arr[left + 1] = arr[left];
// 向前移动
left--;
}
// 最后保存数据数据所在位置
arr[left + 1] = temp;
}
}
}4. 快速排序
他利用递归的思想, 找到一个数, 那个数 ,他左边全部比他小, 右边全部比他大 , 然后无限递归下去 . 就可以快速排序了
/**
* 快速排序
*
* @author: Anthony
*/
public class QuickSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr_1000 = Common.generate_Arr_1000();
quickSort(arr_1000, 0, arr_1000.length);
showarr(arr_1000);
}
private static void quickSort(int[] arr, int low, int high) {
if (low >= high) return;
int index = getIndex2(arr, low, high);
quickSort(arr, low, index - 1);
quickSort(arr, index + 1, high);
}
/**
* 方法一 目的就是找到一个值 , 其实就是low索引所对应的的那个值
* 他的左边全部小于他的右边, 然后返回他的位置, 继续递归
*
* @return 返回low对应的数组中的数据, 所应该对应的真正索引位置
*/
private static int getIndex(int[] arr, int low, int high) {
int tmp = arr[low];
while (low < high) {
while (low < high && arr[high] >= tmp) {
high--;
}
arr[low] = arr[high];
while (low < high && arr[low] <= tmp) {
low++;
}
arr[high] = arr[low];
}
arr[low] = tmp;
return low;
}
/**
* 方法二 : 传统交换方法 和上述一样, 看喜欢用哪个
*
* @return
*/
private static int getIndex2(int[] arr, int low, int high) {
int start = low;
int tmp = arr[low];
while (low < high) {
while (low < high && arr[high] >= tmp) {
high--;
}
while (low < high && arr[low] <= tmp) {
low++;
}
swap(arr, low, high);
}
// 这里最好自己试一试
arr[start] = arr[low];
// 这里也是想一想就理解了
arr[low] = tmp;
return low;
}
private static void swap(int[] arr, int low, int high) {
int temp = arr[low];
arr[low] = arr[high];
arr[high] = temp;
}
private static void showarr(int[] arr) {
int count = 0;
for (int i : arr) {
count++;
System.out.printf("%d\t", i);
if (count % 10 == 0) {
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}