元算法是对其他算法进行组合的一种方式。本章首先讨论不同分类器的集成方法,然后主要关注boosting方法及其代表分类器Adaboost。
Adaboost
优点:泛化错误率低,易编码,可以应用在大部分分类器上,无参数调整
缺点:对离群点敏感
适用数据类型:数值型和标称型数据
bagging:自举汇聚法(bootstrap aggregating),也成为bagging方法,是从原始数据集选择S次吼得到S个新数据集的一种技术。新数据集大小和原始数据集的大小相等。
boosting:通过集中关注被已有分类器错分的那些数据来获得新的分类器。
单层决策树(decision stump,也称决策树桩),是一种简单的决策树。
#adaboost.py
from numpy import *
def loadSimpData():
datMat = matrix([[ 1. , 2.1],
[ 2. , 1.1],
[ 1.3, 1. ],
[ 1. , 1. ],
[ 2. , 1. ]])
classLabels = [1.0, 1.0, -1.0, -1.0, 1.0]
return datMat,classLabels
并加入
import adaboost
datMat,classLabels = adaboost.loadSimpData()
接下来可以通过构建多个函数来建立单层决策树,伪代码如下
将最小错误率minError设为正无穷
对数据集中的每一个特征(每一层循环):
对每一个步长(第二层循环):
对每一个不等号(第三层循环):
建立一颗单层决策树并利用加权数据集对它进行测试
如果错误率低于minError,则将当前单层决策树设为最佳单层决策树
返回最佳单层决策树
接下来开始构造这个函数
#7-1 单层决策树生成函数
def stumpClassify(dataMatrix,dimen,threshVal,threshIneq):#阈值比较分类
retArray = ones((shape(dataMatrix)[0],1))
if threshIneq == "lt":
retArray[dataMatrix[:,dimen] <= threshVal] = -1.0
else:
retArray[dataMatrix[:,dimen] > threshVal] = -1.0
return retArray
def buildStump(dataArr,classLabels,D):#遍历所有可能输入值,找到最佳单层决策树
dataMatrix = mat(dataArr); labelMat = mat(classLabels).T
m,n = shape(dataMatrix)
numSteps = 10.0; bestStump = {}; bestClasEst = mat(zeros((m,1)))
minError = inf#无穷大
for i in range(n):#所有特征遍历
rangeMin = dataMatrix[:,i].min(); rangeMax = dataMatrix[:,i].max();
stepSize = (rangeMax-rangeMin)/numSteps
for j in range(-1,int(numSteps)+1):
for inequal in["lt","gt"]:
threshVal = (rangeMin + float(j)*stepSize)
predictedVals = stumpClassify(dataMatrix,i,threshVal,inequal)
errArr = mat(ones((m,1)))
errArr[predictedVals == labelMat] = 0
weightedError = D.T*errArr
print "split: dim %d, thresh %.2f, thresh ineqal: %s, the weighted error is %.3f" % (i, threshVal, inequal, weightedError)
#将当前错误率与已有的最小错误率进行对比,如果当前的值比较小,那么就在词典bestStump中保存该单层决策树
if weightedError < minError:
minError = weightedError
bestClasEst = predictedVals.copy()
bestStump["dim"] = i
bestStump["thresh"] = threshVal
bestStump['ineq'] = inequal
return bestStump,minError,bestClasEst
#开始运行
D = mat(ones((5,1))/5)
adaboost.buildStump(datMat, classLabels,D)
#省略部分
split: dim 1, thresh 1.88, thresh ineqal: gt, the weighted error is 0.600
split: dim 1, thresh 1.99, thresh ineqal: lt, the weighted error is 0.600
split: dim 1, thresh 1.99, thresh ineqal: gt, the weighted error is 0.600
split: dim 1, thresh 2.10, thresh ineqal: lt, the weighted error is 0.400
split: dim 1, thresh 2.10, thresh ineqal: gt, the weighted error is 0.400
Out[26]:
({'dim': 0, 'ineq': 'lt', 'thresh': 2.0}, matrix([[ 0.4]]), array([[ 1.],
[ 1.],
[ 1.],
[ 1.],
[ 1.]]))
上述单层决策树的生成函数时决策树的简化版本,也是所谓的弱学习器。
下面实现一个完整AdaBoost算法所需要的所有信息,伪代码如下:
对每次迭代:
利用buildStump()函数找到最佳的单词决策树
将最佳单层决策树加入到单层决策树数组
计算alpha
计算新的权重向量D
更新累计类别估计值
如果错误率等于0.0,则退出循环
继续补充adaboost.py
#7-2 基于单层决策树的AdaBoost训练过程
def adaBoostTrainDS(dataArr,classLabels,numIt=40):#数据集,类别标签,迭代次数
weakClassArr = []
m = shape(dataArr)[0]
D = mat(ones((m,1))/m)
aggClassEst = mat(zeros((m,1)))
for i in range(numIt):
#找到最佳决策树
bestStump,error,classEst = buildStump(dataArr,classLabels,D)
print "D:",D.T
alpha = float(0.5*log((1.0-error)/max(error,1e-16)))#确保没有除0溢出
bestStump["alpha"] = alpha
weakClassArr.append(bestStump)
print "classEst:",classEst.T
expon = multiply(-1*alpha*mat(classLabels).T,classEst)
D = multiply(D,exp(expon))
D = D/D.sum()
aggClassEst += alpha*classEst#更新累计估计值
print "aggClassEst:", aggClassEst.T
aggErrors = multiply(sign(aggClassEst) != mat(classLabels).T,ones((m,1)))
errorRate = aggErrors.sum()/m
print "total error:",errorRate
if errorRate == 0.0:break
return weakClassArr
并使用该函数
In [48]: runfile('E:/上学/机器学习实战/7.利用AdaBoost元算法提高分类性能/adaboost.py', wdir='E:/上学/机器学习实战/7.利用AdaBoost元算法提高分类性能')
Reloaded modules: adaboost
D: [[ 0.2 0.2 0.2 0.2 0.2]]
classEst: [[-1. 1. -1. -1. 1.]]
aggClassEst: [[-0.69314718 0.69314718 -0.69314718 -0.69314718 0.69314718]]
total error: 0.2
D: [[ 0.5 0.125 0.125 0.125 0.125]]
classEst: [[ 1. 1. -1. -1. -1.]]
aggClassEst: [[ 0.27980789 1.66610226 -1.66610226 -1.66610226 -0.27980789]]
total error: 0.2
D: [[ 0.28571429 0.07142857 0.07142857 0.07142857 0.5 ]]
classEst: [[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]]
aggClassEst: [[ 1.17568763 2.56198199 -0.77022252 -0.77022252 0.61607184]]
total error: 0.0
D: [[ 0.2 0.2 0.2 0.2 0.2]]
classEst: [[-1. 1. -1. -1. 1.]]
aggClassEst: [[-0.69314718 0.69314718 -0.69314718 -0.69314718 0.69314718]]
total error: 0.2
D: [[ 0.5 0.125 0.125 0.125 0.125]]
classEst: [[ 1. 1. -1. -1. -1.]]
aggClassEst: [[ 0.27980789 1.66610226 -1.66610226 -1.66610226 -0.27980789]]
total error: 0.2
D: [[ 0.28571429 0.07142857 0.07142857 0.07142857 0.5 ]]
classEst: [[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]]
aggClassEst: [[ 1.17568763 2.56198199 -0.77022252 -0.77022252 0.61607184]]
total error: 0.0
#观察classifierArray的值
In [62]: classifierArray
Out[62]:
([{'alpha': 0.6931471805599453, 'dim': 0, 'ineq': 'lt', 'thresh': 1.3},
{'alpha': 0.9729550745276565, 'dim': 1, 'ineq': 'lt', 'thresh': 1.0},
{'alpha': 0.8958797346140273,
'dim': 0,
'ineq': 'lt',
'thresh': 0.90000000000000002}],
matrix([[ 1.17568763],
[ 2.56198199],
[-0.77022252],
[-0.77022252],
[ 0.61607184]]))
我们已经实际写完了大部分的代码,现在需要将弱分类器的训练过程从程序中抽出来,然后应用到某个具体的实例上去。
def adaClassify(datToClass,classifierArr):#待分类样本,多个弱分类器组成的数组
dataMatrix = mat(datToClass)
m = shape(dataMatrix)[0]
aggClassEst = mat(zeros((m,1)))
for i in range(len(classifierArr)):
classEst = stumpClassify(dataMatrix,classifierArr[i]['dim'], classifierArr[i]['thresh'],classifierArr[i]['ineq'])
aggClassEst += classifierArr[i]['alpha']*classEst
print aggClassEst
return sign(aggClassEst)#返回符号
datArr,labelArr = adaboost.loadSimpData()
classifierArr = adaboost.adaBoostTrainDS(datArr,labelArr,30)
In [75]: adaboost.adaClassify([0,0],classifierArr)
[[-0.69314718]]
[[-1.66610226]]
[[-2.56198199]]
Out[75]: matrix([[-1.]])
In [76]: adaboost.adaClassify([[5,5],[0,0]],classifierArr)
[[ 0.69314718]
[-0.69314718]]
[[ 1.66610226]
[-1.66610226]]
[[ 2.56198199]
[-2.56198199]]
Out[76]:
matrix([[ 1.],
[-1.]])
我们可以看到,数据点的分类结果也会随着迭代的进行而越来越强,接下来我们将会将该分类器应用到一个规模更大,难度也更大的真实数据集中。
首先我们向文件加载数据
#自适应加载函数
def loadDataSet(fileName):
numFeat = len(open(fileName).readline().split('\t'))
dataMat = []; labelMat = []
fr = open(fileName)
for line in fr.readlines():
lineArr = []
curLine = line.strip().split('\t')#\t是tab键
for i in range(numFeat-1):
lineArr.append(float(curLine[i]))
dataMat.append(lineArr)
labelMat.append(float(curLine[-1]))
return dataMat,labelMat
并且测试该函数
In [18]: import adaboost
...: datArr, labelArr = loadDataSet("horseColicTraining2.txt")
...: classifierArray = adaBoostTrainDS(datArr, labelArr, 10)
...:
total error: 0.284280936455
total error: 0.284280936455
total error: 0.247491638796
total error: 0.247491638796
total error: 0.254180602007
total error: 0.240802675585
total error: 0.240802675585
total error: 0.220735785953
total error: 0.247491638796
total error: 0.230769230769
In [19]: testArr,testLabelArr = adaboost.loadDataSet('horseColicTest2.txt')
In [20]: prediction10 = adaboost.adaClassify(testArr,classifierArray)
[[ 0.46166238]
[ 0.46166238]
[-0.46166238]
...,
#省略部分
...,
[ 0.80958618]
[ 0.54030781]
[ 0.5273375 ]]
In [21]: errArr = mat(ones((67,1)))
In [22]: errArr[prediction10!=mat(testLabelArr).T].sum()
Out[22]: 16.0
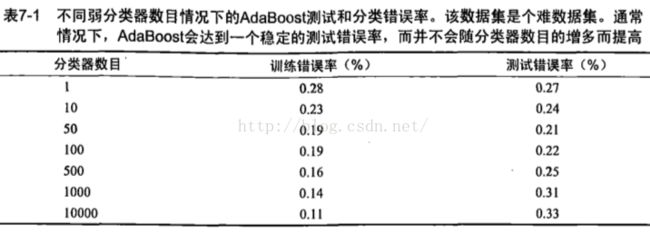
如图7-1所示,使用50个分类器就可以获得较高的性能。但是错误率在达到一个最小值以后又开始上升,这类现象称为过拟合。
很多人认为AdaBoost和SVM是监督机器学习中最强大的两种方法。实际上,这两者之间有不少相似之处。我们可以吧弱分类器想象成SVM中的一个核函数,也可以按照最大化某个最小间隔的方式重写AdaBoost算法。而他们的不同就在于其所定义的间隔计算方式有所不同,因此导致的结果也不同。
ROC曲线代表接受者特征。在最佳的分类器下,点应该尽可能在左上角,不同的ROC曲线进行比较的一个参数是曲线下面积。一个完美的分类器的AUC为1.0,而随机猜测的未0.5。
def plotROC(predStrengths, classLabels):#分类器的预测强度
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
cur = (1.0,1.0)#绘制光标的位置
ySum = 0.0#计算AUC的值
numPosClas = sum(array(classLabels)==1.0)
yStep = 1/float(numPosClas); xStep = 1/float(len(classLabels)-numPosClas)#步长
sortedIndicies = predStrengths.argsort()
fig = plt.figure()
fig.clf()
ax = plt.subplot(111)
for index in sortedIndicies.tolist()[0]:
if classLabels[index] == 1.0:
delX = 0; delY =yStep;
else:
delX = xStep; delY = 0;
ySum += cur[1]
ax.plot([cur[0],cur[0]-delX],[cur[1],cur[1]-delY], c='b')
cur = (cur[0]-delX,cur[1]-delY)
ax.plot([0,1],[0,1],'b--')
plt.xlabel('False positive rate'); plt.ylabel('True positive rate')
plt.title('ROC curve for AdaBoost horse colic detection system')
ax.axis([0,1,0,1])
plt.show()
print "the Area Under the Curve is:",ySum*xStep
datArr, labelArr = loadDataSet("horseColicTraining2.txt")
classifierArray,aggClassEst = adaboost.adaBoostTrainDS(datArr,labelArr,10)
plotROC(aggClassEst.T,labelArr)
the Area Under the Curve is: 0.858296963506