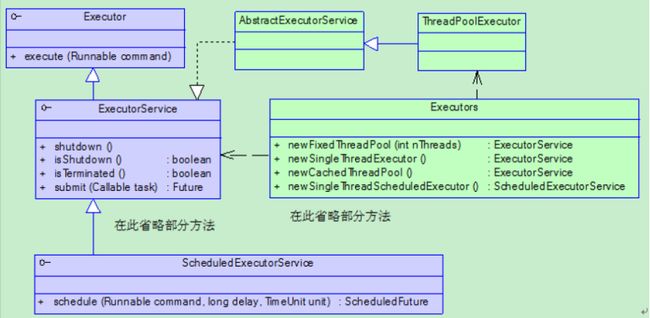
问题:
Java并发库提供的线程池有哪几种?分别有什么特点?
知识点补充
Executor框架
ThreadPoolExecutor 线程池类
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue workQueue) {
this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), defaultHandler);
}
参数说明:
corePoolSize:核心线程数。
maximumPoolSize:最大线程数。
keepAliveTime:线程存活时间。当线程数大于core数,那么超过该时间的线程将会被终结。
unit:keepAliveTime的单位。java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit类存在静态静态属性: NANOSECONDS、MICROSECONDS、MILLISECONDS、SECONDS
workQueue:Runnable的阻塞队列。若线程池已经被占满,则该队列用于存放无法再放入线程池中的Runnable。
回答问题:
通常开发者都是利用Executors提供的通用线程池创建方法,去创建不同配置的线程池,主要区别在于不同的ExecutorService类型或者不同的初始参数。
Executors目前提供了5种不同的线程池创建配置:
- newCachedThreadPool(),它是一种用来处理大量短时间工作任务的线程池;它会试图缓存线程并且重用,当无缓存线程可用时,就会创建新的工作线程;如果线程闲置的时间超过60s,则被终止并移除缓存;长时间闲置时,这种线程池,不会消耗什么资源。其内部使用SynchronousQueue作为工作队列。
构造方法(看英文注释是最好的理解哈):
/**
* Creates a thread pool that creates new threads as needed, but
* will reuse previously constructed threads when they are
* available. These pools will typically improve the performance
* of programs that execute many short-lived asynchronous tasks.
* Calls to {@code execute} will reuse previously constructed
* threads if available. If no existing thread is available, a new
* thread will be created and added to the pool. Threads that have
* not been used for sixty seconds are terminated and removed from
* the cache. Thus, a pool that remains idle for long enough will
* not consume any resources. Note that pools with similar
* properties but different details (for example, timeout parameters)
* may be created using {@link ThreadPoolExecutor} constructors.
*
* @return the newly created thread pool
*/
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue());
}
- newFixedThreadPool(int nThreadPool),重要指定数目(nThreads)的线程,其背后使用的无界的工作队列,任何时候最多有nThreads个工作线程是活动的。这意味着,如果数量超过了活动队列数目,将在工作队列中等待空闲线程出现;如果有工作线程退出,将会有新的工作线程被创建,以补足指定的数目nThreads。
构造方法(看英文注释是最好的理解哈):
/**
* Creates a thread pool that reuses a fixed number of threads
* operating off a shared unbounded queue. At any point, at most
* {@code nThreads} threads will be active processing tasks.
* If additional tasks are submitted when all threads are active,
* they will wait in the queue until a thread is available.
* If any thread terminates due to a failure during execution
* prior to shutdown, a new one will take its place if needed to
* execute subsequent tasks. The threads in the pool will exist
* until it is explicitly {@link ExecutorService#shutdown shutdown}.
*
* @param nThreads the number of threads in the pool
* @return the newly created thread pool
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code nThreads <= 0}
*/
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue());
}
- newSingleThreadExcutor(),它的特点在于工作线程数目被限制为1,操作了一个无界的工作队列,所以它保证了所有任务都是被顺序执行的。最多会有一个任务处于活动状态,并且不允许使用者改动线程池实例,因此可以避免其改变线程数目。
构造方法(看英文注释是最好的理解哈):
/**
* Creates an Executor that uses a single worker thread operating
* off an unbounded queue. (Note however that if this single
* thread terminates due to a failure during execution prior to
* shutdown, a new one will take its place if needed to execute
* subsequent tasks.) Tasks are guaranteed to execute
* sequentially, and no more than one task will be active at any
* given time. Unlike the otherwise equivalent
* {@code newFixedThreadPool(1)} the returned executor is
* guaranteed not to be reconfigurable to use additional threads.
*
* @return the newly created single-threaded Executor
*/
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue()));
}
- newSingleThreadScheduledExcutor()和newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize),创建的是个ScheduledExecutorService,可以进行定时或周期性的工作调度,区别在于单一工作线程还是多个工作线程。
构造方法(注释是最好的解释哈)
/**
* Creates a thread pool that can schedule commands to run after a
* given delay, or to execute periodically.
* @param corePoolSize the number of threads to keep in the pool,
* even if they are idle
* @return a newly created scheduled thread pool
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code corePoolSize < 0}
*/
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize) {
return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize);
}
- newWorkStealingPool(int parallelism)这是一个经常被人忽略的线程池,它是Java 8 才加入这个创建方法,其内部会创建ForkJoinPool,利用Work-Stealing算法,并行的处理任务,不保证处理顺序。
构造方法:
/**
* Creates a thread pool that maintains enough threads to support
* the given parallelism level, and may use multiple queues to
* reduce contention. The parallelism level corresponds to the
* maximum number of threads actively engaged in, or available to
* engage in, task processing. The actual number of threads may
* grow and shrink dynamically. A work-stealing pool makes no
* guarantees about the order in which submitted tasks are
* executed.
*
* @param parallelism the targeted parallelism level
* @return the newly created thread pool
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code parallelism <= 0}
* @since 1.8
*/
public static ExecutorService newWorkStealingPool(int parallelism) {
return new ForkJoinPool
(parallelism,
ForkJoinPool.defaultForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory,
null, true);
}
参考:
- https://www.cnblogs.com/shijiaqi1066/p/3412300.html
- 戏(细)说Executor框架线程池任务执行全过程(上)
- 极客时间APP核心技术第21讲| Java并发类库提供的线程池有哪几种?分别有什么特点?
声明:此为原创,转载请联系作者
作者:微信公众号添加公众号-遛狗的程序员 ,或者可以扫描以下二维码关注相关技术文章。
当然喜爱技术,乐于分享的你也可以可以添加作者微信号: