知识简介
-
在移动互联网时代,移动app能解决用户的很多生活琐事,比如
- 导航:去任意陌生的地方
- 周边:找餐馆、找酒店、找银行、找电影院
-
在上述应用中,都用到了地图和定位功能,在iOS开发中,要想加入这2大功能,必须基于2个框架进行开发
- Map Kit :用于地图展示
- Core Location :用于地理定位
-
2个热门专业术语
- LBS :Location Based Service
- SoLoMo :Social Local Mobile(索罗门)
经纬度基本知识
经纬度基本知识.png
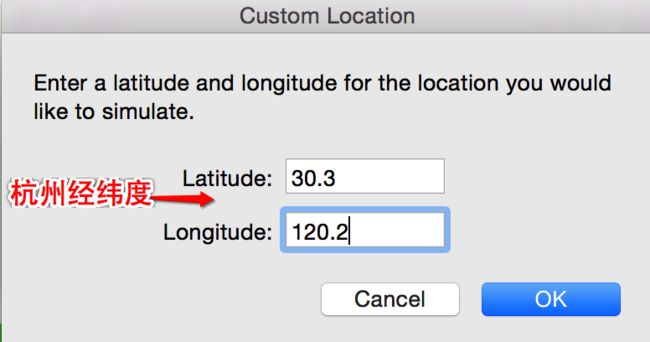
如何设置模拟器的经纬度
- 例如设置为杭州经纬度
用户隐私的保护
-
从iOS 6开始,苹果在保护用户隐私方面做了很大的加强,以下操作都必须经过用户批准授权
- 要想获得用户的位置
- 想访问用户的通讯录、日历、相机、相册等等
当想访问用户的隐私信息时,系统会自动弹出一个对话框让用户授权
注意:一旦用户选择了“Don’t Allow”,意味着你的应用以后就无法使用定位功能
为了严谨起见,最好在使用定位功能之前判断当前应用的定位功能是否可用
CLLocationManager有个类方法可以判断当前应用的定位功能是否可用
+ (BOOL)locationServicesEnabled;
从iOS 8开始,用户定位分两种情况
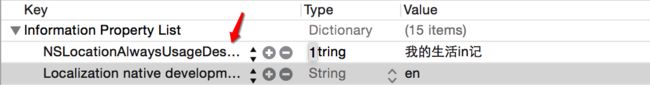
总是使用用户位置: NSLocationAlwaysUsageDescription
使用应用时定位: NSLocationWhenInUseDescription
需要在plist中添加字段
CoreLocation框架的使用
- 导入主头文件
#import
- CoreLocation框架使用须知
- CoreLocation框架中所有数据类型的前缀都是CL
- CoreLocation中使用CLLocationManager对象来做用户定位
CLLocationManager的常用属性及操作
- 每隔多少米定位一次
@property(assign, nonatomic) CLLocationDistance distanceFilter;
- 定位精确度(越精确就越耗电)
@property(assign, nonatomic) CLLocationAccuracy desiredAccuracy;
- 开始用户定位
- (void)startUpdatingLocation;
- 停止用户定位
- (void) stopUpdatingLocation;
- 当调用了startUpdatingLocation方法后,就开始不断地定位用户的位置,中途会频繁地调用代理的下面方法
// locations参数里面装着CLLocation对象
- (void)locationManager:(CLLocationManager *)manager didUpdateLocations:(NSArray *)locations;
CLLocation用来表示某个位置的地理信息,比如经纬度、海拔等等
- 经纬度
@property(readonly, nonatomic) CLLocationCoordinate2D coordinate;
- 海拔
@property(readonly, nonatomic) CLLocationDistance altitude;
- 路线,航向(取值范围是0.0° ~ 359.9°,0.0°代表真北方向)
@property(readonly, nonatomic) CLLocationDirection course;
- 行走速度(单位是m/s)
@property(readonly, nonatomic) CLLocationSpeed speed;
- 计算2个位置之间的距离
- (CLLocationDistance)distanceFromLocation:(const CLLocation *)location
CoreLocation基本使用
- 获取当前位置经纬度
- 计算2个位置之间的距离
实现步骤
1.获取用户的授权状态-->请求授权(info.plist-->NSLocationAlwaysUsageDescription/string)
2.请求用户的位置
- 创建CLLocationManager
- 设置代理
- 实现代理方法
- 请求获取用户的位置(startUpdatingLocation)
3.获取用户的位置(CLLocation)
- coordinate-->latitude/longitude
4.设置定位精确度desiredAccuracy/设置当用户移动多少距离,重新定位distanceFilter
5.计算两个经纬度之间距离(包装CLLocation对象-->distanceFromLocation)
#######代码如下
#import "ViewController.h"
#import
@interface ViewController ()
/** 用户位置管理者对象 */
@property (nonatomic, strong) CLLocationManager *mgr;
@end
@implementation ViewController
#pragma mark - 懒加载
- (CLLocationManager *)mgr
{
if (_mgr == nil) {
self.mgr = [[CLLocationManager alloc] init];
// 设置代理,在代理方法中可以拿到用户的位置
self.mgr.delegate = self;
// 设置定位的精度(精度越高越耗电)
self.mgr.desiredAccuracy = kCLLocationAccuracyBestForNavigation;
// 设置当用户移动的时候,重新来定位
self.mgr.distanceFilter = 10.0;
}
return _mgr;
}
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
// 1.获取用户的授权状态(iOS7只要使用到定位,就会直接请求授权)
CLAuthorizationStatus status = [CLLocationManager authorizationStatus];
if (status == kCLAuthorizationStatusNotDetermined) {
/*
if ([[UIDevice currentDevice].systemVersion doubleValue] >= 8.0) {
[mgr requestAlwaysAuthorization];
}
*/
if ([self.mgr respondsToSelector:@selector(requestAlwaysAuthorization)]) {
[self.mgr requestAlwaysAuthorization];
}
}
// 2.开始定位(当调用该方法,系统就会不停的更新用户的位置)
[self.mgr startUpdatingLocation];
// 3.计算两个经纬度之间的距离
[self countDistance];
}
- (void)countDistance
{
// 北京:39.6 116.39
// 杭州:30.3 120.2
CLLocation *location1 = [[CLLocation alloc] initWithLatitude:39.6 longitude:116.39];
CLLocation *location2 = [[CLLocation alloc] initWithLatitude:30.3 longitude:120.2];
// 计算距离
CLLocationDistance distance = [location1 distanceFromLocation:location2];
NSLog(@"%.2f", distance);
}
#pragma mark - 实现CLLocationManager的代理方法
/**
* 当获取到用户的位置就会执行该方法(如果仅仅是想拿到用户的位置,可以在获取到用户位置之后停止停止定位)
*
* @param locations 数组中就存放着用户的位置(每更新到用户的一个位置,就会将用户位置的对象加入数组中)
*/
- (void)locationManager:(CLLocationManager *)manager didUpdateLocations:(NSArray *)locations
{
/*
@property(readonly, nonatomic) CLLocationDistance altitude; // 海拔
@property(readonly, nonatomic) CLLocationAccuracy horizontalAccuracy; // 水平精度
@property(readonly, nonatomic) CLLocationAccuracy verticalAccuracy; // 垂直精度@property(readonly, nonatomic) CLLocationSpeed speed 手机当前的速度
@property(readonly, nonatomic, copy) NSDate *timestamp; 时间戳
@property(readonly, nonatomic, copy) CLFloor *floor 楼层
*/
// 1.拿到用户位置的对象
CLLocation *location = [locations lastObject];
// 2.拿到用户当前位置的经纬度
CLLocationCoordinate2D coordinate = location.coordinate;
NSLog(@"latitude = %.2f", coordinate.latitude);
NSLog(@"longitude = %.2f", coordinate.longitude);
// [manager stopUpdatingLocation];
}
@end
注意点:使用模拟器获取当前位置时可能出现的不打印的情况,可能是以下原因
- 未设置模拟器经纬度(设置方法在上文中)
- 模拟器自身问题(更换模拟器比如6s换成5s,最好还是用真机测试)
地理编码与反地理编码
CLGeocoder
- 使用CLGeocoder可以完成“地理编码”和“反地理编码”
- 地理编码:根据给定的地名,获得具体的位置信息(比如经纬度、地址的全称等)
- 反地理编码:根据给定的经纬度,获得具体的位置信息
地理编码方法
- (void)geocodeAddressString:(NSString *)addressString completionHandler:(CLGeocodeCompletionHandler)completionHandler;
反地理编码方法
- (void)reverseGeocodeLocation:(CLLocation *)location completionHandler:(CLGeocodeCompletionHandler)completionHandler;
- 当地理\反地理编码完成时,就会调用
CLGeocodeCompletionHandler
typedef void (^CLGeocodeCompletionHandler)(NSArray *placemarks, NSError *error);
- 这个block传递2个参数
- error :当编码出错时(比如编码不出具体的信息)有值
- placemarks :里面装着CLPlacemark对象
CLPlacemark
- CLPlacemark的字面意思是地标,封装详细的地址位置信息
地理位置
@property (nonatomic, readonly) CLLocation *location;
- 区域
@property (nonatomic, readonly) CLRegion *region;
- 详细的地址信息
@property (nonatomic, readonly) NSDictionary *addressDictionary;
- 地址名称
@property (nonatomic, readonly) NSString *name;
- 城市
@property (nonatomic, readonly) NSString *locality;
示例
#import "ViewController.h"
#import
@interface ViewController ()
// 地理编码
@property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UITextField *textField;
// 反地理编码
@property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UITextField *longitudeText;
@property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UITextField *latitudeText;
/**编码使用的对象*/
@property (strong, nonatomic) CLGeocoder *geoCoder;
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
// Do any additional setup after loading the view, typically from a nib.
}
// 反地理编码
- (IBAction)geoCoder:(id)sender {
if (self.textField.text.length == 0) {
NSLog(@"请输入详细信息");
return;
}
// 地理编码
[self.geoCoder geocodeAddressString:self.textField.text completionHandler:^(NSArray * _Nullable placemarks, NSError * _Nullable error) {
if (error || placemarks.count == 0) {
return ;
}
for (CLPlacemark *pm in placemarks) {
CLLocationCoordinate2D coordinate = pm.location.coordinate;
// 获取经纬度
NSLog(@"%.2f", coordinate.latitude);
NSLog(@"%.2f", coordinate.longitude);
// 获取所在的省
NSLog(@"%@", pm.administrativeArea);
// 获取详细信息(省、市)
NSLog(@"%@", pm.name);
}
}];
}
// 反地理编码
- (IBAction)reverseGeocoder:(id)sender {
NSString *latitude = self.latitudeText.text;
NSString *longitude = self.longitudeText.text;
if (latitude.length == 0 || longitude.length == 0 ){
NSLog(@"请输入经纬度");
return;
}
CLLocation *location = [[CLLocation alloc] initWithLatitude:latitude.doubleValue longitude:longitude.doubleValue];
[self.geoCoder reverseGeocodeLocation:location completionHandler:^(NSArray * _Nullable placemarks, NSError * _Nullable error) {
for (CLPlacemark *pm in placemarks) {
// 获取地址的全称
NSLog(@"%@", pm.name);
// 获取经纬度
CLLocationCoordinate2D coordinate = pm.location.coordinate;
NSLog(@"纬度:%.2f", coordinate.latitude);
NSLog(@"经度:%.2f", coordinate.longitude);
// 获取城市
NSLog(@"所在城市:%@", pm.administrativeArea);
NSLog(@"所在城市:%@", pm.locality);
}
}];
}
#pragma mark - 懒加载
- (CLGeocoder *)geoCoder
{
if (_geoCoder == nil) {
_geoCoder = [[CLGeocoder alloc] init];
}
return _geoCoder;
}
@end