最近用到了sunnyxx的forkingdog系列《UIView-FDCollapsibleConstraints》,纪录下关联对象和MethodSwizzling在实际场景中的应用。
基本概念
关联对象
-
关联对象操作函数
- 设置关联对象:
/** * 设置关联对象 * * @param object 源对象 * @param key 关联对象的key * @param value 关联的对象 * @param policy 关联策略 */ void objc_setAssociatedObject(id object, const void *key, id value, objc_AssociationPolicy policy)
- 获取关联对象:
```objc
/**
* 获取关联对象
*
* @param object 源对象
* @param key 关联对象的key
*
* @return 关联的对象
*/
id objc_getAssociatedObject(id object, const void *key)
其中设置关联对象的策略有以下5种:
- 和MRC的内存操作retain、assign方法效果差不多
- 比如设置的关联对象是一个UIView,并且这个UIView已经有父控件时,可以使用OBJC_ASSOCIATION_ASSIGN
OBJC_ASSOCIATION_ASSIGN // 对关联对象进行弱引用
OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC // 对关联对象进行强引用(非原子)
OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY_NONATOMIC // 对关联对象进行拷贝引用(非原子)
OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN // 对关联对象进行强引用
OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY // 对关联对象进行拷贝引用
关联对象在一些第三方框架的分类中常常见到,这里在分析前先看下分类的结构:
struct category_t {
// 类名
const char *name;
// 类
classref_t cls;
// 实例方法
struct method_list_t *instanceMethods;
// 类方法
struct method_list_t *classMethods;
// 协议
struct protocol_list_t *protocols;
// 属性
struct property_list_t *instanceProperties;
};
从以上的分类结构,可以看出,分类中是不能添加成员变量的,也就是Ivar类型。所以,如果想在分类中存储某些数据时,关联对象就是在这种情况下的常用选择。
需要注意的是,关联对象并不是成员变量,关联对象是由一个全局哈希表存储的键值对中的值。
全局哈希表的定义如下:
class AssociationsManager {
static spinlock_t _lock;
static AssociationsHashMap *_map; // associative references: object pointer -> PtrPtrHashMap.
public:
AssociationsManager() { spinlock_lock(&_lock); }
~AssociationsManager() { spinlock_unlock(&_lock); }
AssociationsHashMap &associations() {
if (_map == NULL)
_map = new AssociationsHashMap();
return *_map;
}
};
其中的AssociationsHashMap就是那个全局哈希表,而注释中也说明的很清楚了:哈希表中存储的键值对是(源对象指针 : 另一个哈希表)。而这个value,即ObjectAssociationMap对应的哈希表如下:
// hash_map和unordered_map是模版类
// 查看源码后可以看出AssociationsHashMap的key是disguised_ptr_t类型,value是ObjectAssociationMap *类型
// ObjectAssociationMap的key是void *类型,value是ObjcAssociation类型
#if TARGET_OS_WIN32
typedef hash_map ObjectAssociationMap;
typedef hash_map AssociationsHashMap;
#else
typedef ObjcAllocator > ObjectAssociationMapAllocator;
class ObjectAssociationMap : public std::map {
public:
void *operator new(size_t n) { return ::_malloc_internal(n); }
void operator delete(void *ptr) { ::_free_internal(ptr); }
};
typedef ObjcAllocator > AssociationsHashMapAllocator;
class AssociationsHashMap : public unordered_map {
public:
void *operator new(size_t n) { return ::_malloc_internal(n); }
void operator delete(void *ptr) { ::_free_internal(ptr); }
};
#endif
其中的ObjectAssociationMap就是value的类型。同时,也可以知道ObjectAssociationMap的键值对类型为(关联对象对应的key : 关联对象),也就是函数objc_setAssociatedObject的对应的key:value参数。
大部分情况下,关联对像会使用getter方法的SEL当作key(getter方法中可以这样表示:_cmd)。
更多和关联对象有关的底层信息,可以查看Dive into Category
MethodSwizzling
MethodSwizzling主要原理就是利用runtime的动态特性,交换方法对应的实现,也就是IMP。
通常,MethodSwizzling的封装为:
+ (void)load
{
// 源方法--原始的方法
// 目的方法--我们自己实现的,用来替换源方法
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
// MethodSwizzling代码只需要在类加载时调用一次,并且需要线程安全环境
dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{
Class class = [self class];
// 获取方法的SEL
SEL origionSel = @selector(viewDidLoad);
SEL swizzlingSel = @selector(tpc_viewDidLoad);
// IMP origionMethod = class_getMethodImplementation(class, origionSel);
// IMP swizzlingMethod = class_getMethodImplementation(class, swizzlingSel);
// 根据SEL获取对应的Method
Method origionMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(class, origionSel);
Method swizzlingMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(class, swizzlingSel);
// 向类中添加目的方法对应的Method
BOOL hasAdded = class_addMethod(class, origionSel, method_getImplementation(swizzlingMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(swizzlingMethod));
// 交换源方法和目的方法的Method方法实现
if (hasAdded) {
class_replaceMethod(class, swizzlingSel, method_getImplementation(origionMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(origionMethod));
} else {
method_exchangeImplementations(origionMethod, swizzlingMethod);
}
});
}
为了便于区别,这里列出Method的结构:
typedef struct method_t *Method;
// method_t
struct method_t {
SEL name;
const char *types;
IMP imp;
...
}
实现MethodSwizzling需要了解的有以下几个常用函数:
// 返回方法的具体实现
IMP class_getMethodImplementation ( Class cls, SEL name )
// 返回方法描述
Method class_getInstanceMethod ( Class cls, SEL name )
// 添加方法
BOOL class_addMethod ( Class cls, SEL name, IMP imp, const char *types )
// 替代方法的实现
IMP class_replaceMethod ( Class cls, SEL name, IMP imp, const char *types )
// 返回方法的实现
IMP method_getImplementation ( Method m );
// 获取描述方法参数和返回值类型的字符串
const char * method_getTypeEncoding ( Method m );
// 交换两个方法的实现
void method_exchangeImplementations ( Method m1, Method m2 );
介绍MethodSwizzling的文章很多,更多和MethodSwizzling有关的信息,可以查看Objective-C的hook方案(一): Method Swizzling
针对UIView-FDCollapsibleConstraints的应用
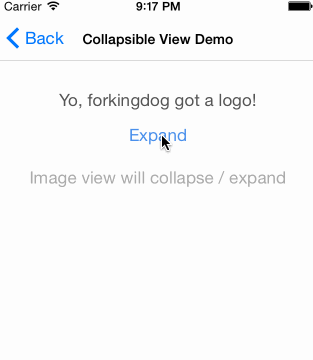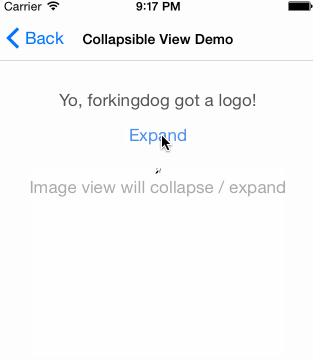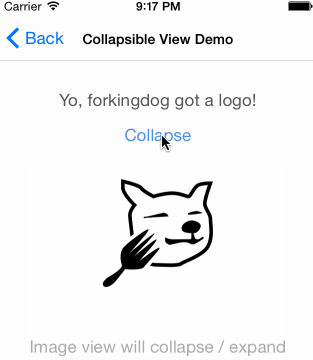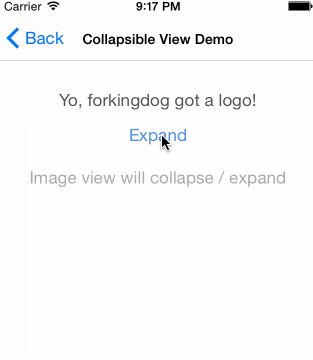
UIView-FDCollapsibleConstraints是sunnyxx阳神写的一个UIView分类,可以实现仅在IB中对UIView上的约束进行设置,就达到以下效果,而不需要编写改变约束的代码:(图片来源UIView-FDCollapsibleConstraints)
这里介绍下自己对这个分类的理解:
- 实现思路
将需要和UIView关联且需要动态修改的约束添加进一个和UIView绑定的特定的数组里面根据UIView的内容是否为nil,对这个特定数组中的约束值进行统一设置
而在分类不能增加成员变量的情况下,和UIView绑定的特定的数组就是用关联对象实现的。
先从分类的头文件开始:
头文件
@interface UIView (FDCollapsibleConstraints)
/// Assigning this property immediately disables the view's collapsible constraints'
/// by setting their constants to zero.
@property (nonatomic, assign) BOOL fd_collapsed;
/// Specify constraints to be affected by "fd_collapsed" property by connecting in
/// Interface Builder.
@property (nonatomic, copy) IBOutletCollection(NSLayoutConstraint) NSArray *fd_collapsibleConstraints;
@end
@interface UIView (FDAutomaticallyCollapseByIntrinsicContentSize)
/// Enable to automatically collapse constraints in "fd_collapsibleConstraints" when
/// you set or indirectly set this view's "intrinsicContentSize" to {0, 0} or absent.
///
/// For example:
/// imageView.image = nil;
/// label.text = nil, label.text = @"";
///
/// "NO" by default, you may enable it by codes.
@property (nonatomic, assign) BOOL fd_autoCollapse;
/// "IBInspectable" property, more friendly to Interface Builder.
/// You gonna find this attribute in "Attribute Inspector", toggle "On" to enable.
/// Why not a "fd_" prefix? Xcode Attribute Inspector will clip it like a shit.
/// You should not assgin this property directly by code, use "fd_autoCollapse" instead.
@property (nonatomic, assign, getter=fd_autoCollapse) IBInspectable BOOL autoCollapse;
分析几点:
-
IBOutletCollection,详情参考IBAction / IBOutlet / IBOutletCollection- 表示将SB中相同的控件连接到一个数组中;这里使用这个方式,将在SB中的
NSLayoutConstraint添加到fd_collapsibleConstraints数组中,以便后续对约束进行统一操作 - IBOutletCollectionh和IBOutlet操作方式一样,需要
在IB中进行相应的拖拽才能把对应的控件加到数组中(UIView->NSLayoutConstraint) - 设置了IBOutletCollection之后,当从storybooard或者xib中加载进行解档时,最终会调用fd_collapsibleConstraints的
setter方法,然后就可以在其setter方法中做相应的操作了
- 表示将SB中相同的控件连接到一个数组中;这里使用这个方式,将在SB中的
-
IBInspectable表示这个属性可以在IB中更改,如下图
- 还有一个这里没用,
IB_DESIGNABLE,这个表示可以在IB中实时显示修改的效果,详情参考 @IBDesignable和@IBInspectable
主文件
NSLayoutConstraint (_FDOriginalConstantStorage)
- 因为在
修改约束值后,需要还原操作,但是分类中无法添加成员变量,所以在这个分类中,给NSLayoutConstraint约束关联一个存储约束初始值的浮点数,以便在修改约束值后,可以还原
/// A stored property extension for NSLayoutConstraint's original constant.
@implementation NSLayoutConstraint (_FDOriginalConstantStorage)
// 给NSLayoutConstraint关联一个初始约束值
- (void)setFd_originalConstant:(CGFloat)originalConstant
{
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, @selector(fd_originalConstant), @(originalConstant), OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN);
}
- (CGFloat)fd_originalConstant
{
#if CGFLOAT_IS_DOUBLE
return [objc_getAssociatedObject(self, _cmd) doubleValue];
#else
return [objc_getAssociatedObject(self, _cmd) floatValue];
#endif
}
@end
UIView (FDCollapsibleConstraints)
同样,因为需要
对UIView上绑定的约束进行改动,所以需要在分类中添加一个可以记录所有约束的对象,需要用到关联对象-
实现fd_collapsibleConstraints属性的setter和getter方法 (
关联一个存储约束的对象)- 在
getter方法中创建关联对象constraints(和懒加载的方式类似,不过不是创建成员变量) - 在
setter方法中设置约束的初始值,并添加进关联对象constraints中,方便统一操作
- 在
-
从IB中关联的约束,最终会调用setFd_collapsibleConstraints:方法,也就是这一步不需要手动调用,系统自己完成(在awakeFromNib之前完成IB这些值的映射)
- (NSMutableArray *)fd_collapsibleConstraints { // 获取对象的所有约束关联值 NSMutableArray *constraints = objc_getAssociatedObject(self, _cmd); if (!constraints) { constraints = @[].mutableCopy; // 设置对象的所有约束关联值 objc_setAssociatedObject(self, _cmd, constraints, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN); } return constraints; } // IBOutletCollection表示xib中的相同的控件连接到一个数组中 // 因为设置了IBOutletCollection,所以从xib进行解档时,最终会调用set方法 // 然后就来到了这个方法 - (void)setFd_collapsibleConstraints:(NSArray *)fd_collapsibleConstraints { // Hook assignments to our custom `fd_collapsibleConstraints` property. // 返回保存原始约束的数组,使用关联对象 NSMutableArray *constraints = (NSMutableArray *)self.fd_collapsibleConstraints; [fd_collapsibleConstraints enumerateObjectsUsingBlock:^(NSLayoutConstraint *constraint, NSUInteger idx, BOOL *stop) { // Store original constant value // 保存原始的约束 constraint.fd_originalConstant = constraint.constant; [constraints addObject:constraint]; }]; } -
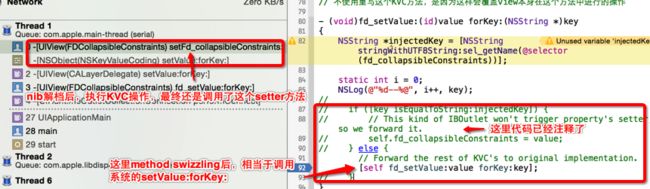
使用Method Swizzling交换自己的和系统的-setValue:forKey:方
- 实现自己的KVC的-setValue:forKey:方法
// load先从原类,再调用分类的开始调用
// 也就是调用的顺序是
// 原类
// FDCollapsibleConstraints
// FDAutomaticallyCollapseByIntrinsicContentSize
// 所以并不冲突
+ (void)load
{
// Swizzle setValue:forKey: to intercept assignments to `fd_collapsibleConstraints`
// from Interface Builder. We should not do so by overriding setvalue:forKey:
// as the primary class implementation would be bypassed.
SEL originalSelector = @selector(setValue:forKey:);
SEL swizzledSelector = @selector(fd_setValue:forKey:);
Class class = UIView.class;
Method originalMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(class, originalSelector);
Method swizzledMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(class, swizzledSelector);
method_exchangeImplementations(originalMethod, swizzledMethod);
}
// xib也就是xml,再加载进行decode时,会调用setValue:forKey:,把他的方法替换成自身的,然后获取添加的约束
// 作者说明不使用重写这个KVC方法的方式,是因为这样会覆盖view本身在这个方法中进行的操作
- (void)fd_setValue:(id)value forKey:(NSString *)key
{
NSString *injectedKey = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:sel_getName(@selector(fd_collapsibleConstraints))];
if ([key isEqualToString:injectedKey]) {
// This kind of IBOutlet won't trigger property's setter, so we forward it.
// 作者的意思是,IBOutletCollection不会触发对应属性的setter方法,所以这里执行手动调用
self.fd_collapsibleConstraints = value;
} else {
// Forward the rest of KVC's to original implementation.
[self fd_setValue:value forKey:key];
}
}
- 上面使用Method Swizzling的原因
作者认为是这种类型的IBOutlet不会触发其setter方法,但是经过测试,注释掉这段代码后,系统还是自己触发了setter方法,说明这种IBOutlet还是可以触发setter方法的。所以,即使没有这一段代码,应该也是可行的
-
设置对应的约束值
- 这里给UIView对象提供一个关联对象,来判断是否将约束值清零
- 注意,这里只要传入的是YES,那么,这个UIView对应存入
constraints关联对象的所有约束,都会置为0
#pragma mark - Dynamic Properties - (void)setFd_collapsed:(BOOL)collapsed { [self.fd_collapsibleConstraints enumerateObjectsUsingBlock: ^(NSLayoutConstraint *constraint, NSUInteger idx, BOOL *stop) { if (collapsed) { // 如果view的内容为nil,则将view关联的constraints对象所有值设置为0 constraint.constant = 0; } else { // 如果view的内容不为nil,则将view关联的constraints对象所有值返回成原值 constraint.constant = constraint.fd_originalConstant; } }]; // 设置fd_collapsed关联对象,供自动collapsed使用 objc_setAssociatedObject(self, @selector(fd_collapsed), @(collapsed), OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN); } - (BOOL)fd_collapsedFDAutomaticallyCollapseByIntrinsicContentSize{ return [objc_getAssociatedObject(self, _cmd) boolValue]; } @end
######UIView (FDAutomaticallyCollapseByIntrinsicContentSize)
- 使用Method Swizzling交换自己实现的-fd_updateConstraints和系统的updateConstraints方法
- [self fd_updateConstraints]调用的是self的updateConstraints方法,fd_updateConstraints和updateConstraints方法的IMP,即方法实现已经调换了
- 可以看到,加入这里不使用Method Swizzling,那么要实现在更新约束时就需要`重写updateConstraints`方法,而这只能在`继承UIView`的情况下才能完成的;而实用了Method Swizzling,就可以直接在`分类`中实现在`调用系统updateConstraints的前提下`,又`添加自己想要执行的附加代码`
- `intrinsicContentSize(控件的内置大小)`默认为UIViewNoIntrinsicMetric,当`控件中没有内容时`,调用intrinsicContentSize返回的即为`默认值`,详情参考([intrinsicContentSize和Content Hugging Priority](http://www.mgenware.com/blog/?p=491))
```objc
#pragma mark - Hacking "-updateConstraints"
+ (void)load
{
// Swizzle to hack "-updateConstraints" method
SEL originalSelector = @selector(updateConstraints);
SEL swizzledSelector = @selector(fd_updateConstraints);
Class class = UIView.class;
Method originalMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(class, originalSelector);
Method swizzledMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(class, swizzledSelector);
method_exchangeImplementations(originalMethod, swizzledMethod);
}
- (void)fd_updateConstraints
{
// Call primary method's implementation
[self fd_updateConstraints];
if (self.fd_autoCollapse && self.fd_collapsibleConstraints.count > 0) {
// "Absent" means this view doesn't have an intrinsic content size, {-1, -1} actually.
const CGSize absentIntrinsicContentSize = CGSizeMake(UIViewNoIntrinsicMetric, UIViewNoIntrinsicMetric);
// 当设置控件显示内容为nil时,计算出来的contentSize和上面的相等
// Calculated intrinsic content size
const CGSize contentSize = [self intrinsicContentSize];
// When this view doesn't have one, or has no intrinsic content size after calculating,
// it going to be collapsed.
if (CGSizeEqualToSize(contentSize, absentIntrinsicContentSize) ||
CGSizeEqualToSize(contentSize, CGSizeZero)) {
// 当控件没有内容时,则设置控件关联对象constraints的所有约束值为0
self.fd_collapsed = YES;
} else {
// 当控件有内容时,则设置控件关联对象constraints的所有约束值返回为原值
self.fd_collapsed = NO;
}
}
}
-
设置一些动态属性(关联对象)
- 给UIView关联一个对象,来判断是否需要自动对约束值进行清零
#pragma mark - Dynamic Properties - (BOOL)fd_autoCollapse
{
return [objc_getAssociatedObject(self, _cmd) boolValue];
}
- (void)setFd_autoCollapse:(BOOL)autoCollapse
{
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, @selector(fd_autoCollapse), @(autoCollapse), OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN);
}
- (void)setAutoCollapse:(BOOL)collapse
{
// Just forwarding
self.fd_autoCollapse = collapse;
}
##总结
总体来说,在分类中要想实现相对复杂的逻辑,却`不能添加成员变量`,也`不想对需要操作的类进行继承`,这时就需要runtime中的`关联对象和MethodSwizzling`技术了。
forkingdog系列分类都用到了runtime的一些知识,代码简洁注释齐全风格也不错,比较适合需要学习runtime应用知识的我。