传送门:链式编程小Demo
这篇文章是 Masonry 框架源码的解析和笔记。学习Masonry之前,先了解这个框架设计的初衷---传统的利用系统API进行纯代码布局的不足。然后,根据Masonry常见的几个链式语法中,顺藤摸瓜地了解Masonry的调用栈。最后,学习并思考这个框架用到的设计模式和链式编程思想。
1. 之前的不足:系统API纯代码布局
- 系统给的自动布局(AutoLayout)的API
+(instancetype)constraintWithItem:(id)view1
attribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)attr1
relatedBy:(NSLayoutRelation)relation
toItem:(nullable id)view2
attribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)attr2
multiplier:(CGFloat)multiplier
constant:(CGFloat)c;
- 传统代码中使用系统API进行布局
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
// Do any additional setup after loading the view, typically from a nib.
self.view.backgroundColor = [UIColor yellowColor];
UIView *subView = [[UIView alloc] init];
subView.backgroundColor = [UIColor redColor];
// 在设置约束前,先将子视图添加进来
[self.view addSubview:subView];
// 使用autoLayout约束,禁止将AutoresizingMask转换为约束
[subView setTranslatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints:NO];
// 设置subView相对于VIEW的上左下右各40像素
NSLayoutConstraint *constraintTop = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintWithItem:subView attribute:NSLayoutAttributeTop relatedBy:NSLayoutRelationEqual toItem:self.view attribute:NSLayoutAttributeTop multiplier:1.0 constant:40];
NSLayoutConstraint *constraintLeft = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintWithItem:subView attribute:NSLayoutAttributeLeft relatedBy:NSLayoutRelationEqual toItem:self.view attribute:NSLayoutAttributeLeft multiplier:1.0 constant:40];
// 由于iOS坐标系的原点在左上角,所以设置下,右边距使用负值
NSLayoutConstraint *constraintBottom = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintWithItem:subView attribute:NSLayoutAttributeBottom relatedBy:NSLayoutRelationEqual toItem:self.view attribute:NSLayoutAttributeBottom multiplier:1.0 constant:-40];
NSLayoutConstraint *constraintRight = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintWithItem:subView attribute:NSLayoutAttributeRight relatedBy:NSLayoutRelationEqual toItem:self.view attribute:NSLayoutAttributeRight multiplier:1.0 constant:-40];
// 将四条约束加进数组中
NSArray *array = [NSArray arrayWithObjects:constraintTop, constraintLeft, constraintBottom, constraintRight, nil];
// 把约束条件设置到父视图的Contraints中
[self.view addConstraints:array];
}
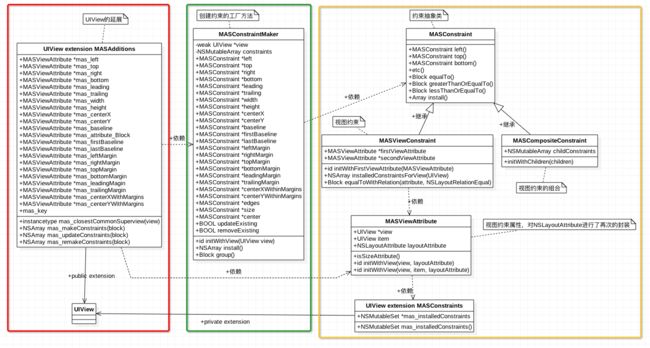
可见,系统传统的代码布局有点繁琐。为了简化上述传统布局代码,被广泛应用的第三方框架 Masonry 对AutoLayout 进行了封装,Swift版则是 SnapKit。这篇文章就是针对 Masonry 源代码的解析与学习笔记。在这之前,如下图所示,是 Masonry 源代码的结构图:
2. 顺藤摸瓜:Masonry链式语法的调用栈解析
2.1 mas_makeConstraints:外部调用
- 调用例子
#import "Masonry.h"
[self.containerView addSubview:self.bannerView];
[self.bannerView mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.leading.equalTo(self.containerView.mas_leading);
make.top.equalTo(self.containerView.mas_top);
make.trailing.equalTo(self.containerView.mas_trailing);
make.height.equalTo(@(kViewWidth(131.0)));
}];
2.2 mas_makeConstraints:实现原理,通过导入的头文件分析
- Masonry.h
#import
//! Project version number for Masonry.
FOUNDATION_EXPORT double MasonryVersionNumber;
//! Project version string for Masonry.
FOUNDATION_EXPORT const unsigned char MasonryVersionString[];
#import "MASUtilities.h"
#import "View+MASAdditions.h"
#import "View+MASShorthandAdditions.h"
#import "ViewController+MASAdditions.h"
#import "NSArray+MASAdditions.h"
#import "NSArray+MASShorthandAdditions.h"
#import "MASConstraint.h"
#import "MASCompositeConstraint.h"
#import "MASViewAttribute.h"
#import "MASViewConstraint.h"
#import "MASConstraintMaker.h"
#import "MASLayoutConstraint.h"
#import "NSLayoutConstraint+MASDebugAdditions.h"
其中
View+MASAdditions分类为UIView添加了mas_makeConstraints方法
- View+MASAdditions.m
- (NSArray *)mas_makeConstraints:(void(^)(MASConstraintMaker *))block {
self.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = NO;
MASConstraintMaker *constraintMaker = [[MASConstraintMaker alloc] initWithView:self];
block(constraintMaker);
return [constraintMaker install];
}
- MASConstraintMaker.m
@interface MASConstraintMaker ()
@property (nonatomic, weak) MAS_VIEW *view;
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSMutableArray *constraints;
@end
- (id)initWithView:(MAS_VIEW *)view {
self = [super init];
if (!self) return nil;
self.view = view;
self.constraints = NSMutableArray.new;
return self;
}
2.3 .top:通过MASConstraintMaker类源码分析
先分析设置 第一个约束属性 的情况(且唯一一个):例如
make.top.equalTo(self.containerView.mas_top);
2.3.1 MASConstraintMaker的分析
- MASConstraintMaker.m
- (MASConstraint *)top {
return [self addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:NSLayoutAttributeTop];
}
- (MASConstraint *)addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)layoutAttribute {
return [self constraint:nil addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:layoutAttribute];
}
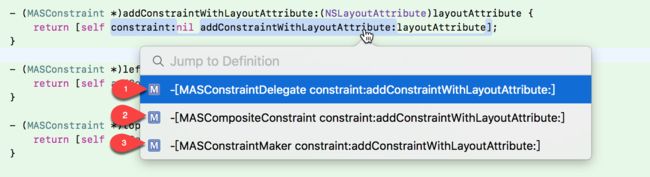
- (MASConstraint *)constraint:(MASConstraint *)constraint addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)layoutAttribute {
MASViewAttribute *viewAttribute = [[MASViewAttribute alloc] initWithView:self.view layoutAttribute:layoutAttribute];
MASViewConstraint *newConstraint = [[MASViewConstraint alloc] initWithFirstViewAttribute:viewAttribute];
if ([constraint isKindOfClass:MASViewConstraint.class]) {
//replace with composite constraint
NSArray *children = @[constraint, newConstraint];
MASCompositeConstraint *compositeConstraint = [[MASCompositeConstraint alloc] initWithChildren:children];
compositeConstraint.delegate = self;
[self constraint:constraint shouldBeReplacedWithConstraint:compositeConstraint];
return compositeConstraint;
}
if (!constraint) {
newConstraint.delegate = self;
[self.constraints addObject:newConstraint];
}
return newConstraint;
}
该方法返回的newConstraint是一个MASViewConstraint类的示例,而MASViewConstraint类又是MASConstraint的子类,返回类型写成MASConstraint没毛病。
代码较多,暂时可以只先看if (!constraint)里面的代码。可见,最后设置 newConstraint对象代理为self (即 MASConstraintMaker),并添加到一开始准备好的 self.constraints 数组中,返回。
其中,设置 MASViewConstraint 类 newConstraint 对象的 MASConstraintDelegate 代理为self (即 MASConstraintMaker),其作用就是为了能够同时设置多个约束属性!即链式语法。
- MASConstraint+Private.h
@protocol MASConstraintDelegate
/**
* Notifies the delegate when the constraint needs to be replaced with another constraint. For example
* A MASViewConstraint may turn into a MASCompositeConstraint when an array is passed to one of the equality blocks
*/
- (void)constraint:(MASConstraint *)constraint shouldBeReplacedWithConstraint:(MASConstraint *)replacementConstraint;
- (MASConstraint *)constraint:(MASConstraint *)constraint addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)layoutAttribute;
@end
2.3.2 MASConstraintMaker的继续分析
第2.3.1节的MASConstraintMaker.m代码中,先是初始化了 MASViewAttribute 对象并保存了 view、item以及 NSLayoutAttribute 三个属性。
- MASViewAttribute.m
- (id)initWithView:(MAS_VIEW *)view layoutAttribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)layoutAttribute {
self = [self initWithView:view item:view layoutAttribute:layoutAttribute];
return self;
}
- (id)initWithView:(MAS_VIEW *)view item:(id)item layoutAttribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)layoutAttribute {
self = [super init];
if (!self) return nil;
_view = view;
_item = item;
_layoutAttribute = layoutAttribute;
return self;
}
然后又初始化了 MASViewConstraint 对象,内部配置了些默认参数并保存了如上的第一个约束参数 MASViewAttribute。
- MASViewConstraint.m
- (id)initWithFirstViewAttribute:(MASViewAttribute *)firstViewAttribute {
self = [super init];
if (!self) return nil;
_firstViewAttribute = firstViewAttribute;
self.layoutPriority = MASLayoutPriorityRequired;
self.layoutMultiplier = 1;
return self;
}
2.4 .equalTo :通过基类MASConstraint及其子类MASViewConstraint分析
第一个约束属性 设置完后,走到.equalTo时,前面返回已经是一个 MASViewConstraint(继承自MASConstraint) 对象了,因而调用的是在基类MASConstraint中声明并实现的block属性getter方法。
- MASConstraint.m
- (MASConstraint * (^)(id))equalTo {
return ^id(id attribute) {
return self.equalToWithRelation(attribute, NSLayoutRelationEqual);
};
}
其中,基类 MASConstraint 仅仅声明,并没有实现equalToWithRelation抽象方法。但是,如2.3节中的链式语法.top,该方法返回的newConstraint实际是其子类--MASViewConstraint类的实例,故而可调用子类MASViewConstraint实现的equalToWithRelation方法:
- MASViewConstraint.m
- (MASConstraint * (^)(id, NSLayoutRelation))equalToWithRelation {
return ^id(id attribute, NSLayoutRelation relation) {
if ([attribute isKindOfClass:NSArray.class]) {
NSAssert(!self.hasLayoutRelation, @"Redefinition of constraint relation");
NSMutableArray *children = NSMutableArray.new;
for (id attr in attribute) {
MASViewConstraint *viewConstraint = [self copy];
viewConstraint.layoutRelation = relation;
viewConstraint.secondViewAttribute = attr;
[children addObject:viewConstraint];
}
MASCompositeConstraint *compositeConstraint = [[MASCompositeConstraint alloc] initWithChildren:children];
compositeConstraint.delegate = self.delegate;
[self.delegate constraint:self shouldBeReplacedWithConstraint:compositeConstraint];
return compositeConstraint;
} else {
NSAssert(!self.hasLayoutRelation || self.layoutRelation == relation && [attribute isKindOfClass:NSValue.class], @"Redefinition of constraint relation");
self.layoutRelation = relation;
self.secondViewAttribute = attribute;
return self;
}
};
}
代码较多,暂时可先看else {里面的代码。
(1) self.layoutRelation = relation;
首先是 self.layoutRelation 保存了约束关系且重写了 set 方法,在里面用 self.hasLayoutRelation 这个 BOOL 标识已经有约束关系。
- MASViewConstraint.m
- (void)setLayoutRelation:(NSLayoutRelation)layoutRelation {
_layoutRelation = layoutRelation;
self.hasLayoutRelation = YES;
}
(2) self.secondViewAttribute = attribute;
然后同样是重写了 self.secondViewAttribute 的 set 方法,这里会根据不同的情况做不同的操作。
- (void)setSecondViewAttribute:(id)secondViewAttribute {
if ([secondViewAttribute isKindOfClass:NSValue.class]) {
[self setLayoutConstantWithValue:secondViewAttribute];
} else if ([secondViewAttribute isKindOfClass:MAS_VIEW.class]) {
_secondViewAttribute = [[MASViewAttribute alloc] initWithView:secondViewAttribute layoutAttribute:self.firstViewAttribute.layoutAttribute];
} else if ([secondViewAttribute isKindOfClass:MASViewAttribute.class]) {
MASViewAttribute *attr = secondViewAttribute;
if (attr.layoutAttribute == NSLayoutAttributeNotAnAttribute) {
_secondViewAttribute = [[MASViewAttribute alloc] initWithView:attr.view item:attr.item layoutAttribute:self.firstViewAttribute.layoutAttribute];;
} else {
_secondViewAttribute = secondViewAttribute;
}
} else {
NSAssert(NO, @"attempting to add unsupported attribute: %@", secondViewAttribute);
}
}
其中,第1种情况对应的是:
make.height.equalTo(@20.0f)
传入 NSValue 的时, 会直接设置 constraint 的 offset, centerOffset, sizeOffset, 或者 insets。调用栈如下:
//MASViewConstraint.m
if ([secondViewAttribute isKindOfClass:NSValue.class]) {
[self setLayoutConstantWithValue:secondViewAttribute];
}
//MASConstraint.m
- (void)setLayoutConstantWithValue:(NSValue *)value {
if ([value isKindOfClass:NSNumber.class]) {
self.offset = [(NSNumber *)value doubleValue];
} else if (strcmp(value.objCType, @encode(CGPoint)) == 0) {
CGPoint point;
[value getValue:&point];
self.centerOffset = point;
} else if (strcmp(value.objCType, @encode(CGSize)) == 0) {
CGSize size;
[value getValue:&size];
self.sizeOffset = size;
} else if (strcmp(value.objCType, @encode(MASEdgeInsets)) == 0) {
MASEdgeInsets insets;
[value getValue:&insets];
self.insets = insets;
} else {
NSAssert(NO, @"attempting to set layout constant with unsupported value: %@", value);
}
}
//MASViewConstraint.m
- (void)setOffset:(CGFloat)offset {
self.layoutConstant = offset;
}
//MASViewConstraint.m
- (void)setLayoutConstant:(CGFloat)layoutConstant {
_layoutConstant = layoutConstant;
#if TARGET_OS_MAC && !(TARGET_OS_IPHONE || TARGET_OS_TV)
if (self.useAnimator) {
[self.layoutConstraint.animator setConstant:layoutConstant];
} else {
self.layoutConstraint.constant = layoutConstant;
}
#else
self.layoutConstraint.constant = layoutConstant;
#endif
}
第2种情况,一般是直接传入一个视图:
make.top.equalTo(self)
这时, 就会初始化一个 layoutAttribute 属性与 firstViewArribute 相同的 MASViewAttribute, 上面的代码就会使视图与 view 顶部对齐。
第3种情况,会传入一个视图的 MASViewAttribute:
make.top.equalTo(view.mas_bottom);
使用这种写法时, 一般是因为约束的方向不同. 这行代码会使视图的顶部与 view 的底部对齐。
2.5 .height.width:Masonry的链式语法特性
- 调用例子
make.height.width.equalTo(@20);
其中,.height 设置第一个约束属性时,调用的是 MASConstraintMaker.m 中的 .height, addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute,以及- (MASConstraint *)constraint:(MASConstraint *)constraint addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)layoutAttribute。
- MASConstraintMaker.m
- (MASConstraint *)height {
return [self addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:NSLayoutAttributeHeight];
}
- (MASConstraint *)addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)layoutAttribute {
return [self constraint:nil addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:layoutAttribute];
}
- (MASConstraint *)constraint:(MASConstraint *)constraint addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)layoutAttribute {
MASViewAttribute *viewAttribute = [[MASViewAttribute alloc] initWithView:self.view layoutAttribute:layoutAttribute];
MASViewConstraint *newConstraint = [[MASViewConstraint alloc] initWithFirstViewAttribute:viewAttribute];
if ([constraint isKindOfClass:MASViewConstraint.class]) {
//replace with composite constraint
NSArray *children = @[constraint, newConstraint];
MASCompositeConstraint *compositeConstraint = [[MASCompositeConstraint alloc] initWithChildren:children];
compositeConstraint.delegate = self;
[self constraint:constraint shouldBeReplacedWithConstraint:compositeConstraint];
return compositeConstraint;
}
if (!constraint) {
newConstraint.delegate = self;
[self.constraints addObject:newConstraint];
}
return newConstraint;
}
该方法调用栈返回的是一个MASViewConstraint(父类是 MASConstraint) 对象。
因此,通过 .width 设置第二个约束属性的时候,调用的先是基类 MASConstraint.m 中的.width,然后调用由子类MASViewConstraint实现的addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute方法。这时候的调用栈为:
- MASConstraint.m
- (MASConstraint *)width {
return [self addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:NSLayoutAttributeWidth];
}
- (MASConstraint *)addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:(NSLayoutAttribute __unused)layoutAttribute {
MASMethodNotImplemented();
}
- MASViewConstraint.m
- (MASConstraint *)addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)layoutAttribute {
NSAssert(!self.hasLayoutRelation, @"Attributes should be chained before defining the constraint relation");
return [self.delegate constraint:self addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:layoutAttribute];
}
这其中,self.delegate 是什么呢?如2.3.1节所述,MASConstraintMaker.m 中设置了 MASViewConstraint 类 newConstraint 对象的 MASConstraintDelegate 代理为“self” (即 MASConstraintMaker),其作用就是为了能够同时设置多个约束属性,即链式语法。所以,第二个设置约束属性跟第一个设置约束属性最终 调用的方法一样(都是MASConstraintMaker.m中实现的addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute)。
- MASConstraintMaker.m
- (MASConstraint *)constraint:(MASConstraint *)constraint addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)layoutAttribute {
MASViewAttribute *viewAttribute = [[MASViewAttribute alloc] initWithView:self.view layoutAttribute:layoutAttribute];
MASViewConstraint *newConstraint = [[MASViewConstraint alloc] initWithFirstViewAttribute:viewAttribute];
if ([constraint isKindOfClass:MASViewConstraint.class]) {
//replace with composite constraint
NSArray *children = @[constraint, newConstraint];
MASCompositeConstraint *compositeConstraint = [[MASCompositeConstraint alloc] initWithChildren:children];
compositeConstraint.delegate = self;
[self constraint:constraint shouldBeReplacedWithConstraint:compositeConstraint];
return compositeConstraint;
}
if (!constraint) {
newConstraint.delegate = self;
[self.constraints addObject:newConstraint];
}
return newConstraint;
}
当设置 第二次约束属性 并执行完之后,我们还可以发现 constraint 不为 nil,而是一个 MASViewConstraint 对象 ,所以该方法调用栈返回的不是 MASViewConstraint 对象,而是 MASCompositeConstraint 这个对象了,下面我们来看看这个类。
2.6 约束的集合: MASCompositeConstraint
MASCompositeConstraint 是约束的集合,它里面有个私有的数组用来存放多个 MASViewAttribute 对象。
make.height.width.equalTo(@20)
当设置 第二个约束属性,走到 .width 时,最终走的是:
- MASConstraintMaker.m
- (MASConstraint *)constraint:(MASConstraint *)constraint addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)layoutAttribute {
MASViewAttribute *viewAttribute = [[MASViewAttribute alloc] initWithView:self.view layoutAttribute:layoutAttribute];
MASViewConstraint *newConstraint = [[MASViewConstraint alloc] initWithFirstViewAttribute:viewAttribute];
if ([constraint isKindOfClass:MASViewConstraint.class]) {
//replace with composite constraint
NSArray *children = @[constraint, newConstraint];
MASCompositeConstraint *compositeConstraint = [[MASCompositeConstraint alloc] initWithChildren:children];
compositeConstraint.delegate = self;
[self constraint:constraint shouldBeReplacedWithConstraint:compositeConstraint];
return compositeConstraint;
}
....
}
其中,可以成功的走进 if判读里面,将 .height .wight 两条约束 MASViewConstraint对象塞到数组里,创建 MASCompositeConstraint 对象,并且同样设置了 delegate,最后还把 self.constraints 里面事先添加好的约束 MASViewConstraint 对象替换成了 MASCompositeConstraint 对象。
#pragma mark - MASConstraintDelegate
- (void)constraint:(MASConstraint *)constraint shouldBeReplacedWithConstraint:(MASConstraint *)replacementConstraint {
NSUInteger index = [self.childConstraints indexOfObject:constraint];
NSAssert(index != NSNotFound, @"Could not find constraint %@", constraint);
[self.childConstraints replaceObjectAtIndex:index withObject:replacementConstraint];
}
另外,我们可以点击 MASCompositeConstraint 初始化方法里看看,它内部会通过 for 循环,把数组里面的所有 MASViewConstraint 对象同样设置了 delegate。
- (id)initWithChildren:(NSArray *)children {
self = [super init];
if (!self) return nil;
_childConstraints = [children mutableCopy];
for (MASConstraint *constraint in _childConstraints) {
constraint.delegate = self;
}
return self;
}
这么做的目的同时是为了能够继续链式调用,比如我们再设置第三个约束属性 .left
make.height.width.left.equalTo(@20);
这时候的调用栈如下:
- MASConstraint.m
- (MASConstraint *)left {
return [self addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:NSLayoutAttributeLeft];
}
- MASCompositeConstraint.m
- (MASConstraint *)addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)layoutAttribute {
[self constraint:self addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:layoutAttribute];
return self;
}
- (MASConstraint *)constraint:(MASConstraint __unused *)constraint addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)layoutAttribute {
id strongDelegate = self.delegate;
MASConstraint *newConstraint = [strongDelegate constraint:self addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:layoutAttribute];
newConstraint.delegate = self;
[self.childConstraints addObject:newConstraint];
return newConstraint;
}
可以发现,这里又是通过 delegate 方式,调用 MASConstraintMaker 工厂类中的:
- MASConstraintMaker.m
- (MASConstraint *)constraint:(MASConstraint *)constraint addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)layoutAttribute {
MASViewAttribute *viewAttribute = [[MASViewAttribute alloc] initWithView:self.view layoutAttribute:layoutAttribute];
MASViewConstraint *newConstraint = [[MASViewConstraint alloc] initWithFirstViewAttribute:viewAttribute];
if ([constraint isKindOfClass:MASViewConstraint.class]) {
//replace with composite constraint
NSArray *children = @[constraint, newConstraint];
MASCompositeConstraint *compositeConstraint = [[MASCompositeConstraint alloc] initWithChildren:children];
compositeConstraint.delegate = self;
[self constraint:constraint shouldBeReplacedWithConstraint:compositeConstraint];
return compositeConstraint;
}
if (!constraint) {
newConstraint.delegate = self;
[self.constraints addObject:newConstraint];
}
return newConstraint;
}
此时,注意到两个 if 体都没有走进去,既不像第一次,也不像第二次约束设置的时候。所以,这次仅仅是初始化了个 MASViewConstraint 对象就直接返回了,然后回到上个方法中添加到 MASCompositeConstraint 的私有数组 self.childConstraints 中返回备用。
关于三次 约束设置之后的 .equalTo(@20),因为执行完 .left 时,返回的是 MASCompositeConstraint 对象,到这一步的时候会有点变化,调用栈如下:
- MASConstraint.m
- (MASConstraint * (^)(id))equalTo {
return ^id(id attribute) {
return self.equalToWithRelation(attribute, NSLayoutRelationEqual);
};
}
- MASCompositeConstraint.m
- (MASConstraint * (^)(id, NSLayoutRelation))equalToWithRelation {
return ^id(id attr, NSLayoutRelation relation) {
for (MASConstraint *constraint in self.childConstraints.copy) {
constraint.equalToWithRelation(attr, relation);
}
return self;
};
}
可以发现,这里会循环之前准备好的私有数组 self.childConstraints,调用 MASViewConstraint.m 的 equalToWithRelation 方法,和上面讲的一样了。
2.7 添加约束到视图
mas_makeConstraints 方法的最后会调用 [constraintMaker install] 方法来添加所有存储在 self.constraints 数组中的所有约束。
- MASConstraintMaker.m
- (NSArray *)install {
if (self.removeExisting) {
NSArray *installedConstraints = [MASViewConstraint installedConstraintsForView:self.view];
for (MASConstraint *constraint in installedConstraints) {
[constraint uninstall];
}
}
NSArray *constraints = self.constraints.copy;
for (MASConstraint *constraint in constraints) {
constraint.updateExisting = self.updateExisting;
[constraint install];
}
[self.constraints removeAllObjects];
return constraints;
}
(1). 如果需要重新构建约束,也就是 调用 mas_remakeConstraints:方法,会先取出视图的所有约束,然后通过一个 for 循环,调用 uninstall 来清空所有约束:
(2). 如果不需要重新构建约束,会取出 self.constraints 数组中准备好的约束,通过 for 循环,调用 install 来把约束添加到视图上。
关于 install ,是基类 MASConstraint 的抽象方法,方法体由MASViewConstraint 或 MASCompositeConstraint 实现。而 MASCompositeConstraint 的 install方法体中其实也是调用的由MASViewConstraint类实现的install。
- MASConstraint.m
- (void)install { MASMethodNotImplemented(); }
- MASCompositeConstraint.m
- (void)install {
for (MASConstraint *constraint in self.childConstraints) {
constraint.updateExisting = self.updateExisting;
[constraint install];
}
}
- MASViewConstraint.m
这里代码较多,就不分开解析了,直接分为7步写到源码的注释中,如下所示:
- (void)install {
//【1】如果约束以及存在并是 active 会直接返回。
if (self.hasBeenInstalled) {
return;
}
//【2】如果 self.layoutConstraint 响应了 isActive 方法并且不为空,会激活这条约束并添加到 mas_installedConstraints 数组中,最后返回。
if ([self supportsActiveProperty] && self.layoutConstraint) {
self.layoutConstraint.active = YES;
[self.firstViewAttribute.view.mas_installedConstraints addObject:self];
return;
}
//【3】这边是获取即将用于初始化 NSLayoutConstraint 的子类 MASLayoutConstraint 的几个属性。
MAS_VIEW *firstLayoutItem = self.firstViewAttribute.item;
NSLayoutAttribute firstLayoutAttribute = self.firstViewAttribute.layoutAttribute;
MAS_VIEW *secondLayoutItem = self.secondViewAttribute.item;
NSLayoutAttribute secondLayoutAttribute = self.secondViewAttribute.layoutAttribute;
// alignment attributes must have a secondViewAttribute
// therefore we assume that is refering to superview
// eg make.left.equalTo(@10)
//【4】这边是判断当前即将添加的约束是否是 size 类型的并且 self.secondViewAttribute 也就是约束的第二个参数是 nil,(eg make.left.equalTo(@10))会自动将约束添加到约束的第一个参数视图的 superview 上。
if (!self.firstViewAttribute.isSizeAttribute && !self.secondViewAttribute) {
secondLayoutItem = self.firstViewAttribute.view.superview;
secondLayoutAttribute = firstLayoutAttribute;
}
//【5】然后就会初始化 NSLayoutConstraint 的子类 MASLayoutConstraint。
MASLayoutConstraint *layoutConstraint
= [MASLayoutConstraint constraintWithItem:firstLayoutItem
attribute:firstLayoutAttribute
relatedBy:self.layoutRelation
toItem:secondLayoutItem
attribute:secondLayoutAttribute
multiplier:self.layoutMultiplier
constant:self.layoutConstant];
layoutConstraint.priority = self.layoutPriority;
layoutConstraint.mas_key = self.mas_key;
//【6】这段代码会先判断是否有约束第二个参数的视图,有的话会寻找约束第一个和第二参数视图的公共 Superview,相当于求两个数的最小公倍数;如果不满足第一个条件,会判断约束第一个参数是否是 size 类型的,是的话直接取到它的视图;最后都不满足会直接取到约束第一个参数视图父视图。
if (self.secondViewAttribute.view) {
MAS_VIEW *closestCommonSuperview = [self.firstViewAttribute.view mas_closestCommonSuperview:self.secondViewAttribute.view];
NSAssert(closestCommonSuperview,
@"couldn't find a common superview for %@ and %@",
self.firstViewAttribute.view, self.secondViewAttribute.view);
self.installedView = closestCommonSuperview;
} else if (self.firstViewAttribute.isSizeAttribute) {
self.installedView = self.firstViewAttribute.view;
} else {
self.installedView = self.firstViewAttribute.view.superview;
}
//【7】如果需要升级当前的约束就会获取原有的约束,并替换为新的约束,这样就不需要再次为 view 安装约束。如果原来的 view 中不存在可以升级的约束,那么就会在上一步寻找到的 installedView 上面添加约束。
MASLayoutConstraint *existingConstraint = nil;
if (self.updateExisting) {
existingConstraint = [self layoutConstraintSimilarTo:layoutConstraint];
}
if (existingConstraint) {
// just update the constant
existingConstraint.constant = layoutConstraint.constant;
self.layoutConstraint = existingConstraint;
} else {
[self.installedView addConstraint:layoutConstraint];
self.layoutConstraint = layoutConstraint;
[firstLayoutItem.mas_installedConstraints addObject:self];
}
}
其中第【6】步中的mas_closestCommonSuperview方法,它会寻找 firstLayoutItem 和 secondLayoutItem 两个视图的公共 superview, 相当于求两个数的最小公倍数.
- View+MASAdditions.m
- (instancetype)mas_closestCommonSuperview:(MAS_VIEW *)view {
MAS_VIEW *closestCommonSuperview = nil;
MAS_VIEW *secondViewSuperview = view;
while (!closestCommonSuperview && secondViewSuperview) {
MAS_VIEW *firstViewSuperview = self;
while (!closestCommonSuperview && firstViewSuperview) {
if (secondViewSuperview == firstViewSuperview) {
closestCommonSuperview = secondViewSuperview;
}
firstViewSuperview = firstViewSuperview.superview;
}
secondViewSuperview = secondViewSuperview.superview;
}
return closestCommonSuperview;
}
3. 顺藤再摸瓜:Masonry其它链式语法的调用栈解析(选读)
3.1 make.edges.equalTo(view)
- 例子
make.edges.equalTo(view)
我们再来看看这种写法,调用栈如下:
- MASConstraintMaker.m
- (MASConstraint *)edges {
return [self addConstraintWithAttributes:MASAttributeTop | MASAttributeLeft | MASAttributeRight | MASAttributeBottom];
}
- (MASConstraint *)addConstraintWithAttributes:(MASAttribute)attrs {
__unused MASAttribute anyAttribute = (MASAttributeLeft | MASAttributeRight | MASAttributeTop | MASAttributeBottom | MASAttributeLeading
| MASAttributeTrailing | MASAttributeWidth | MASAttributeHeight | MASAttributeCenterX
| MASAttributeCenterY |
......
NSMutableArray *attributes = [NSMutableArray array];
if (attrs & MASAttributeLeft) [attributes addObject:self.view.mas_left];
if (attrs & MASAttributeRight) [attributes addObject:self.view.mas_right];
if (attrs & MASAttributeTop) [attributes addObject:self.view.mas_top];
......
NSMutableArray *children = [NSMutableArray arrayWithCapacity:attributes.count];
for (MASViewAttribute *a in attributes) {
[children addObject:[[MASViewConstraint alloc] initWithFirstViewAttribute:a]];
}
MASCompositeConstraint *constraint = [[MASCompositeConstraint alloc] initWithChildren:children];
constraint.delegate = self;
[self.constraints addObject:constraint];
return constraint;
}
代码太多省略了一部分,可以发现这段代码作用就是返回一个包含多条约束的 MASCompositeConstraint 对象,接着后面的操作也都是一样的了。
3.2 make.edges.equalTo(UIEdgeInsetsMake(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f));
上面3.1中例子的写法还可以改成这样:
make.edges.equalTo(UIEdgeInsetsMake(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f));
这里的 equalTo 需要注意下,它是一个宏,定义在 MASConstraint.h 中:
- MASConstraint.h
#define mas_equalTo(...) equalTo(MASBoxValue((__VA_ARGS__)))
#define mas_greaterThanOrEqualTo(...) greaterThanOrEqualTo(MASBoxValue((__VA_ARGS__)))
#define mas_lessThanOrEqualTo(...) lessThanOrEqualTo(MASBoxValue((__VA_ARGS__)))
#define mas_offset(...) valueOffset(MASBoxValue((__VA_ARGS__)))
#ifdef MAS_SHORTHAND_GLOBALS
#define equalTo(...) mas_equalTo(__VA_ARGS__)
#define greaterThanOrEqualTo(...) mas_greaterThanOrEqualTo(__VA_ARGS__)
#define lessThanOrEqualTo(...) mas_lessThanOrEqualTo(__VA_ARGS__)
#define offset(...) mas_offset(__VA_ARGS__)
代入上述宏定义,前面的代码等效成:
make.edges.equalTo(MASBoxValue(UIEdgeInsetsMake(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f)));
可以发现,其实里面调用的是 MASBoxValue 这个宏,它将 C 和 Objective-C 语言中的一些基本数据结构比如说 double CGPoint CGSize 这些值用 NSValue 进行包装。
这里还支持直接调用 size、center 等,具体实现都差不多,就不熬述了:
make.center.equalTo(CGPointMake(0, 50));
make.size.equalTo(CGSizeMake(200, 100));
3.3 make.height.equalTo(@[redView, blueView])
make.height.equalTo(@[redView, blueView])
再来看看这种传数组的,在走到 .equalTo 时,最终会调用 MASViewConstraint.m 里面的 equalToWithRelation 方法
- MASConstraint.m
- (MASConstraint * (^)(id))equalTo {
return ^id(id attribute) {
return self.equalToWithRelation(attribute, NSLayoutRelationEqual);
};
}
- MASViewConstraint.m
- (MASConstraint * (^)(id, NSLayoutRelation))equalToWithRelation {
return ^id(id attribute, NSLayoutRelation relation) {
if ([attribute isKindOfClass:NSArray.class]) {
NSAssert(!self.hasLayoutRelation, @"Redefinition of constraint relation");
NSMutableArray *children = NSMutableArray.new;
for (id attr in attribute) {
MASViewConstraint *viewConstraint = [self copy];
viewConstraint.layoutRelation = relation;
viewConstraint.secondViewAttribute = attr;
[children addObject:viewConstraint];
}
MASCompositeConstraint *compositeConstraint = [[MASCompositeConstraint alloc] initWithChildren:children];
compositeConstraint.delegate = self.delegate;
[self.delegate constraint:self shouldBeReplacedWithConstraint:compositeConstraint];
return compositeConstraint;
} else { .... }
};
}
这边还是遍历数组,并且 MASViewConstraint 实现 NSCopying 协议,调用 [self copy] 会创建 MASViewConstraint 对象
- (id)copyWithZone:(NSZone __unused *)zone {
MASViewConstraint *constraint = [[MASViewConstraint alloc] initWithFirstViewAttribute:self.firstViewAttribute];
constraint.layoutConstant = self.layoutConstant;
constraint.layoutRelation = self.layoutRelation;
constraint.layoutPriority = self.layoutPriority;
constraint.layoutMultiplier = self.layoutMultiplier;
constraint.delegate = self.delegate;
return constraint;
}
然后会根据传的数组里面的 Value 类型来做不同的操作,前面讲过就不熬述了:
- (void)setSecondViewAttribute:(id)secondViewAttribute {
if ([secondViewAttribute isKindOfClass:NSValue.class]) {
[self setLayoutConstantWithValue:secondViewAttribute];
} else if ([secondViewAttribute isKindOfClass:MAS_VIEW.class]) {
_secondViewAttribute = [[MASViewAttribute alloc] initWithView:secondViewAttribute layoutAttribute:self.firstViewAttribute.layoutAttribute];
} else if ([secondViewAttribute isKindOfClass:MASViewAttribute.class]) {
_secondViewAttribute = secondViewAttribute;
} else {
NSAssert(NO, @"attempting to add unsupported attribute: %@", secondViewAttribute);
}
}
最后便是生成 MASCompositeConstraint 对象,并通过 delegate 方式,调用 MASConstraintMaker 的方法,替换 self.constraints 数组里的约束:
- (void)constraint:(MASConstraint *)constraint shouldBeReplacedWithConstraint:(MASConstraint *)replacementConstraint {
NSUInteger index = [self.constraints indexOfObject:constraint];
NSAssert(index != NSNotFound, @"Could not find constraint %@", constraint);
[self.constraints replaceObjectAtIndex:index withObject:replacementConstraint];
}
4. 举一反三:框架源码的学习启示
4.1 简化的设计模式:工厂类&工厂方法
MASConstraintMaker类就是一个工厂类,负责创建MASConstraint类型的对象(依赖于MASConstraint接口,而不依赖于具体实现)。在UIView的View+MASAdditions分类中就是调用的MASConstraintMaker类中的一些方法。上述我们在使用Masonry给subView添加约束时,mas_makeConstraints方法中的Block的参数就是MASConstraintMaker的对象。用户可以通过该Block回调过来的MASConstraintMaker对象给View指定要添加的约束以及该约束的值。该工厂中的constraints属性数组就记录了该工厂创建的所有MASConstraint对象。
MASConstraintMaker 之所以成为约束工厂类,因为MASConstraintMaker赋值创建NSLayoutConstraint对象,因为Masonry将NSLayoutConstraint类进一步封装成了MASViewConstraint,所以MASConstraintMaker是负责创建MASViewConstraint的对象,并调用MASViewConstraint对象的Install方法将该约束添加到相应的视图中。
说了这么多,总结一下,如果你调用maker.top, maker.left等等这些方法都会调用下方的工厂方法来创建相应的MASViewConstraint对象,并记录在工厂对象的约束数组中。之所以能链式调用,就是讲当前的工厂对象(MASConstraintMaker)指定为MASViewConstraint对象的代理,所以一个MASViewConstraint对象就可以通过代理来调用工厂方法来创建另一个新的MASViewConstraint对象了,此处用到了代理模式。
角色分析
Client:
UIView,通过分类View+MASAdditions来扮演工厂类:
MASConstraintMaker抽象产品:
MASConstraint具体产品:
MASViewConstraint,MASCompositeConstraint
4.2 真正的设计模式:组合模式
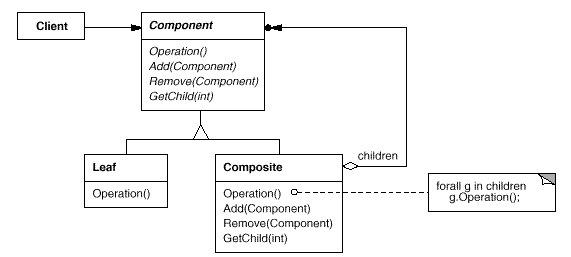
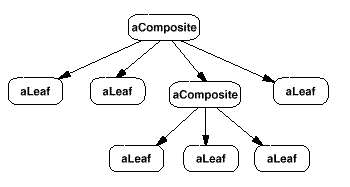
换一种角度看,Masonry 并非单纯的工厂模式,而是采用了经典的 Composite 设计模式,中文可译作组合模式。
4.2.1 经典 组合模式 中的参与者:
Client
- 通过 Component 接口操纵组合部件的对象。
Component
- 为组合中的对象声明接口。
- 在适当的情况下,实现所有类共有接口的缺省行为
- 声明一个接口用于访问和管理 Component 的子组件。
- 在递归结构中定义一个接口,用于访问一个父部件,并在合适的情况下实现它。
Leaf
- 在组合中表示叶节点对象,叶节点没有子节点。
- 在组合中定义图元对象的行为。
Composite
- 定义有子部件的那些部件的行为。
- 在 Composite 接口中实现与子部件有关的操作。
4.2.2 从 组合模式 的角度看,Masonry 框架中的角色分析:
UIView,通过分类View+MASAdditions来调用Masonry
Client
MASConstraintMaker
Component
MASConstraint
Leaf
MASViewConstraint
Composite
MASCompositeConstraint
4.3 编程思想:链式编程
Objective-C是一门动态语言,它使用了一种动态的消息发送机制,即对象(object)或类(class)调用方法。而OC中的点语法则只能通过setter和getter方法作用于类的属性,而不能作用于某个方法。想实现链式语法,只能通过类似block属性的getter方法。
链式编程思想:核心思想为将block作为方法的返回值,且返回值的类型为调用者本身,并将该方法以setter的形式返回,这样就可以实现了连续调用,即为链式编程。
【举例】简单使用链式编程思想实现一个简单计算器的功能:
4.3.1 新建一个名为CaculateMaker的类,用于运算。
4.3.2 在CaculateMaker.h文件中声明一个方法add:
- CaculateMaker.h
// CaculateMaker.h
// ChainBlockTestApp
#import
#import
@interface CaculateMaker : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, assign) CGFloat result;
- (CaculateMaker *(^)(CGFloat num))add;
@end
4.3.3 在CaculateMaker.m文件中实现这个方法:
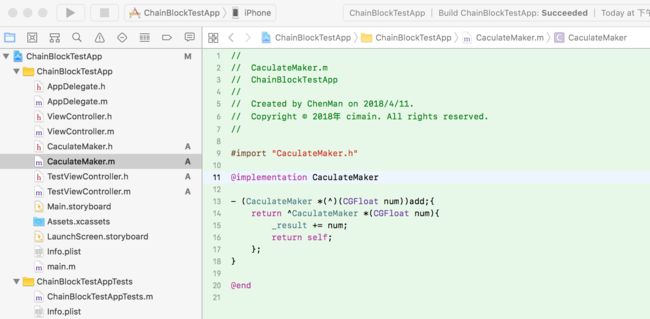
- CaculateMaker.m
// CaculateMaker.m
// ChainBlockTestApp
#import "CaculateMaker.h"
@implementation CaculateMaker
- (CaculateMaker *(^)(CGFloat num))add;{
return ^CaculateMaker *(CGFloat num){
_result += num;
return self;
};
}
@end
4.3.4 在viewController里面导入CaculateMaker.h文件,然后调用add方法就完成了链式语法:
- ViewController.m
CaculateMaker *maker = [[CaculateMaker alloc] init];
maker.add(20).add(30);
通过上面Masonry布局可以看出,它为UIView写了一个category,拓展了mas_makeConstraints方法,并将MASConstraintMaker对象作为block的参数传递,在block的实现里完成UIView的布局,提现了函数式编程思想。
4.3.5 同样,我们也可以给NSObject添加一个NSObject+Caculate的分类,完成加法操作:
- NSObject+Caculate.h
// NSObject+Caculate.h
// ChainBlockTestApp
#import
#import
#import "CaculateMaker.h"
@interface NSObject (Caculate)
- (CGFloat)caculate:(void (^)(CaculateMaker *make))block;
@end
- NSObject+Caculate.m
// NSObject+Caculate.m
// ChainBlockTestApp
#import "NSObject+Caculate.h"
@implementation NSObject (Caculate)
- (CGFloat)caculate:(void (^)(CaculateMaker *make))block;{
CaculateMaker *make = [[CaculateMaker alloc] init];
block(make);
return make.result;
}
@end
4.3.6 最后在viewController里面调用,就很轻松的实现了链式语法:
- ViewController.m
CGFloat result = [NSObject caculate:^(CaculateMaker *maker) {
maker.add(10).add(20).add(30);
}];
NSLog(@"结果为:%.2f",result);
5. 参考阅读
-
Masonry解析
- http://qiufeng.me/masonry
- https://www.cnblogs.com/ludashi/p/5591572.html
-
工厂模式
- https://www.jianshu.com/p/7b89b7f587f9
- https://www.jianshu.com/p/847af218b1f0
-
组合模式
- http://www.runoob.com/design-pattern/composite-pattern.html
- http://www.cnblogs.com/gaochundong/p/design_pattern_composite.html
- http://www.cnblogs.com/peida/archive/2008/09/09/1284686.html
-
链式编程
- https://www.jianshu.com/p/cb9252f5105b
- https://www.jianshu.com/p/ac8bdd3430e7