目录
- RNN
- seq-->seq
- N-1
- N-M
- language model
- pad_sequences()
- LSTM
- Keras preprocessing
- tokenizer 分词
- simpleRNN
- Vanishing and exploding gradients
- SGD梯度下降算法
- GRU and LSTM cells
- stacking
- The Embedding layer
- glove
- 预训练模型
- 提升模型效果的方式
- 防止过拟合dropout
- 一个简单的模型
- Data pre-processing
- 分类变量进行编码
- tokenizer里面的函数可以直接用
- Transfer learning for language models
- Word2Vec
- Neural Machine Translation
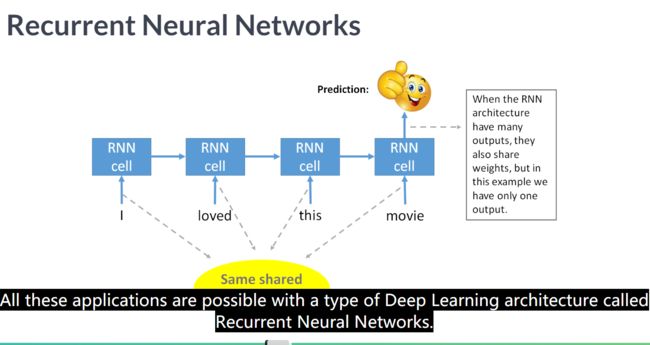
RNN
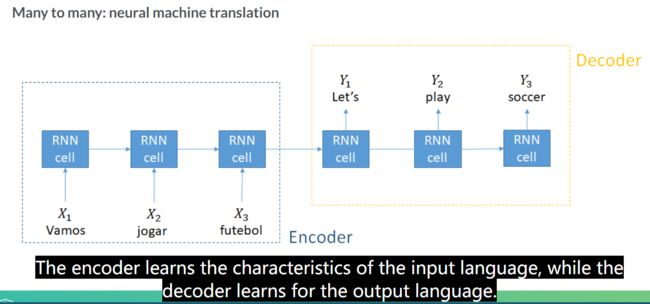
seq-->seq
RNN根据输入输出的数量不同可以分为
N-1
N-M
encoder和decoder一直卡着的是decoder的状态,改如何表示哦?
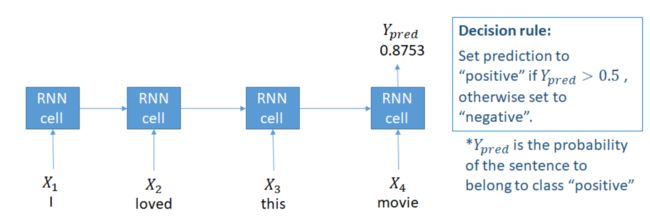
language model
input->embedding->神经网络哦->output

# Transform the list of sentences into a list of words
all_words = ' '.join(sheldon_quotes).split(' ')
# Get number of unique words
unique_words = list(set(all_words))
# Dictionary of indexes as keys and words as values
index_to_word = {i:wd for i, wd in enumerate(sorted(unique_words))}
print(index_to_word)
# Dictionary of words as keys and indexes as values
word_to_index = {wd:i for i, wd in enumerate(sorted(unique_words))}
print(word_to_index)
script.py> output:
{0: '(3', 1: 'Ah,', 2: "Amy's", 3: 'And', 4: 'Explorer', 5: 'Firefox.', 6: 'For', 7: 'Galileo,', 8: 'Goblin', 9: 'Green', 10: 'Hubble', 11: 'I', 12: "I'm", 13: 'Internet', 14: 'Ladybugs', 15: 'Oh', 16: 'Paul', 17: 'Penny', 18: 'Penny!', 19: 'Pope', 20: 'Scissors', 21: 'She', 22: 'Spider-Man,', 23: 'Spock', 24: 'Spock,', 25: 'Thankfully', 26: 'The', 27: 'Two', 28: 'V', 29: 'Well,', 30: 'What', 31: 'Wheaton!', 32: 'Wil', 33: "You're", 34: 'a', 35: 'afraid', 36: 'all', 37: 'always', 38: 'am', 39: 'and', 40: 'appeals', 41: 'are', 42: 'art', 43: 'as', 44: 'at', 45: 'aware', 46: 'based', 47: 'be', 48: 'became', 49: 'because', 50: 'been', 51: 'birthday', 52: 'bitch.', 53: 'black', 54: 'blood', 55: 'bottle.', 56: 'bottom', 57: 'brain', 58: 'breaker.', 59: 'bus', 60: 'but', 61: 'calls', 62: 'can', 63: 'care', 64: 'catatonic.', 65: 'center', 66: 'chance', 67: 'circuit', 68: 'computer', 69: 'could', 70: 'covers', 71: 'crushes', 72: 'cry', 73: 'cuts', 74: 'days', 75: 'decapitates', 76: 'deity.', 77: 'discovering', 78: 'disproves', 79: 'do', 80: 'does', 81: "don't", 82: 'eat', 83: 'eats', 84: 'every', 85: 'example,', 86: 'flashlight', 87: 'for', 88: 'free', 89: 'genitals,', 90: 'genitals.', 91: 'get', 92: 'ghost', 93: 'girlfriend', 94: 'gravity,', 95: 'had', 96: 'hand.', 97: 'has,', 98: 'have', 99: 'have?', 100: 'having', 101: 'heartless', 102: 'here', 103: 'hole', 104: 'humans', 105: 'if', 106: 'impairment;', 107: 'in', 108: 'insane,', 109: 'insects', 110: 'involves', 111: 'is', 112: "isn't", 113: 'it', 114: 'it.', 115: 'just', 116: 'kept', 117: 'knocks)', 118: 'later,', 119: 'little', 120: 'living', 121: 'lizard', 122: 'lizard,', 123: 'loud', 124: 'makes', 125: 'man', 126: 'masturbating', 127: 'me', 128: 'memory', 129: 'messy,', 130: 'money.', 131: 'moon-pie', 132: 'mother', 133: 'moved', 134: 'much', 135: 'must', 136: 'my', 137: 'next', 138: 'not', 139: 'nummy-nummy', 140: 'of', 141: 'on', 142: 'one.', 143: 'other', 144: 'others', 145: 'paper', 146: 'paper,', 147: 'people', 148: 'please', 149: 'poisons', 150: 'present', 151: 'prize', 152: 'relationship', 153: 'render', 154: 'reproduce', 155: 'right', 156: 'rock', 157: 'rock,', 158: 'rushed', 159: 'sad.', 160: 'say', 161: 'scissors', 162: 'scissors,', 163: 'scissors.', 164: 'searching', 165: 'sexual', 166: 'she', 167: 'smashes', 168: 'so', 169: 'sooner', 170: 'stopping', 171: 'stupid,', 172: 'taken', 173: 'telescope', 174: 'tested.', 175: 'that', 176: 'the', 177: 'things', 178: 'think', 179: 'thou', 180: 'three', 181: 'to', 182: 'today', 183: 'town.', 184: 'tried', 185: 'unnecessary', 186: 'unsanitary', 187: 'up.', 188: 'used', 189: 'usually', 190: 'vaporizes', 191: 'vodka', 192: 'way', 193: 'we', 194: 'well,', 195: 'which', 196: 'white', 197: 'will', 198: 'with', 199: 'women,', 200: 'would', 201: 'years,', 202: 'you', 203: 'your'}
{'(3': 0, 'Ah,': 1, "Amy's": 2, 'And': 3, 'Explorer': 4, 'Firefox.': 5, 'For': 6, 'Galileo,': 7, 'Goblin': 8, 'Green': 9, 'Hubble': 10, 'I': 11, "I'm": 12, 'Internet': 13, 'Ladybugs': 14, 'Oh': 15, 'Paul': 16, 'Penny': 17, 'Penny!': 18, 'Pope': 19, 'Scissors': 20, 'She': 21, 'Spider-Man,': 22, 'Spock': 23, 'Spock,': 24, 'Thankfully': 25, 'The': 26, 'Two': 27, 'V': 28, 'Well,': 29, 'What': 30, 'Wheaton!': 31, 'Wil': 32, "You're": 33, 'a': 34, 'afraid': 35, 'all': 36, 'always': 37, 'am': 38, 'and': 39, 'appeals': 40, 'are': 41, 'art': 42, 'as': 43, 'at': 44, 'aware': 45, 'based': 46, 'be': 47, 'became': 48, 'because': 49, 'been': 50, 'birthday': 51, 'bitch.': 52, 'black': 53, 'blood': 54, 'bottle.': 55, 'bottom': 56, 'brain': 57, 'breaker.': 58, 'bus': 59, 'but': 60, 'calls': 61, 'can': 62, 'care': 63, 'catatonic.': 64, 'center': 65, 'chance': 66, 'circuit': 67, 'computer': 68, 'could': 69, 'covers': 70, 'crushes': 71, 'cry': 72, 'cuts': 73, 'days': 74, 'decapitates': 75, 'deity.': 76, 'discovering': 77, 'disproves': 78, 'do': 79, 'does': 80, "don't": 81, 'eat': 82, 'eats': 83, 'every': 84, 'example,': 85, 'flashlight': 86, 'for': 87, 'free': 88, 'genitals,': 89, 'genitals.': 90, 'get': 91, 'ghost': 92, 'girlfriend': 93, 'gravity,': 94, 'had': 95, 'hand.': 96, 'has,': 97, 'have': 98, 'have?': 99, 'having': 100, 'heartless': 101, 'here': 102, 'hole': 103, 'humans': 104, 'if': 105, 'impairment;': 106, 'in': 107, 'insane,': 108, 'insects': 109, 'involves': 110, 'is': 111, "isn't": 112, 'it': 113, 'it.': 114, 'just': 115, 'kept': 116, 'knocks)': 117, 'later,': 118, 'little': 119, 'living': 120, 'lizard': 121, 'lizard,': 122, 'loud': 123, 'makes': 124, 'man': 125, 'masturbating': 126, 'me': 127, 'memory': 128, 'messy,': 129, 'money.': 130, 'moon-pie': 131, 'mother': 132, 'moved': 133, 'much': 134, 'must': 135, 'my': 136, 'next': 137, 'not': 138, 'nummy-nummy': 139, 'of': 140, 'on': 141, 'one.': 142, 'other': 143, 'others': 144, 'paper': 145, 'paper,': 146, 'people': 147, 'please': 148, 'poisons': 149, 'present': 150, 'prize': 151, 'relationship': 152, 'render': 153, 'reproduce': 154, 'right': 155, 'rock': 156, 'rock,': 157, 'rushed': 158, 'sad.': 159, 'say': 160, 'scissors': 161, 'scissors,': 162, 'scissors.': 163, 'searching': 164, 'sexual': 165, 'she': 166, 'smashes': 167, 'so': 168, 'sooner': 169, 'stopping': 170, 'stupid,': 171, 'taken': 172, 'telescope': 173, 'tested.': 174, 'that': 175, 'the': 176, 'things': 177, 'think': 178, 'thou': 179, 'three': 180, 'to': 181, 'today': 182, 'town.': 183, 'tried': 184, 'unnecessary': 185, 'unsanitary': 186, 'up.': 187, 'used': 188, 'usually': 189, 'vaporizes': 190, 'vodka': 191, 'way': 192, 'we': 193, 'well,': 194, 'which': 195, 'white': 196, 'will': 197, 'with': 198, 'women,': 199, 'would': 200, 'years,': 201, 'you': 202, 'your': 203}
- Preparing text data for model input
这步不懂
# Create lists to keep the sentences and the next character
sentences = [] # ~ Training data
next_chars = [] # ~ Training labels
# Define hyperparameters
step = 2 # ~ Step to take when reading the texts in characters
chars_window = 10 # ~ Number of characters to use to predict the next one
# Loop over the text: length `chars_window` per time with step equal to `step`
for i in range(0, len(sheldon_quotes) - chars_window, step):
sentences.append(sheldon_quotes[i:i + chars_window])
next_chars.append(sheldon_quotes[i + chars_window])
# Print 10 pairs
print_examples(sentences, next_chars, 10)
output:
Sentence Next char
You're afr a
u're afrai d
re afraid o
afraid of
fraid of i n
aid of ins e
d of insec t
of insects
insects a n
- 划分句子
这部也不太清晰
# Loop through the sentences and get indexes
new_text_split = []
for sentence in new_text:
sent_split = []
for wd in sentence.split(' '):
index = word_to_index.get(wd, 0)
sent_split.append(index)
new_text_split.append(sent_split)
# Print the first sentence's indexes
print(new_text_split[0])
# Print the sentence converted using the dictionary
print(' '.join([index_to_word[index] for index in new_text_split[0]]))
['A man either lives life as it happens to him meets it head-on and licks it or he turns his back on it and starts to wither away', 'To the brave crew and passengers of the Kobayshi Maru sucks to be you', 'Beware of more powerful weapons They often inflict as much damage to your soul as they do to you enemies', 'They are merely scars not mortal wounds and you must use them to propel you forward', 'You cannot explain away a wantonly immoral act because you think that it is connected to some higher purpose']
output:
[276, 15070, 10160, 14750, 14590, 5715, 13813, 12418, 22564, 12797, 15443, 13813, 0, 5368, 14578, 13813, 16947, 12507, 23031, 12859, 5975, 16795, 13813, 5368, 21189, 22564, 0, 5910]
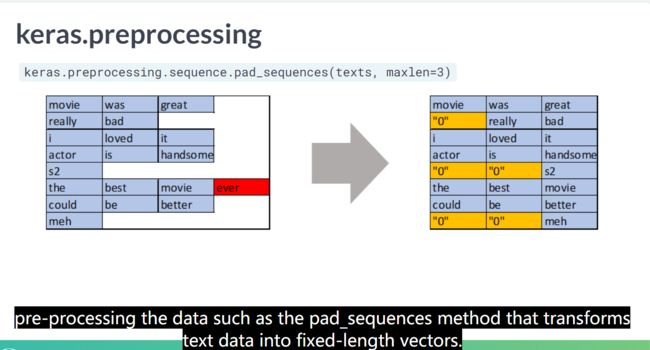
A man either lives life as it happens to him meets it pad_sequences()
为了实现的简便,keras只能接受长度相同的序列输入。因此如果目前序列长度参差不齐,这时需要使用pad_sequences()。该函数是将序列转化为经过填充以后的一个长度相同的新序列新序列。
LSTM
# Define the input layer
main_input = Input(shape=(None, 10), name="input")
# One LSTM layer (input shape is already defined)
lstm_layer = LSTM(128, name="LSTM")(main_input)
# Add a dense layer with one unit
main_output = Dense(1, activation="sigmoid", name="output")(lstm_layer)
# Instantiate the class at the end
model =Model(inputs=main_input, outputs=main_output, name="modelclass_model")
# Same amount of parameters to train as before (71,297)
model.summary()
output:
Model: "modelclass_model"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
input (InputLayer) (None, None, 10) 0
_________________________________________________________________
LSTM (LSTM) (None, 128) 71168
_________________________________________________________________
output (Dense) (None, 1) 129
=================================================================
Total params: 71,297
Trainable params: 71,297
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
Keras preprocessing
tokenizer 分词
# Import relevant classes/functions
from keras.preprocessing.text import Tokenizer
from keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequences
# Build the dictionary of indexes
tokenizer = Tokenizer()
tokenizer.fit_on_texts(texts)
# Change texts into sequence of indexes
texts_numeric = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(texts)
print("Number of words in the sample texts: ({0}, {1})".format(len(texts_numeric[0]), len(texts_numeric[1])))
# Pad the sequences 填充句子等长
texts_pad = pad_sequences(texts_numeric, 60)
print("Now the texts have fixed length: 60. Let's see the first one: \n{0}".format(texts_pad[0]))
output:
Number of words in the sample texts: (54, 78)
Now the texts have fixed length: 60. Let's see the first one:
[ 0 0 0 0 0 0 24 4 1 25 13 26 5 1 14 3 27 6 28 2 7 29 30 13
15 2 8 16 17 5 18 6 4 9 31 2 8 32 4 9 15 33 9 34 35 14 36 37
2 38 39 40 2 8 16 41 42 5 18 6]
simpleRNN
一个简单的rnn模型
# Build model
model = Sequential()
model.add(SimpleRNN(units=128, input_shape=(None, 1)))
model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy',
optimizer='adam',
metrics=['accuracy'])
# Load pre-trained weights
model.load_weights('model_weights.h5')
# Method '.evaluate()' shows the loss and accuracy
loss, acc = model.evaluate(x_test, y_test, verbose=0)
print("Loss: {0} \nAccuracy: {1}".format(loss, acc))
output:
Loss: 0.6991182217597961
Accuracy: 0.495
Vanishing and exploding gradients
梯度消失和梯度爆炸问题
SGD梯度下降算法
# Create a Keras model with one hidden Dense layer
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(25, input_dim=20, activation='relu', kernel_initializer=he_uniform(seed=42)))
model.add(Dense(1, activation='linear'))
# Compile and fit the model
model.compile(loss='mean_squared_error', optimizer=SGD(lr=0.01, momentum=0.9, clipvalue=3.0))
history = model.fit(X_train, y_train, validation_data=(X_test, y_test), epochs=100, verbose=0)
# See Mean Square Error for train and test data
train_mse = model.evaluate(X_train, y_train, verbose=0)
test_mse = model.evaluate(X_test, y_test, verbose=0)
# Print the values of MSE
print('Train: %.3f, Test: %.3f' % (train_mse, test_mse))
# Create the model
model = Sequential()
model.add(SimpleRNN(units=600, input_shape=(None, 1)))
model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer='sgd', metrics=['accuracy'])
# Load pre-trained weights
model.load_weights('model_weights.h5')
# Plot the accuracy x epoch graph
plt.plot(history.history['acc'])
plt.plot(history.history['val_acc'])
plt.legend(['train', 'val'], loc='upper left')
plt.show()
GRU and LSTM cells
细胞单元控制
stacking
# Import the LSTM layer
from keras.layers.recurrent import LSTM
# Build model
model = Sequential()
model.add(LSTM(units=128, input_shape=(None, 1), return_sequences=True))
model.add(LSTM(units=128, return_sequences=True))
model.add(LSTM(units=128, return_sequences=False))
model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])
# Load pre-trained weights
model.load_weights('lstm_stack_model_weights.h5')
print("Loss: %0.04f\nAccuracy: %0.04f" % tuple(model.evaluate(X_test, y_test, verbose=0)))
output:
Loss: 0.6789
Accuracy: 0.5590
The Embedding layer
嵌入层可以实现降维,防止维度爆炸
# Import the embedding layer
from keras.layers import Embedding
# Create a model with embeddings
model = Sequential(name="emb_model")
model.add(Embedding(input_dim=vocabulary_size + 1, output_dim=wordvec_dim, input_length=sentence_len, trainable=True))
model.add(GRU(128))
model.add(Dense(1))
model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])
# Print the summaries of the one-hot model
model_onehot.summary()
# Print the summaries of the model with embeddings
model.summary()
output:
Model: "model_onehot"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
gru_1 (GRU) (None, 128) 49920
_________________________________________________________________
dense_1 (Dense) (None, 1) 129
=================================================================
Total params: 50,049
Trainable params: 50,049
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
Model: "emb_model"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
embedding_1 (Embedding) (None, 200, 300) 24000600
_________________________________________________________________
gru_2 (GRU) (None, 128) 164736
_________________________________________________________________
dense_2 (Dense) (None, 1) 129
=================================================================
Total params: 24,165,465
Trainable params: 24,165,465
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
glove
预训练模型
# Load the glove pre-trained vectors
glove_matrix = load_glove('glove_200d.zip')
# Create a model with embeddings
model = Sequential(name="emb_model")
model.add(Embedding(input_dim=vocabulary_size + 1, output_dim=wordvec_dim,
embeddings_initializer=Constant(glove_matrix),
input_length=sentence_len, trainable=False))
model.add(GRU(128))
model.add(Dense(1))
model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])
# Print the summaries of the model with embeddings
model.summary()
预训练模型
预训练的意思就是提前已经给你一些初始化的参数,这个参数不是随机的,而是通过其他类似数据集上面学得的,然后再用你的数据集进行学习,得到适合你数据集的参数,随机初始化的话,的确不容易得到结果,但是这个结果是因为速度太慢,而不是最终的结果不一样.预训练模型就是一些人用某个较大的数据集训练好的模型(这种模型往往比较大,训练需要大量的内存资源),你可以用这些预训练模型用到类似的数据集上进行模型微调。就比如自然语言处理中的bert。
提升模型效果的方式
防止过拟合dropout
一个简单的模型
output:
Loss: 1.0716214485168456
Accuracy: 0.822
Data pre-processing
数据预处理
分类变量进行编码
# Get the numerical ids of column label
numerical_ids = df.label.cat.codes
# Print initial shape
print(numerical_ids.shape)
# One-hot encode the indexes,挺粗暴的,直接编了
Y = to_categorical(numerical_ids)
# Check the new shape of the variable
print(Y.shape)
# Print the first 5 rows
print(Y[:5])
output:
(1672,)
(1672, 3)
[[1. 0. 0.]
[0. 1. 0.]
[0. 0. 1.]
[0. 1. 0.]
[0. 0. 1.]]
tokenizer里面的函数可以直接用
# Create and fit tokenizer
tokenizer = Tokenizer()
tokenizer.fit_on_texts(news_dataset.data)
# Prepare the data
prep_data = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(news_dataset.data)
prep_data = pad_sequences(prep_data, maxlen=200)
# Prepare the labels
prep_labels = to_categorical(news_dataset.target)
# Print the shapes
print(prep_data.shape)
print(prep_labels.shape)
output:
(5000, 200)
(5000, 20)
Transfer learning for language models
语言模型的迁移学习
Word2Vec
# Word2Vec model
w2v_model = Word2Vec.load("bigbang_word2vec.model")
# Selected words to check similarities
words_of_interest = ['bazinga', 'penny', 'universe', 'spock', 'brain']
# Compute top 5 similar words for each of the words of interest
top5_similar_words = []
for word in words_of_interest:
top5_similar_words.append(
{word: [item[0] for item in w2v_model.wv.most_similar([word], topn=5)]}
)
# Print the similar words
print(top5_similar_words)
# Instantiate the model
model = Sequential()
# Add two LSTM layers
model.add(LSTM(64, input_shape=input_shape, dropout=0.15, recurrent_dropout=0.15, return_sequences=True))
model.add(LSTM(64, dropout=0.15, recurrent_dropout=0.15, return_sequences=False))
# Add the output layer
model.add(Dense(n_vocab, activation='softmax'))
# Compile and load weights
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='adam')
model.load_weights('model_weights.h5')
output:
Model: "sequential_1"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
lstm_1 (LSTM) (None, 20, 64) 34304
_________________________________________________________________
lstm_2 (LSTM) (None, 64) 33024
_________________________________________________________________
dense_1 (Dense) (None, 69) 4485
=================================================================
Total params: 71,813
Trainable params: 71,813
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
Neural Machine Translation
这里总体来说学的有点糊,感觉可以把武神的栗子复现一般先了解大致流程。