Python 模块学习 logging(2)
一、模块级函数
除了上面描述的类,有许多模块级功能。
1、logging.getLogger([name])
见上小节
2、logging.debug(msg[,*args[,*kwargs]])
在 root logger 上记录消息以level DEBUG;
msg:表示消息格式字符串。
args:作用于msg,是使用字符串格式操作符(注意,这意味着您可以使用关键字的格式字符串,连同一个字典参数。)
kwargs:两个关键字参数,exc_info.
exc_info which, if it does not evaluate as false, causes exception information to be added to the logging message. If an exception tuple (in the format returned by sys.exc_info()) is provided, it is used; otherwise, sys.exc_info() is called to get the exception information.
另一个参数是extra,which can be used to pass a dictionary which is used to populate(填充) the __dict__ of the LogRecord created for the logging event with user-defined attributes.
import logging FORMAT = '%(asctime)s:[%(IP)s--%(user)-8s]%(message)s' logging.basicConfig(format=FORMAT) d = {'IP':'192.168.0.1','user':'BeginMan'} logging.warning('msg:%s','OK',extra=d) #2013-09-23 15:58:31,619:[192.168.0.1--BeginMan]msg:OK
这里关键字参数传递不能与logging系统的关键字参数冲突。如'message'
3、下同
logging.info(msg[, *args[, **kwargs]])
- logging. warning ( msg [, *args [, **kwargs ] ] )
- logging. error ( msg [, *args [, **kwargs ] ] )
- logging. critical ( msg [, *args [, **kwargs ] ] )
4、logging.exception(msg[, *args])
用法同上上
try: raise Exception,u'错误异常' except: logging.exception('msg:%s','Error') # ERROR:root:msg:Error # Traceback (most recent call last): # File "E:\project\py\src\log4.py", line 15, in <module> # raise Exception,u'错误异常' # Exception: 错误异常
5、logging.log(level, msg[, *args[, **kwargs]])
参数用法同logging.debug()
import logging FORMAT = '%(asctime)s:[%(IP)s--%(user)-8s]%(message)s' logging.basicConfig(format=FORMAT) d = {'IP':'192.168.0.1','user':'BeginMan'} logging.log(logging.DEBUG, 'Great:%s','Python',extra=d)
6、logging.disable(level)
其作用是禁用所有日志当其级别在给定级及以下,当出现需要暂时截流日志输出下来整个应用程序,这个函数可以是有用的。
logging.disable(logging.WARNING)#提供一个覆盖所有优先于日志级别的级别 logging.warn('msg') #没有输出 logging.critical('msg') #CRITICAL:msg
撤销的话,就使用logging.disable(levle)或logging.disable(logging.NOSET)
7、logging.addLevelName(lel,levelname)
增加自定义的logging level,并起名。
logging.addLevelName(88,'myLevelName') logging.log(88, '自定义设置级别') #myLevelName:root:自定义设置级别
级别是整数,系统设置如下:
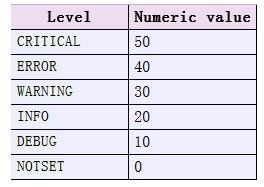
8、logging.getLevelName(lvl)
返回的文本表示的日志级别
logging.addLevelName(88,'myLevelName') logging.log(88, '自定义设置级别') #myLevelName:root:自定义设置级别 print logging.getLevelName(88) #myLevelName print logging.getLevelName(logging.INFO) #INFO
9、logging.basicConfig()
Does basic configuration for the logging system by creating a StreamHandler with a default Formatter and adding it to the root logger. The functions debug(), info(), warning(), error() and critical() will call basicConfig() automatically if no handlers are defined for the root logger.
This function does nothing if the root logger already has handlers configured for it.
见上节详解。
二、logging.handlers
接下来学习logging的控制器,有三类:StreamHandler、FileHandler、NullHandler。
StreamHandler类,在logging包中,发送日志输出流 如sys.stdout
The FileHandler class,发送日志输出到磁盘文件,它继承了StreamHandler输出功能。
class logging.FileHandler(filename, mode='a', encoding=None, delay=False)
返回一个FileHandler类的实例,如果存在延时(delay=True),那么,文件打开推迟到第一次调用emit()。
它有如下方法:close():关闭一个文件;emit(record):输出文件的记录。
import os import logging import datetime '''FileHandler''' '''FileHandler类,存在于logging包中,发送日志输出到磁盘文件中,它继承了StreamHandler输出功能。 class logging.FileHandler(filename, mode='a', encoding=None, delay=False) 返回一个FileHandler类的实例,如果存在延时(delay=True),那么,文件打开推迟到第一次调用emit()。 它有如下方法:close():关闭一个文件;emit(record):输出文件的记录。 ''' logger = logging.getLogger() #生成一个日志对象 hdlr = logging.FileHandler(os.path.join(os.getcwd(),'log.txt'),'w') #返回一个FileHandler对象 formatter = logging.Formatter('%(asctime)s:%(name)s-->%(levelname)s %(message)s') hdlr.setFormatter(formatter) #将格式器设置到处理器上 logger.addHandler(hdlr) #将处理器加到日志对象上 logger.setLevel(logging.NOTSET) #设为NOTSET(值为0),输出所有 try: lis = [] lis+'s' print lis except Exception,e: logger.error('出现异常:%s',e) #打开log.txt文件查看错误: # 2013-09-23 17:33:16,418:root-->ERROR 出现异常:can only concatenate list (not "str") to list
三、使用fileConfig来使用logger