大话数据结构(十)图Graph的相关程序实现
1.图的定义
首先声明一下相关的函数声明`
class Graph
{
public:
CreateGraph(*G, V, VR); //按照顶点集合V和边VR的定义构造图G
DestrotyGraph(*G); //删除一个图
LocateVex(G, u); //若图G中存在顶点u,则返回图中的位置
GetVex(G, v); //返回图G中顶点v的值
PutVex(G, v, value); //将图G中顶点v赋值value
FirstAdjVex(G, *v); //返回顶点v的一个邻接节点,若顶点在G中无邻接节点返回空
NextAdjVex(G, v, *w); //返回顶点v相对于顶点w的下一个邻接节点,若w是v的最后一个邻接节点则返回空
InsertArc(*G, v, w); //在图中增加弧,若G是无向图,还需要增添对称弧
DeleteArc(*G, v, w); //在图G中删除弧,若G是无向图,则还需要删除对称弧
InsertVex(*G, v); //在图G中增添新顶点v
DeleteVex(*G, v); //删除图G中顶点v以及相关的弧
};
2. 图的五种存储结构
(1).邻接矩阵
图的邻接矩阵存储方式是用两个数组来表示图。一个一维数组存储图中顶点信息,一个二维数组(称为邻接矩阵)存储图中的边或弧的信息。
/*构建图结构代码*/
void Graphic::CreateGraph(Graph *G) //按照顶点集合V和边VR的定义构造图G
{
int i, j, k,w;
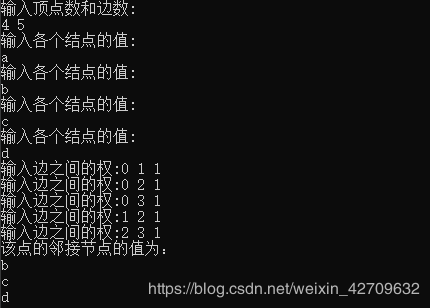
cout << "输入顶点数和边数:" << endl;
cin >> G->numVertexes;
cin>>G->numEdges;
for (i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++)
{
cout << "输入各个结点的值:"<<endl;
cin >> G->vexs[i];
}
for (i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < G->numVertexes; j++)
{
G->arc[i][j] = INFINITY_l; //邻接矩阵初始化
}
}
for (k = 0; k < G->numEdges; k++)
{
cout << "输入边之间的权:";
cin >> i >> j >> w;
G->arc[i][j] = w;
G->arc[j][i] = G->arc[i][j];
}
}
/*若图G中存在顶点u,则返回图中的位置*/
void Graphic::LocateVex(Graph G, VertexType u)const
{
int MAXSIZE = 1;
int k = 0;
int *i = new int[MAXSIZE];
if (!(&G) || !u)
throw new exception("输入错误!");
for(int j=0;j<G.numVertexes;j++)
{
if (u == G.vexs[j])
{
i[k] = j;
k++;
MAXSIZE++;
}
}
for (int j = 0; j < k; j++)
cout << i[j] << endl;
}
/*返回图G中下标v的值*/
void Graphic::GetVex(Graph G, int v)const
{
if (!(&G) || !v)
throw new exception("输入错误!");
cout<<"输出指定下标存储的字符值:"
cout << G.vexs[v] << endl;
}
/*将图G中顶点下标v赋值value*/
void Graphic::PutVex(Graph G, int v, char value)const
{
if (!(&G) || !v || !value)
throw new exception("输入错误!");
G.vexs[v] = value;
return;
}
/*返回顶点下标为v的邻接节点,若顶点在G中无邻接节点返回空*/
void Graphic::FirstAdjVex(Graph G, const int v)const
{
int j = 0;
VertexType *VTS = new VertexType[100]; //定义一个邻接节点数组
for (int i = 0; i < G.numVertexes; i++)
{
if (G.arc[i][v] != INFINITY_l)
{
VTS[j] = G.vexs[i]; //将邻接节点存入数组中
j++;
}
}
cout << "该点的邻接节点的值为:\n";
for (int i = 0; i < j; i++)
{
cout << VTS[i] << endl;
}
}
/*返回顶点v相对于顶点w之后的邻接节点,若w是v的最后一个邻接节点则返回空*/
void Graphic::NextAdjVex(Graph G,const int &v,const char &w)
{
int j = 0;
VertexType *VTS = new VertexType[100]; //定义一个邻接节点数组
for (int i = 0; i < G.numVertexes; i++)
{
if (G.vexs[i] == w)
int k = i;
}
for (int i = 0; i < G.numVertexes; i++)
{
if (G.arc[i][v] != INFINITY_l)
{
VTS[j] = G.vexs[i]; //将邻接节点存入数组中
j++;
}
}
cout << "该点的邻接节点的值为:\n";
for (int i = 0; i < j; i++)
{
if(VTS[i] !=w && i>k)
{
cout << VTS[i] << endl;
}
}
}
/*在图中增加弧,若G是无向图,还需要增添对称弧*/
void Graphic::InsertArc(Graph *G, const &VertexType v,const &VertexType w,const int &Edge)const
{
int v_i, w_i;
for (int i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++)
{
if (G->vexs[i] == v)
int v_i = i; //存储v的下标
if (G->vexs[i] == w)
int w_i = i; //存储v的下标
}
G->arc[v_i][w_i] = Edge;
}
/*在图G中删除弧,若G是无向图,则还需要删除对称弧*/
void Graphic::DeleteArc(Graph *G, const VertexType &v, const VertexType &w)
{
if (v == nullptr && w == nullptr)
{
G->arc[v_i][w_i] = INFINITY_l;
G->arc[w_i][v_i] = INFINITY_l;
}
}
/*在图G中增添新顶点v*/
void Graphic::InsertVex(Graph *G, const VertexType &v)
{
G->numVertexes += 1;
G->vexs[numVertexes] = v;
}
/*删除图G中顶点v以及相关的弧*/
void Graphic::DeleteVex(Graph *G, const VertexType &v)
{
for (int i = 0; i < numVertexes; i++)
{
if (G->vexs[i] == v)
int v_i = i; //返回v的下标
}
/*删弧*/
for (int i = 0; i < numVertexes; i++)
{
G->arc[i][v_i] = INFINITY_l;
G->arc[v_i][i] = INFINITY_l; //将邻接矩阵相关的元素设为极限值,相当于删掉相关的弧
}
/*删点*/
for (int i = v_i; i < numVertexes; i++)
G->vexs[i] = G->vex[i+1]; //顶点表中v之后的元素下标前移一位
numVertexes -= 1;
}
/*删除一个图*/
void Graphic::DestrotyGraph(Graph *G)
{
delete G;
}
(2).邻接表
邻接矩阵适合结点饱和度较高的图,但是当边相对于顶点较少的时候,这种结构会造成存储空间的大量浪费,用链式的实现存储图结点。
所以把这种数组和链表相结合的存储方式称为邻接表。
/*邻接表结点定义*/
typedef char VertexType;
typedef int EdgeType;
typedef struct
{
int adjvex; //下标
EdgeType weight; //权值
struct EdgeNode *next; //递归结构
}EdgeNode;//边表结点
typedef struct VertexNode
{
VertexType data; //存储顶点信息
EdgeNode *firstedge; //头指针
}AdjList; //顶点表结点
typedef struct
{
AdjList adjList[MAXVEX];
int numVertexes, numEdges; //当前顶点数和边数
}GraphAdjList;
/*建立图的邻接表结构*/
void CreateALGraph(GraphAdjList *G)
{
int i, j, k;
EdgeNode *e;
cout << "输入顶点数和边数:\n";
cin >> G->numVertexes >> G->numEdges;
for (i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++)
{
cin >> G->adjList[i].data;
G->adjList[i].firstedge = nullptr;
for (k = 0; k < G->numEdges; k++)
{
cout << "输入边(vi,vj)上的顶点序号:\n";
cin >> i >> j;
EdgeNode *e = new EdgeNode;
e->adjvex = j;
e->next = G->adjList[i].firstedge;
G->adjList[i].firstedge = e;
EdgeNode *e = new EdgeNode;
e->adjvex = i;
e->next = G->adjList[j].firstedge;
G->adjList[j].firstedge = e;
}
}
}
(3).十字链表和临接多重表
这两种表是为了优化图的存储结构,将邻接表和逆邻接表结合起来。具体的实现方法不多加赘述。
(4) 边集数组
边集数组是由两个一维数组构成。一个是存储顶点的信息;另一个是存储边的信息,这个边数组每个数据元素由一条边的起点下标begin、终点下标end和权weight组成。