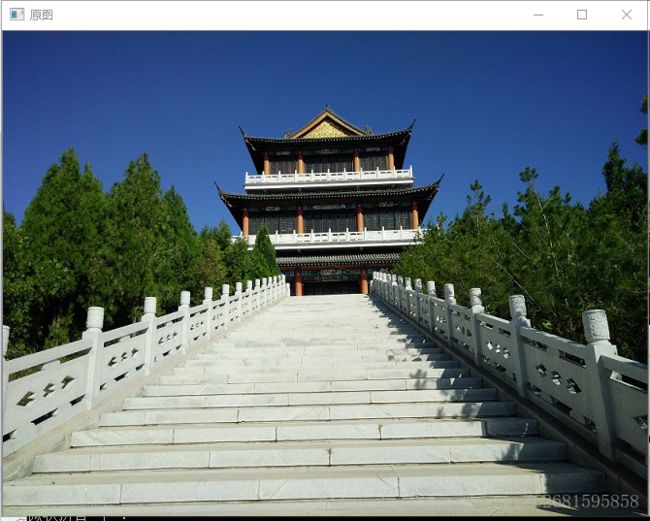
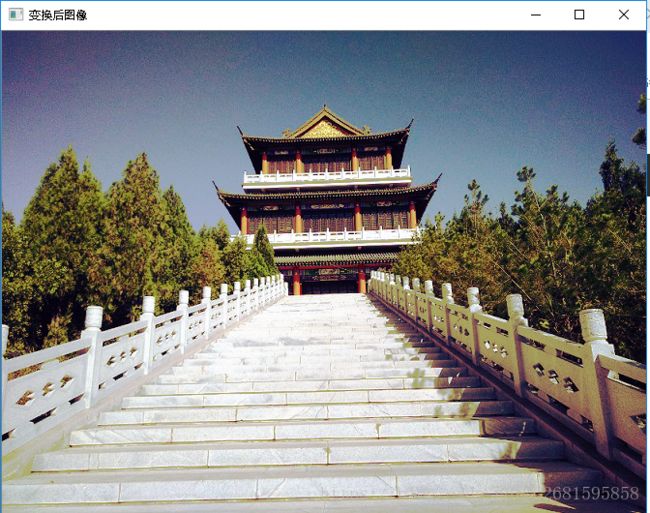
【数字图像处理】实验二 直方图均衡(vs2017+opencv)
文章目录
- 一、实验原理
- 二、设计思路
- 三、实验过程
- 四、结果分析
- 五、实验心得
代码包: 直方图均衡处理
一、实验原理
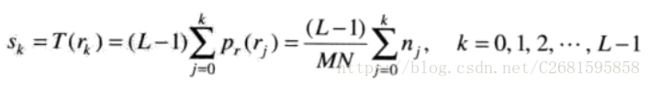
上述表达式, r k r_k rk表示输入的灰度级k, s k s_k sk表示对应输出的灰度级k, n j n_j nj表示输入图像中灰度级为K的像素个数。M和N分别是输入图像的长宽。L是灰度级。
二、设计思路
- 上面的式子是对灰度图像处理的方法。但是我们一般处理的既有灰度图像也有彩色图像。所以如果是彩色图像我们要分别统计彩色图像R,G,B三者在各个灰度级上的像素数。然后进行处理。
- 设计一个类如下:
#include 三、实验过程
- 下面需要注意的是数据类型的转换,如果只将const_num定义为double类型,而不管后面运算数的类型。编译器会直接拿int类型的数据去计算,得到的结果当然不一定是整数,但是编译器会直接把算得的值当作int来处理。就算你声明的const_num是double类型,也不管用。**所以在进行除运算之前要先将int类型强制转换为double类型。**就这句
double const_num = (double)(LEAVE - 1) /(double) (this->image.cols*this->image.rows); - 还有一点是计算上面的 s k s_k sk的时候,结果是小数double类型,但我们最终需要的是int类型,所以要进行类型转换。但是直接强制类型转换会截取整数部分,不管小数部分的大小。而为了转换准确一点,我们最好采用四舍五入,就是给每个计算结果加上0.5,这样小数部分大于等于0.5的数,其整数就会被加一,然后进行强制类型转换,达到四舍五入的目的。
#include "Equalization.h"
//初始化各个私有成员。
Equalization::Equalization()
{
memset(this->statistic_R, 0, LEAVE*sizeof(int));
memset(this->statistic_G, 0, LEAVE * sizeof(int));
memset(this->statistic_B, 0, LEAVE * sizeof(int));
}
//设置要处理的图片的路径
void Equalization::setImage(Mat &image_in)
{
this->image = image_in;
}
//分别对图片的RGB值进行直方图统计
void Equalization::statistic()
{
for (int counter1 = 0; counter1 < this->image.rows; counter1++)
{
for (int counter2 = 0; counter2 < this->image.cols; counter2++)
{
//数组下标代表灰度值,里面存储的数是该灰度值对应的像素数
if (this->image.channels() == 1)//如果是灰度图像
{
this->statistic_R[this->image.at<uchar>(counter1, counter2)]++;
}
else//如果是彩色图像
{
this->statistic_R[this->image.at<Vec3b>(counter1, counter2)[0]]++;
this->statistic_G[this->image.at<Vec3b>(counter1, counter2)[1]]++;
this->statistic_B[this->image.at<Vec3b>(counter1, counter2)[2]]++;
}
}
}
}
//对原图进行均衡处理
Mat Equalization::queProcess()
{
/*计算原来的各个灰度值经过均衡以后应该变成多少
temp数组下标代表原先图像的灰度值
temp中存储的数是变换后各个灰度值对应的灰度值
*/
int temp_R[LEAVE], temp_G[LEAVE], temp_B[LEAVE];
memset(temp_R, 0, LEAVE * sizeof(int));
memset(temp_G, 0, LEAVE * sizeof(int));
memset(temp_B, 0, LEAVE * sizeof(int));
int sumR = 0, sumB = 0, sumG = 0;
double const_num = (double)(LEAVE - 1) /(double) (this->image.cols*this->image.rows);
for (int counter0 = 0; counter0 < LEAVE; counter0++)
{
if (this->image.channels() == 1)
{
sumR += this->statistic_R[counter0];
temp_R[counter0] = (int)(const_num * sumR + 0.5);
}
else
{
sumR += this->statistic_R[counter0];
sumG += this->statistic_G[counter0];
sumB += this->statistic_B[counter0];
//进行四舍五入
temp_R[counter0] = (int)(const_num * sumR + 0.5);
temp_G[counter0] = (int)(const_num * sumG + 0.5);
temp_B[counter0] = (int)(const_num * sumB + 0.5);
}
}
Mat imEqu;
if (image.channels() == 1)
{
Mat imEqu1(this->image.rows, this->image.cols, CV_8UC1);
imEqu1.copyTo(imEqu);
}
else
{
Mat imEqu1(this->image.rows, this->image.cols, CV_8UC3);
imEqu1.copyTo(imEqu);
}
//逐个像素进行处理
for (int counter1 = 0; counter1 < this->image.rows; counter1++)
{
for (int counter2 = 0; counter2 < this->image.cols; counter2++)
{
if (this->image.channels() == 1)
{
imEqu.at<uchar>(counter1, counter2) = temp_R[image.at<uchar>(counter1, counter2)];
}
else
{
imEqu.at<Vec3b>(counter1, counter2)[0] = temp_R[image.at<Vec3b>(counter1, counter2)[0]];
imEqu.at<Vec3b>(counter1, counter2)[1] = temp_G[image.at<Vec3b>(counter1, counter2)[1]];
imEqu.at<Vec3b>(counter1, counter2)[2] = temp_B[image.at<Vec3b>(counter1, counter2)[2]];
}
}
}
return imEqu;
}
四、结果分析
- 这里顺便贴出main函数:
#include "Equalization.h"
#include 五、实验心得
- 基本都写在前面了
- 欢迎大家在评论中探讨、斧正。