Numpy基本用法
文章目录
- 一、Numpy基本用法
- 二、Numpy创建数组
- 1.使用np.array()由python list创建
- 2.使用np的routines函数创建
- 2.1 np.ones()
- 2.2 zeros()
- 2.3 np.full()
- 2.4 np.eye()
- 2.5 np.linspace()
- 2.6 arange()
- 2.7 randint()
- 2.8 randn() 正太分布
- 2.9 normal() 正太分布
- 2.10 random_sample() 生成0到1的随机数
- 三、Numpy查看数组属性
- 1.数组元素个数
- 2.数组形状
- 3.数组维度
- 4.数组元素类型
- 四、数组的基本操作
- 1.索引
- 2.切片
- 3.变形
- 4.级联
- np.hstack与np.vstack
- 5.切分
- 6.副本
- 五、Numpy计算
- 条件运算
- 统计运算
- 数组运算
- 矩阵运算np.dot()
- 矩阵的广播
- 六、排序
- 1.快速排序
- 2.部分排序
- numpy案例
一、Numpy基本用法
NumPy是Python语言的一个扩充程序库。支持高级大量的维度数组与矩阵运算,此外也针对数组运算提供大量的数学函数库。Numpy内部解除了Python的PIL(全局解释器锁),运算效率极好,是大量机器学习框架的基础库!
#导入numpy库,并查看numpy库版本
In [1]: import numpy as np
In [2]: np.__version__
Out[2]: '1.14.3'
#利用numpy+matplotlib处理图片
In [7]: import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
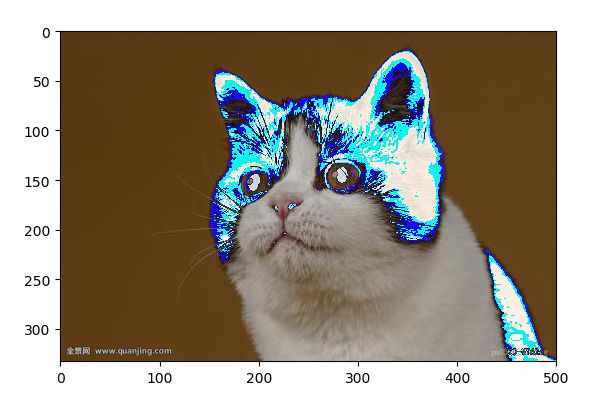
In [8]: cat = plt.imread('D:\myProject\Python\Jupyter\image\cat.jpg')
In [9]: type(cat)
Out[9]: numpy.ndarray
In [10]: cat1 = cat -50
#图片是一个三维数组,长、宽、颜色
In [11]: cat.shape
Out[11]: (333, 500, 3)
In [12]: plt.imshow(cat1)
Out[12]: <matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x222924b0320>
In [13]: plt.show()
二、Numpy创建数组
1.使用np.array()由python list创建
In [14]: import numpy as np
#创建列表
In [15]: a = [1,2,3,4,5]
#将列表转换为数组
In [16]: b = np.array(a)
In [17]: b
Out[17]: array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
2.使用np的routines函数创建
2.1 np.ones()
# 1、np.ones(shape, dtype=None, order='C')
In [18]: np.ones(shape = (10,8),dtype= int)
Out[18]:
array([[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]])
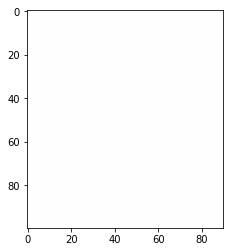
In [19]: ones = np.ones(shape=(100,90,4),dtype=int)
In [20]: plt.imshow(ones)
...: plt.show()
2.2 zeros()
# 2、zeros(shape, dtype=float, order='C')
In [21]: np.zeros((4,4))
Out[21]:
array([[0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0.]])
2.3 np.full()
# 3、 np.full(shape, fill_value, dtype=None, order='C')
In [22]: np.full((10,10),fill_value=20)
Out[22]:
array([[20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20],
[20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20],
[20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20],
[20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20],
[20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20],
[20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20],
[20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20],
[20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20],
[20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20],
[20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20, 20]])
2.4 np.eye()
# 4、np.eye(N, M=None, k=0, dtype=, order='C')
#对角线位1,其他位置位0
In [23]: np.eye(10)
Out[23]:
array([[1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1.]])
2.5 np.linspace()
# 5、np.linspace(start, stop, num=50, endpoint=True, retstep=False, dtype=None)
#lin = linear 线性
In [24]: np.linspace(1,100,20)
Out[24]:
array([ 1. , 6.21052632, 11.42105263, 16.63157895,
21.84210526, 27.05263158, 32.26315789, 37.47368421,
42.68421053, 47.89473684, 53.10526316, 58.31578947,
63.52631579, 68.73684211, 73.94736842, 79.15789474,
84.36842105, 89.57894737, 94.78947368, 100. ])
2.6 arange()
# 6、arange([start,] stop[, step,], dtype=None)
In [25]: np.arange(0,10,2)
Out[25]: array([0, 2, 4, 6, 8])
2.7 randint()
# 7、randint(low, high=None, size=None, dtype='l')
In [26]: np.random.randint(0,10,size = 10)
Out[26]: array([0, 9, 8, 9, 5, 5, 2, 6, 8, 7])
2.8 randn() 正太分布
# 8、randn(d0, d1, ..., dn) 正太分布
In [27]: np.random.randn(4,5)
Out[27]:
array([[ 1.05035386, 0.77231903, -0.33446991, -0.54562315, -0.84341866],
[ 0.6616944 , 0.89325969, -0.89042489, 1.61227272, -0.05136764],
[-0.5346068 , -2.39236557, -0.54563468, -1.07850467, 0.56603284],
[-0.33361988, 1.11445864, -0.11636709, 0.57361067, 0.80099792]])
2.9 normal() 正太分布
# 9、normal(loc=0.0, scale=1.0, size=None) 正太分布
In [28]: np.random.normal(loc=170,scale=1,size=20)
Out[28]:
array([168.56872023, 168.30641964, 169.98891802, 168.6781631 ,
169.63611345, 167.81502056, 169.69833366, 169.05166886,
170.96688262, 168.30677654, 170.15970816, 169.59783795,
170.77979873, 170.20138558, 169.75464312, 172.16309013,
169.37900208, 171.23951841, 169.7903996 , 168.62081606])
2.10 random_sample() 生成0到1的随机数
# 10、random_sample(size=None) 生成0到1的随机数
#np.random.random(size=20)
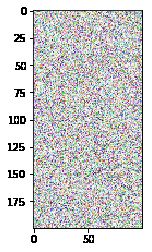
In [29]: r = np.random.random(size=(200,100,4)) #生成一张图片
In [30]: plt.imshow(r)
Out[30]: <matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x22293b60dd8>
In [31]: plt.show()
三、Numpy查看数组属性
1.数组元素个数
In [33]: b
Out[33]: array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
In [34]: b.size
Out[34]: 5
2.数组形状
In [35]: b.shape
Out[35]: (5,)
3.数组维度
In [36]: b.ndim
Out[36]: 1
4.数组元素类型
In [37]: b.dtype
Out[37]: dtype('int32')
四、数组的基本操作
1.索引
In [39]: array1 = np.random.randint(0,100,(4,4))
In [40]: array1
Out[40]:
array([[85, 18, 96, 92],
[42, 49, 76, 85],
[42, 1, 80, 99],
[33, 91, 74, 95]])
In [41]: array1[0,1]
Out[41]: 18
2.切片
#切片时,左闭右开
In [42]: array1[1:3,2:4]
Out[42]:
array([[76, 85],
[80, 99]])
In [43]: array2 = np.arange(0,10)
In [44]: array2
Out[44]: array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
#将数组反转
In [45]: array2[::-1]
Out[45]: array([9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0])
#通过两个::进行切片
In [46]: print(array2[::2])
[0 2 4 6 8]
In [47]: print(array2[::-2])
[9 7 5 3 1]
3.变形
- 使用reshape函数,注意参数用tuple
In [48]: import numpy as np
In [49]: n = np.arange(0,10)
In [50]: n
Out[50]: array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
In [51]: n.shape
Out[51]: (10,)
#使用reshape函数进行变形
In [52]: n.reshape((5,2))
Out[52]:
array([[0, 1],
[2, 3],
[4, 5],
[6, 7],
[8, 9]])
In [53]: n1 = np.random.randint(0,100,(3,4,5))
In [54]: n1
Out[54]:
array([[[48, 8, 2, 35, 65],
[81, 56, 20, 85, 76],
[94, 65, 62, 59, 78],
[48, 57, 7, 3, 63]],
[[56, 27, 4, 21, 28],
[92, 10, 73, 63, 82],
[88, 28, 10, 76, 99],
[49, 6, 39, 21, 50]],
[[84, 87, 65, 15, 52],
[94, 44, 40, 2, 94],
[ 7, 90, 78, 18, 94],
[94, 64, 83, 54, 6]]])
In [55]: n1.shape
Out[55]: (3, 4, 5)
In [56]: n1.reshape(3*4*5)
Out[56]:
array([48, 8, 2, 35, 65, 81, 56, 20, 85, 76, 94, 65, 62, 59, 78, 48, 57,
7, 3, 63, 56, 27, 4, 21, 28, 92, 10, 73, 63, 82, 88, 28, 10, 76,
99, 49, 6, 39, 21, 50, 84, 87, 65, 15, 52, 94, 44, 40, 2, 94, 7,
90, 78, 18, 94, 94, 64, 83, 54, 6])
#使用负数直接转换成一维数组
In [57]: n1.reshape(-1)
Out[57]:
array([48, 8, 2, 35, 65, 81, 56, 20, 85, 76, 94, 65, 62, 59, 78, 48, 57,
7, 3, 63, 56, 27, 4, 21, 28, 92, 10, 73, 63, 82, 88, 28, 10, 76,
99, 49, 6, 39, 21, 50, 84, 87, 65, 15, 52, 94, 44, 40, 2, 94, 7,
90, 78, 18, 94, 94, 64, 83, 54, 6])
4.级联
- np.concatenate()级联需要注意的点:
- 1.级联的参数是列表:一定要加中括号或小括号
- 2.维度必须相同
- 3.形状相符
- 4.【重点】级联的方向默认是shape这个tuple的第一个值所代表的维度方向
- 5.可通过axis参数改变级联的方向
In [58]: import numpy as np
In [59]: n1 = np.random.randint(0,10,(5,5))
In [60]: n1
Out[60]:
array([[1, 0, 1, 3, 2],
[0, 1, 9, 2, 9],
[2, 4, 1, 1, 1],
[5, 2, 2, 6, 2],
[8, 8, 8, 7, 2]])
#列级联
In [61]: np.concatenate((n1,n1),axis = 0)
Out[61]:
array([[1, 0, 1, 3, 2],
[0, 1, 9, 2, 9],
[2, 4, 1, 1, 1],
[5, 2, 2, 6, 2],
[8, 8, 8, 7, 2],
[1, 0, 1, 3, 2],
[0, 1, 9, 2, 9],
[2, 4, 1, 1, 1],
[5, 2, 2, 6, 2],
[8, 8, 8, 7, 2]])
#行级联
In [62]: np.concatenate((n1,n1),axis = 1)
Out[62]:
array([[1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2],
[0, 1, 9, 2, 9, 0, 1, 9, 2, 9],
[2, 4, 1, 1, 1, 2, 4, 1, 1, 1],
[5, 2, 2, 6, 2, 5, 2, 2, 6, 2],
[8, 8, 8, 7, 2, 8, 8, 8, 7, 2]])
np.hstack与np.vstack
- 水平级联与垂直级联,处理自己。进行维度的变更
In [63]: n2 = np.random.randint(0,100,size=10)
In [64]: n2
Out[64]: array([73, 65, 92, 23, 32, 47, 78, 83, 97, 37])
#vertical 垂直
In [65]: n3 = np.vstack(n2)
In [66]: print(n3.shape)
(10, 1)
In [67]: n3
Out[67]:
array([[73],
[65],
[92],
[23],
[32],
[47],
[78],
[83],
[97],
[37]])
# 水平
In [68]: n4 = np.array([[1,2,3,4,5],[6,7,8,9]])
In [69]: n4
Out[69]: array([list([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]), list([6, 7, 8, 9])], dtype=object)
In [70]: np.hstack(n4)
Out[70]: array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
In [71]: np.hstack(n3)
Out[71]: array([73, 65, 92, 23, 32, 47, 78, 83, 97, 37])
5.切分
- 与级联类似,常用函数:
- np.split
- np.vsplit
- np.hsplit
In [72]: n5 = np.random.randint(0,150,size=(5,7))
In [73]: n5
Out[73]:
array([[122, 102, 37, 69, 28, 102, 131],
[ 48, 84, 27, 119, 7, 65, 61],
[ 17, 125, 142, 145, 132, 21, 57],
[ 96, 23, 72, 45, 77, 54, 65],
[120, 31, 104, 132, 64, 72, 145]])
In [74]: np.split(n5,(1,3))
Out[74]:
[array([[122, 102, 37, 69, 28, 102, 131]]),
array([[ 48, 84, 27, 119, 7, 65, 61],
[ 17, 125, 142, 145, 132, 21, 57]]),
array([[ 96, 23, 72, 45, 77, 54, 65],
[120, 31, 104, 132, 64, 72, 145]])]
#水平切分,即按行进行切分
In [75]: np.split(n5,(1,3),axis=1)
Out[75]:
[array([[122],
[ 48],
[ 17],
[ 96],
[120]]), array([[102, 37],
[ 84, 27],
[125, 142],
[ 23, 72],
[ 31, 104]]), array([[ 69, 28, 102, 131],
[119, 7, 65, 61],
[145, 132, 21, 57],
[ 45, 77, 54, 65],
[132, 64, 72, 145]])]
In [76]: np.split(n5,(1,3))[1]
Out[76]:
array([[ 48, 84, 27, 119, 7, 65, 61],
[ 17, 125, 142, 145, 132, 21, 57]])
In [81]: cat.shape
Out[81]: (333, 500, 3)
In [77]: import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
In [78]: cat1 = np.split(cat,(100,200))[1]
In [79]: plt.imshow(cat1)
Out[79]: <matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x22293e9b978>
In [80]: plt.show()
#垂直切分
In [82]: np.vsplit(n5,(1,3))
Out[82]:
[array([[122, 102, 37, 69, 28, 102, 131]]),
array([[ 48, 84, 27, 119, 7, 65, 61],
[ 17, 125, 142, 145, 132, 21, 57]]),
array([[ 96, 23, 72, 45, 77, 54, 65],
[120, 31, 104, 132, 64, 72, 145]])]
#水平切分
In [83]: np.hsplit(n5,(1,3))
Out[83]:
[array([[122],
[ 48],
[ 17],
[ 96],
[120]]), array([[102, 37],
[ 84, 27],
[125, 142],
[ 23, 72],
[ 31, 104]]), array([[ 69, 28, 102, 131],
[119, 7, 65, 61],
[145, 132, 21, 57],
[ 45, 77, 54, 65],
[132, 64, 72, 145]])]
6.副本
- 所有赋值运算不会为ndarray的任何元素创建副本,对赋值后的对象的操作也对原来的对象生效。
In [84]: a = [x for x in range(5)]
In [85]: n = np.array(a)
In [86]: n
Out[86]: array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4])
In [87]: n[2] = 512
In [88]: n
Out[88]: array([ 0, 1, 512, 3, 4])
#当数据是ndarray,用=赋值,内存没有改变
In [89]: n2 = n
In [90]: n2[2] = 1024
In [91]: display(n,n2)
array([ 0, 1, 1024, 3, 4])
array([ 0, 1, 1024, 3, 4])
- 使用copy()函数创建副本
In [92]: n3 = n.copy()
In [93]: n3
Out[93]: array([ 0, 1, 1024, 3, 4])
In [94]: n3[2] = 0
In [95]: display(n,n3)
array([ 0, 1, 1024, 3, 4])
array([0, 1, 0, 3, 4])
五、Numpy计算
条件运算
# 条件判断
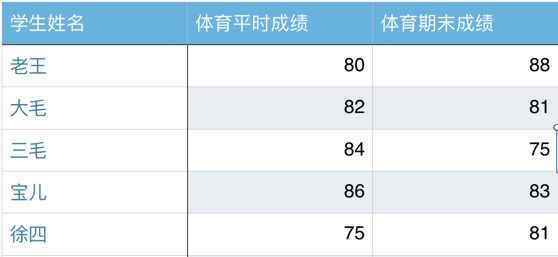
In [97]: stus_score = np.array([[80,88],[82,81],[84,75],[86,83],[75,81]])
In [98]: stus_score > 80
Out[98]:
array([[False, True],
[ True, True],
[ True, False],
[ True, True],
[False, True]])
# 三目运算(如果数值小于80,替换为0,如果大于80,替换为90)
In [100]: stus_score = np.array([[80, 88], [82, 81], [84, 75], [86, 83], [75, 81]])
In [101]: np.where(stus_score < 80, 0, 90)
Out[101]:
array([[90, 90],
[90, 90],
[90, 0],
[90, 90],
[ 0, 90]])
统计运算
# 指定轴最大值amax(参数1: 数组; 参数2: axis=0/1; 0表示列1表示行)
stus_score = np.array([[80, 88], [82, 81], [84, 75], [86, 83], [75, 81]])
# 求每一列的最大值(0表示列)
In [106]: print("每一行的最大值为:")
每一行的最大值为:
In [107]: print("每一列的最大值为:")
...: result = np.amax(stus_score, axis=0)
...: print(result)
...: print("每一行的最大值为:")
...: result = np.amax(stus_score, axis=1)
...: print(result)
...:
...:
每一列的最大值为:
[86 88]
每一行的最大值为:
[88 82 84 86 81]
# 指定轴最大值amax(参数1: 数组; 参数2: axis=0/1/2;分别对应各个维度)
In [108]: import numpy as np
In [109]: n = np.random.randint(0,150,(4,4,4))
In [110]: n
Out[110]:
array([[[ 91, 45, 10, 51],
[102, 88, 129, 100],
[148, 72, 52, 114],
[ 99, 5, 67, 26]],
[[ 23, 102, 125, 116],
[140, 61, 107, 15],
[ 39, 125, 139, 38],
[ 95, 148, 100, 109]],
[[ 92, 68, 140, 75],
[ 49, 113, 68, 70],
[149, 107, 78, 69],
[120, 109, 27, 138]],
[[126, 79, 113, 89],
[ 29, 126, 3, 90],
[ 40, 23, 20, 14],
[ 72, 38, 99, 55]]])
In [111]: n.max(axis=0)
Out[111]:
array([[126, 102, 140, 116],
[140, 126, 129, 100],
[149, 125, 139, 114],
[120, 148, 100, 138]])
In [112]: n.max(axis=1)
Out[112]:
array([[148, 88, 129, 114],
[140, 148, 139, 116],
[149, 113, 140, 138],
[126, 126, 113, 90]])
In [113]: n.max(axis=2)
Out[113]:
array([[ 91, 129, 148, 99],
[125, 140, 139, 148],
[140, 113, 149, 138],
[126, 126, 40, 99]])
# 指定轴最小值amin
In [114]: stus_score = np.array([[80, 88], [82, 81], [84, 75], [86, 83], [75, 81]])
# 求每一行的最小值(0表示列)
In [115]: print("每一列的最小值为:")
...: result = np.amin(stus_score, axis=0)
...: print(result)
...:
...: # 求每一行的最小值(1表示行)
...: print("每一行的最小值为:")
...: result = np.amin(stus_score, axis=1)
...: print(result)
...:
...:
每一列的最小值为:
[75 75]
每一行的最小值为:
[80 81 75 83 75]
# 指定轴平均值mean
In [116]: stus_score = np.array([[80, 88], [82, 81], [84, 75], [86, 83], [75, 81]])
In [117]: # 求每一行的平均值(0表示列)
...: print("每一列的平均值:")
...: result = np.mean(stus_score, axis=0)
...: print(result)
...:
...: # 求每一行的平均值(1表示行)
...: print("每一行的平均值:")
...: result = np.mean(stus_score, axis=1)
...: print(result)
...:
...:
每一列的平均值:
[81.4 81.6]
每一行的平均值:
[84. 81.5 79.5 84.5 78.]
# 方差std
In [118]: stus_score = np.array([[80, 88], [82, 81], [84, 75], [86, 83], [75, 81]])
In [119]: # 求每一行的方差(0表示列)
...: print("每一列的方差:")
...: result = np.std(stus_score, axis=0)
...: print(result)
...:
...: # 求每一行的方差(1表示行)
...: print("每一行的方差:")
...: result = np.std(stus_score, axis=1)
...: print(result)
...:
...:
每一列的方差:
[3.77359245 4.1761226 ]
每一行的方差:
[4. 0.5 4.5 1.5 3. ]
数组运算
# 数组与数的运算
In [120]: import numpy as np
In [121]: stus_score = np.array([[80, 88], [82, 81], [84, 75], [86, 83], [75, 81]])
In [122]: print("加之前:")
...: print(stus_score)
...:
...: #为所有平时成绩都加5分
...: stus_score[:,0]=stus_score[:,0]+5
...: print("加之后:")
...: print(stus_score)
...:
...:
加之前:
[[80 88]
[82 81]
[84 75]
[86 83]
[75 81]]
加之后:
[[85 88]
[87 81]
[89 75]
[91 83]
[80 81]]
# 数组也支持加减乘除运算
In [123]: import numpy as np
In [124]: a = np.array([1,2,3,4])
...: b = np.array([10,20,30,40])
...: c = a + b
...: d = a - b
...: e = a * b
...: f = a / b
...: print("a+b=",c)
...: print("a-b=",d)
...: print("a*b=",e)
...: print("a/b=",f)
...:
...:
a+b= [11 22 33 44]
a-b= [ -9 -18 -27 -36]
a*b= [ 10 40 90 160]
a/b= [0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1]
矩阵运算np.dot()
# 计算规则(计算学生总成绩)
#(M行,N列)*(N行,Z列)=(M行,Z列)
In [125]: import numpy as np
In [126]: stus_score = np.array([[80, 88], [82, 81], [84, 75], [86, 83], [75, 81]])
...: #平时成绩占40%,期末成绩占60%,计算结果
...: q = np.array([[0.4],[0.6]])
...: result = np.dot(stus_score,q)
...: print("最终结果为:")
...: print(result)
...:
...:
最终结果为:
[[84.8]
[81.4]
[78.6]
[84.2]
[78.6]]
# 矩阵拼接
## 矩阵垂直拼接
In [127]: print("v1为:")
...: v1 = [[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
...: [6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]]
...: print(v1)
...: print("v2为:")
...: v2 = [[12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17],
...: [18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23]]
...: print(v2)
...:
v1为:
[[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]]
v2为:
[[12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17], [18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23]]
# 垂直拼接
In [128]: result = np.vstack((v1, v2))
...: print("v1和v2垂直拼接的结果为")
...: print(result)
...:
...:
v1和v2垂直拼接的结果为
[[ 0 1 2 3 4 5]
[ 6 7 8 9 10 11]
[12 13 14 15 16 17]
[18 19 20 21 22 23]]
# 矩阵水平拼接
In [129]: print("v1为:")
...: v1 = [[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
...: [6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]]
...: print(v1)
...: print("v2为:")
...: v2 = [[12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17],
...: [18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23]]
...: print(v2)
...:
v1为:
[[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]]
v2为:
[[12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17], [18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23]]
# 垂直拼接
In [130]: result = np.hstack((v1, v2))
...: print("v1和v2水平拼接的结果为")
...: print(result)
...:
...:
v1和v2水平拼接的结果为
[[ 0 1 2 3 4 5 12 13 14 15 16 17]
[ 6 7 8 9 10 11 18 19 20 21 22 23]]
矩阵的广播
- ndarray广播的两条规则:
- 规则一:为缺失的维度补1
- 规则二:假定缺失元素用已有值填充
#实例1:m = np.ones((2,3)) a = np.arange(3)求m+a
In [131]: import numpy as np
In [132]: m = np.ones((2,3))
...: a = np.arange(3)
...: display(m,a)
...:
...:
array([[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]])
array([0, 1, 2])
#numpy广播,维度不同,自动补全
In [133]: m + a
Out[133]:
array([[1., 2., 3.],
[1., 2., 3.]])
#实例2:a = np.arange(3).reshape((3,1)) b = np.arange(3) 求a+b
In [134]: a = np.arange(3).reshape((3,1))
...: b = np.arange(3)
...: display(a,b)
...:
...:
array([[0],
[1],
[2]])
array([0, 1, 2])
In [135]: a + b
Out[135]:
array([[0, 1, 2],
[1, 2, 3],
[2, 3, 4]])
六、排序
1.快速排序
- np.sort()与ndarray.sort(),区别:
- np.sort()不改变输入
- ndarray.sort()本地处理,不占用空间,改变输入
In [136]: n1 = np.random.randint(0,150,size=15)
In [137]: n1
Out[137]:
array([ 80, 11, 31, 68, 83, 73, 42, 6, 40, 125, 147, 147, 88,
117, 85])
In [138]: n2 = n1.sort()
In [139]: display(n1,n2)
array([ 6, 11, 31, 40, 42, 68, 73, 80, 83, 85, 88, 117, 125,
147, 147])
None
In [140]: n3 = np.sort(n1)
...: display(n1,n3)
...:
...:
array([ 6, 11, 31, 40, 42, 68, 73, 80, 83, 85, 88, 117, 125,
147, 147])
array([ 6, 11, 31, 40, 42, 68, 73, 80, 83, 85, 88, 117, 125,
147, 147])
2.部分排序
- np.partition(a,k)
- 当k为正时:我们想要得到最小的k个数
- 当k为负时:我们想要得到最大的k个数
In [141]: n4 = np.random.randint(0,150,size=20)
In [142]: n4
Out[142]:
array([ 37, 74, 41, 53, 31, 11, 23, 108, 12, 128, 27, 88, 74,
114, 97, 127, 60, 47, 130, 135])
In [143]: np.partition(n4,-5)
Out[143]:
array([ 37, 12, 41, 27, 31, 11, 23, 47, 74, 60, 53, 74, 88,
97, 108, 114, 127, 128, 130, 135])
In [144]: np.partition(n4,5)
Out[144]:
array([ 12, 23, 11, 27, 31, 37, 41, 47, 108, 74, 53, 88, 74,
114, 97, 127, 60, 128, 130, 135])
#取数组中最大的k个数
In [145]: np.partition(n4,-2)[-2:]
Out[145]: array([130, 135])
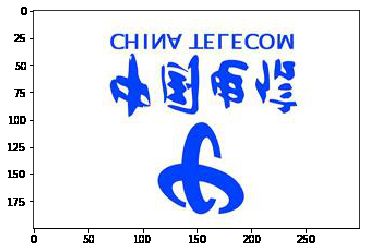
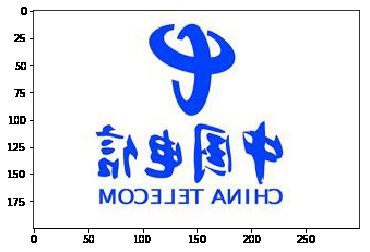
numpy案例
- 使用numpy将图片进行翻转
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
%matplotlib inline
dianxin = plt.imread('./image/dianxin.jpg')
plt.imshow(dianxin)
#将图片在竖直方向翻转
dianxin1 = dianxin[::-1]
plt.imshow(dianxin1)
#在水平方向翻转
dianxin2 = dianxin[::,::-1]
plt.imshow(dianxin2)
# 即在水平方向翻转又在垂直方向翻转
dianxin3 = dianxin[::-1,::-1]
plt.imshow(dianxin3)
# 改变图片颜色
dianxin4 = dianxin[::,::,-2]
plt.imshow(dianxin4)
#修改图片,是图片模糊
dianxin5 = dianxin[::3,::3]
plt.imshow(dianxin5)