关键词: 异常类:计算异常、空指针异常、越界异常、内存不足异常、参数错误异常; 可复用代码库设计原则;数据结构依赖异常类
写在前面的话: 前面学习到的异常类都是抛出的基本类型的异常类,是否也可以抛出类类型的异常?也就是说异常的类型是否可以支持自定义类类型?这节课重点讲解异常类的构建和使用。
1. 异常的类型
- 异常的类型可以是自定义类类型
- 对于类类型异常的匹配依旧是至上而下严格匹配
- 赋值兼容性原则在异常匹配中依然适用
- 一般而言:匹配子类异常的catch放在上部,匹配父类异常的catch放下下部
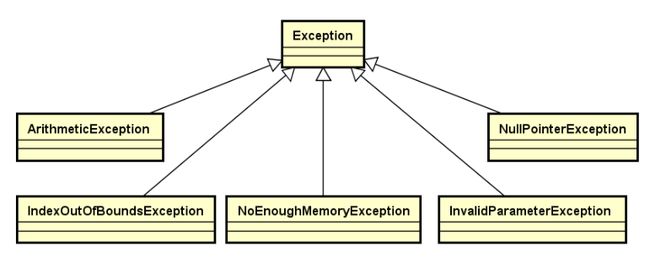
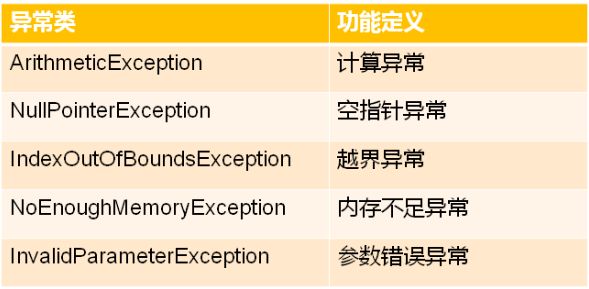
2. 现代C++库包含的异常类族
异常类是其它数据结构类所依赖的“基础设施”
由上面类图可知:
Exception为抽象类,是其他异常类的父类, 它不能定义对象
3. 异常类中的接口定义
class Exception
{
protected:
char* m_message; // 指向一个字符串,字符串用于说明当前异常的详细信息
char* m_location; // 指向一个字符串,字符串用于说明当前异常发生的地点
void init(const char* message, const char* file, int line); // 辅助构造函数进行初始化
public:
Exception(const char* message);
Exception(const char* file, int line);
Exception(const char* message, const char* file, int line);
Exception(const Exception& e);
Exception& operator= (const Exception& e);
virtual const char* message() const;
virtual const char* location() const;
virtual ~Exception();
};
编程说明:创建异常类族
Exception.h
#ifndef EXCEPTION_H
#define EXCEPTION_H
namespace DTLib
{
#define THROW_EXCEPTION(e, m) (throw e(m, __FILE__, __LINE__)) // 添加宏是为了使用时只需要写异常名和异常说明,文件名和行号可以自动填充
class Exception
{
protected:
char* m_message; // 指向一个字符串,字符串用于说明当前异常的详细信息
char* m_location; // 指向一个字符串,字符串用于说明当前异常发生的地点
void init(const char* message, const char* file, int line); // 辅助构造函数进行初始化
public:
Exception(const char* message);
Exception(const char* file, int line);
Exception(const char* message, const char* file, int line);
Exception(const Exception& e);
Exception& operator= (const Exception& e);
virtual const char* message() const;
virtual const char* location() const;
virtual ~Exception();
};
class ArithmeticException : public Exception
{
public:
ArithmeticException() : Exception(0){}
ArithmeticException(const char* message) : Exception(message){}
ArithmeticException(const char* file, int line) : Exception(file, line){}
ArithmeticException(const char* message, const char* file, int line) : Exception(message, file, line){}
ArithmeticException(const ArithmeticException& e) : Exception(e){}
ArithmeticException& operator =(const ArithmeticException& e)
{
Exception::operator=(e);
return *this;
}
};
class NullPointerException : public Exception
{
public:
NullPointerException() : Exception(0){}
NullPointerException(const char* message) : Exception(message){}
NullPointerException(const char* file, int line) : Exception(file, line){}
NullPointerException(const char* message, const char* file, int line) : Exception(message, file, line){}
NullPointerException(const NullPointerException& e) : Exception(e){}
NullPointerException& operator =(const NullPointerException& e)
{
Exception::operator=(e);
return *this;
}
};
class IndexOutOfBoundsException : public Exception
{
public:
IndexOutOfBoundsException() : Exception(0){}
IndexOutOfBoundsException(const char* message) : Exception(message){}
IndexOutOfBoundsException(const char* file, int line) : Exception(file, line){}
IndexOutOfBoundsException(const char* message, const char* file, int line) : Exception(message, file, line){}
IndexOutOfBoundsException(const IndexOutOfBoundsException& e) : Exception(e){}
IndexOutOfBoundsException& operator =(const IndexOutOfBoundsException& e)
{
Exception::operator=(e);
return *this;
}
};
class NoEnoughMemoryExcetion : public Exception
{
public:
NoEnoughMemoryExcetion() : Exception(0){}
NoEnoughMemoryExcetion(const char* message) : Exception(message){}
NoEnoughMemoryExcetion(const char* file, int line) : Exception(file, line){}
NoEnoughMemoryExcetion(const char* message, const char* file, int line) : Exception(message, file, line){}
NoEnoughMemoryExcetion(const NoEnoughMemoryExcetion& e) : Exception(e){}
NoEnoughMemoryExcetion& operator =(const NoEnoughMemoryExcetion& e)
{
Exception::operator=(e);
return *this;
}
};
class InvalidParameterExcetion : public Exception
{
public:
InvalidParameterExcetion() : Exception(0){}
InvalidParameterExcetion(const char* message) : Exception(message){}
InvalidParameterExcetion(const char* file, int line) : Exception(file, line){}
InvalidParameterExcetion(const char* message, const char* file, int line) : Exception(message, file, line){}
InvalidParameterExcetion(const InvalidParameterExcetion& e) : Exception(e){}
InvalidParameterExcetion& operator =(const InvalidParameterExcetion& e)
{
Exception::operator=(e);
return *this;
}
};
}
#endif // EXCEPTION_H
Exception.cpp
#include "Exception.h"
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
namespace DTLib
{
void Exception::init(const char* message, const char* file, int line)
{
/*
* m_message = message; // 这样赋值是不安全的,参数 message 指向的字符串位置不缺定,
* // 可能位于栈空间、可能位于堆空间、也可能位于静态存储区。
* // 解决方案:使用strdup函数,在堆空间中申请内存,拷贝字符串。
*/
m_message = strdup(message);
if( file != NULL ) // 首先判断file是否为空, 如果file不为空,
{ // file 指向的是发生异常的文件名,
char sl[16] = {0}; // 接下来,将发生异常的行号转化为字符串。定义一个辅助的字符数组
sprintf(sl, "%d", line); // 将line从int转换为字符数组,并且存储于sl中。
// 在Linux环境下没有itoa函数,因此需要用sprintf函数替代,并包含头文件
// 接下来将异常的文件名和行号拼接
// 通过malloc申请一片内存空间,大小为strlen(file)m+strlen(ls)+2
m_location = static_cast(malloc(strlen(file) + strlen(sl) + 2)); // +2 的目的是为了保存":"和"\n"
m_location = strcpy(m_location, file); // 将file中的字符串拷贝到m_location中
m_location = strcat(m_location, ":"); // 将":"拼接到输出字符串中,保持格式为 文件名:行号
m_location = strcat(m_location, sl); // 将异常的行号拼接到输出字符串中
}
else
{
m_location = NULL;
}
}
Exception::Exception(const char* message)
{
init(message, NULL, 0);
}
Exception::Exception(const char* file, int line)
{
init(NULL, file, line);
}
Exception::Exception(const char* message, const char* file, int line)
{
init(message, file, line);
}
Exception::Exception(const Exception& e) // 拷贝构造函数
{
m_message = strdup(e.m_message);
m_location = strdup(e.m_location);
}
Exception& Exception::operator= (const Exception& e)
{
if( this != &e )
{
free(m_message);
free(m_location);
m_message = strdup(e.m_message);
m_location = strdup(e.m_location);
}
return *this;
}
const char*Exception:: message() const
{
return m_message;
}
const char* Exception::location() const
{
return m_location;
}
Exception::~Exception()
{
free(m_message);
free(m_location);
}
}
测试代码:
#include
#include "SmartPointer.h"
#include "Exception.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace DTLib;
int main()
{
try
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(InvalidParameterExcetion, "test");
}
catch(const InvalidParameterExcetion& e)
{
cout << "catch(const InvalidParameterExcetion& e)" << endl;
cout << e.message() << endl;
cout << e.location() << endl;
}
catch(const NoEnoughMemoryExcetion& e)
{
cout << "catch(const NoEnoughMemoryExcetion& e)" << endl;
cout << e.message() << endl;
cout << e.location() << endl;
}
catch(const IndexOutOfBoundsException& e)
{
cout << "catch(const IndexOutOfBoundsException& e)" << endl;
cout << e.message() << endl;
cout << e.location() << endl;
}
catch(const NullPointerException& e)
{
cout << "catch(const NullPointerException& e)" << endl;
cout << e.message() << endl;
cout << e.location() << endl;
}
catch(const ArithmeticException& e)
{
cout << "catch(const ArithmeticException& e)" << endl;
cout << e.message() << endl;
cout << e.location() << endl;
}
catch(const Exception& e)
{
cout << "catch(const Exception& e)" << endl;
cout << e.message() << endl;
cout << e.location() << endl;
}
return 0;
}
4. 设计原则
在可复用代码库设计时,尽量使用面向对象技术进行架构,尽量使用异常处理机制分离正常逻辑和异常逻辑。
5. 小结
- 现代C++库必然包含必要的异常类族
- 所有库中的数据结构类都依赖于异常机制
- 异常机制能够分离库中代码的正常逻辑和异常逻辑
声明:此文章仅是本人在学习狄泰学院《数据结构实战开发教程》所做的笔记,文章中包含狄泰软件资料内容,一切版权归狄泰软件所有!
实验环境:ubuntu10 + Qt Creator2.4.1 + Qt SDK 4.7.4